![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define unit cell
|
The smallest group of atoms with both the characteristic chemical composition and crystal structure of a mineral.
|
|
|
Under the right conditions, and when all the right elements are present in the correct concentrations, atoms come together to form__________
|
Gem crystals
|
|
|
A solution that's highly saturated in nutrients produces
|
Many small crystals
|
|
|
Define aggregate
|
A mass of many small crystals formed by nutrient saturated solution or rapid cooling
|
|
|
Rapid cooling produces what type of crystals
|
Many small
|
|
|
What type of crystals does basalt contain and why
|
Many small due to rapid cooling
|
|
|
Slow cooling produces what type of crystals
|
Larger single crystals
|
|
|
Which has larger crystals: basalt or granite. Why?
|
Granite due to slower cooling
|
|
|
Solution with a lower concentration of nutrients yields
|
Larger single crystals
|
|
|
What is the best example of fewer crystallization centers and larger single crystals
|
Pegmatites
|
|
|
Gem minerals that are made iPod sense, closely packed masses of tiny randomly oriented crystals are called
|
Aggregates
|
|
|
Name two types of individual crystals in aggregates
|
Microcrystalline and Cryptocrystalline
|
|
|
Define Microcyrstalline
|
An aggregate made up of individual crystals visible under magnification
|
|
|
Name 3 microcrystalline gems
|
Nephrite, jadeite and quartzite
|
|
|
Define Cryptocrystalline
|
An aggregate made up of individual crystals detectable only under very high magnification
|
|
|
Name 2 cryptocrystalline gems
|
Chalcedony and turquoise
|
|
|
Explain crystallization process
|
Atoms come closer and closer together until they finally form connection bonds
|
|
|
How are brick structures like crystal structures
|
They are repetitions of tiny, identical units that are stacked to give shape and structure.
|
|
|
Differences between gems are due to differences in the ______ and _____ of their unit cells
|
Proportion and Symmetry
|
|
|
Crystalline minerals are classified into 7 crystal systems depending on _________
|
The symmetry of their unit cells.
|
|
|
Name the 7 crystal systems
|
Cubic, Tetragonal, Hexagonal, Trigonal, Orthorhombic, Monoclinic and Triclinic
|
|
|
Which is the most symmetrical of the crystal systems
|
Cubic
|
|
|
Which is the least symmetrical of the crystal systems
|
Triclinic
|
|
|
4 Cubic gems
|
Diamond, spinel, garnet, fluorite
|
|
|
Name a Tetragonal gem
|
Zircon
|
|
|
2 Hexagonal gems
|
Apatite, Beryl
|
|
|
3 Trigonal (Rhombohedral) gems
|
Corundum, quartz, tourmaline
|
|
|
5 Orthorhombic gems
|
topaz, ioite, tanzanite, chrysoberyl and peridot
|
|
|
Name 2 monoclinic gems
|
Kunzite and moonstone
|
|
|
Name 2 Triclinic gems
|
Amazonite and rhodonite
|
|
|
Spinel's typical shape
|
cubic-system crystal: it's top is an eight-sided octahedron
|
|
|
Garnet's typical shape
|
rhombic dodecahedron with twelve equal diamond shaped faces
|
|
|
Zircon's typical shape
|
Tetragonal system: They feature four rectangular sides and a pyramid shaped top with four triangular faces that meet in a point
|
|
|
Beryl's typical shape
|
hexagonal crystal system: six flat faces and columnar shape. Elongated in one direction.
|
|
|
Tourmaline's typical shape
|
Trigonal system: Long and slender with vertical grooves parallel to their length
|
|
|
Topaz's usual shape
|
Orthorhombic system: Usually elongated with obvious vertical grooves with triangular faces that give the top a chisel shape
|
|
|
Kunzite's typical shape
|
Monoclinic system: asymmetrical form with vertical grooves often capped by angled flat faces that form an irregular surface
|
|
|
Most rock and mineral crystals are formed from the 8 most abundant chemical elements in the earth's crust. Name them.
|
Oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium and magnesium
|
|
|
Which rare element is responsible for emerald green and ruby red
|
Chromium
|
|
|
What does quartz require to form
|
oxygen and silicon
|
|
|
What does an emerald require to form (Elements)
|
Silicon, oxygen, aluminum, beryllium and chromium
|
|
|
Define Twinning
|
change in a gem's crystal direction during or after growth
|
|
|
Define twinning plane
|
Location of a change in crystal growth direction
|
|
|
Primary twinning
|
when twinning happens during a crystal's original growth period
|
|
|
In one type of primary twinning, the twinned crystals look like one half is a mirror image, these are known as ____ and are most often seen in ____gems
|
contact twins seen most often in spinel and are sometimes called spinel twins.
|
|
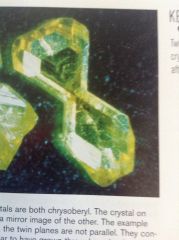
What type of twin is this
|
contact twin, one side is a mirror image of the other.
|
|
|
Define penetration twinning
|
when 2 crystals look as though 2 crystals have grown through one another
|
|
|
2 gems that show penetration twinning
|
Fluorite and quartz
|
|

type of twinning
|
penetration
|
|
|
Define cyclic twinning
|
occurs when the twinning planes aren't parallel and results in a wheel shaped crystal
|
|

type of twinning
|
cyclic
|
|
|
What causes secondary twinning
|
changes in environment after the crystal has formed, such as cooling temperatures or the pressure of metamorphism
|
|
|
define polysynthetic-lamellar-twins
|
the boundaries between the twinned crystals are parallel.
|
|
|
Gem materials that are commonly twinned: (5)
|
quartz, spinel, corundum, feldspar and chrysoberyl
|
|
|
Define inclusion
|
A characteristic enclosed within a gemstone, or reaching its surface from the interior
|
|
|
Define liquid inclusion
|
small pocket in a gem that's filled with fluids and sometimes gas bubbles and tiny crystals
|
|
|
Which gems are prone to include liquid inclusions (3)
|
Topaz, emerald and amethyst
|
|
|
define two-phase inclusion
|
A hollow cavity in a gem, usually filled with a liquid and a gas
|
|
|
Define three-phase inclusion
|
A hollow cavity in a gem filled with a liquid, a gas, and one or more crystals.
|
|
|
Which gem has characteristic three-phase inclusions that are key to their identification
|
Columbian emeralds
|
|
|
define trace elements
|
Atoms in a gem that aren't part of its essential chemical composition.
|
|
|
growth tubes are common in which gem
|
tourmaline
|
|
|
what effect can growth tubes produce if cut correctly
|
cat's eye
|
|
|
which trace elements cause sapphire's blue color
|
Iron and titanium
|
|
|
Define habit
|
The characteristic external crystal shape or form of a mineral
|
|
|
crystals without obvious crystal faces are described as
|
anhedral
|
|

Describe this rough
|
Ruby: Squat flattened crystals with triangular surface features on the top.
|
|
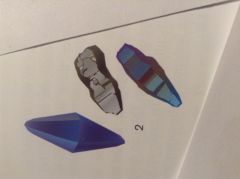
describe this rough
|
sapphire: two sets of six triangular faces joined back to back. Linear markings run horizontally across the crystal faces.
|
|

Describe this rough and where commonly found
|
Chrysoberyl twins, star shaped. Common in gem gravels of Brazil
|
|

Describe this rough
|
Imperial topaz: Diamond shaped cross section, vertically grooved sides and a chisel-shaped top
|
|

Describe this rough and what they look like in gem gravel
|
Garnet: Occurs as 12-sided (dodecahedral) crystals. In gem gravel they're mostly worn to a rounded ball-like shape.
|
|
|
Define tubular & give an example
|
Squat and flat. Corundum crystals.
|
|
|
Define prism or prismatic & give an example
|
Columnar, with 3, 4, 6, 8 or 12 parallel faces. Many aquamarine and tourmaline crystals.
|
|
|
Define Euhedral and give an example
|

Well formed with sharp crystal faces. Most gems from pegmatite pockets.
|
|
|
Define striations (both types) and give examples of each
|
Growth marks on a crystal. Horizontal (quartz, corundum) or vertical (tourmaline, topaz)
|
|
|
define pyramid
|
shape with equal triangular faces that meet in a point
|
|
|
Define bipyramid and give an example.
|
Shape with two pyramids, back to back. Seen in sapphires.
|
|
|
define density
|
how heavy an object is in relation to size
|
|
|
define specific gravity (SG)
|
Ratio of the weight of a material to the weight of an equal volume of water
|
|
|
define durability
|
a gemstone's ability to withstand wear, heat and chemicals
|
|
|
define hardness
|
how well a gemstone resists scratches
|
|
|
define toughness
|
how well a gemstone resists breaking and chipping
|
|
|
what does the Mohs scale measure?
|
A gems hardness
|
|
|
a gem crystal's hardness is directly related to the strength of
|
the chemical bonds between its atoms. The stronger the bond, the harder the crystal
|
|
|
which takes a better polish when cut: A hard stone or a soft stone?
|
A hard stone.
|
|
|
most of the dust in the air is composed of _____ which has a hardness of __
|
Quartz 7
|
|
|
name the 5 levels of toughness
|
exceptional excellent good fair poor
|
|
|
Name 2 exceptional gems on the toughness scale
|
jadeite and nephrite
|
|
|
name an excellent gem on the toughness scale
|
conrundum
|
|
|
name 2 good gems on the tougness scale
|
quartz and spinel
|
|
|
name a fair gem on the toughness scale
|
tourmaline
|
|
|
name 2 poor gems on the toughness scale
|
feldspar and topaz
|
|
|
The different ways a gem breaks are called: 1. 2. 3.
|
1. cleavage 2. parting 3. fracture
|
|
|
define cleavage
|
A smooth flat break in a gemstone parallel to planes of atomic weakness caused by weak or fewer bonds between atoms, or both.
|
|
|
broken surfaces due to cleavage may have what kind of appearance
|
step like
|
|
|
How should gems subject to cleavage be mounted?
|
mountings that protect a gem's corners and points provide the best protection.
|
|
|
define parting
|
a flat break in a gemstone caused by concentrated included minerals parallel to a twinning plane
|
|
|
define fracture
|
any break in a gem other than cleavage or parting
|
|
|
define conchoidal fracture
|
a curved and ridged fracture in a gemstone, extending from the surface inward.
|
|
|
define stability
|
how well a gemstone resists light, heat and chemicals
|
|
|
define thermal shock
|
damage caused by sudden, extreme temperature changes
|
|
|
A unit cell defines a mineral's
|
basic identity
|
|
|
If a crystal grows in a flux that is highly saturated with the necessary elements, it tends to be
|
small
|
|
|
which type of twinning is caused by environmental change after the gem forms
|
polysynthetic
|

