![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of drugs will be effective
in preventing motion sickness? |
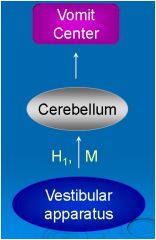
Muscarinic Blockers
H1 Blockers |
|
|
What type of drugs will be effective
in preventing PONV? |
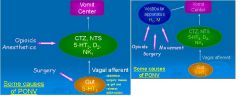
Muscarinic antagonists
H1 antagonists D2 antagonists 5-HT3 antagonists NK1 antagonists |
|
|
Drugs that block Vestibular Apparatus?
(Motion Sickness) |
M blockers
H1 Blockers |
|
|
Drugs That block CTZ, NTS and Gut caused nausea and vomiting?
|
D1 antagonists
5-HT3 antagonists NK1 antagonists |
|
|
What type of drugs will be effective in
preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting? |
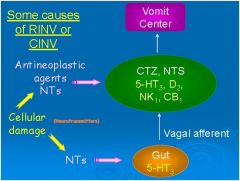
D2 antagonists
5-HT3 antagonists NK1 antagonists Cannabinoids Corticosteroids |
|
|
**Summary**
What receptors would you want to block for: -Motion Sickness -CINV -PONV |
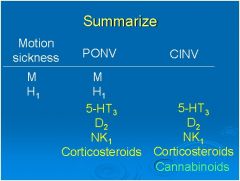
|
|
|
Which muscarinic blocker is used for motion sickness?
|
Scopalomine
|
|
|
Name the Histamine H1 receptor blockers (2)
|
Dimenhydrinate
Promethazine |
|
|
Are 2nd generation antihistamines antiemetic?
|
Second generation antihistamines do not cross the BBB.
Therefore they are not sedating, and are not antiemetic. |
|
|
What drug could you use to block both H1 and M receptors when treating motion sickness or PONV?
|
Dimenhydrinate
**Blocks H1 and M receptors** (Note: Scopalomine only blocks M receptors) |
|
|
Prochlorperazine blocks what receptor?
|
Dopamine (D2) receptor
|
|
|
MOA:
- Block dopamine receptors (D2) in the CTZ and NTS to prevent nausea and vomiting - Block D2 receptors in the GI tract to prevent the inhibition of intestinal motility associated with NV |
Prochlorperazine and Doperidol
(Antipsychotics) |
|
|
Emetogenic potential of antineoplastic agents:
Cisplatin |
High Emetogenic Potential
|
|
|
Emetogenic potential of antineoplastic agents:
Methotrexate |
Low Emetogenic Potential
|
|
|
Will prochlorperazine be useful in preventing motion sickness?
|
No
Doesn't hit H1 and M receptors |
|
|
MOA:
- Blocks D2 receptors in the CTZ and NTS - HIGH DOSES also block 5-HT3 receptors in the CTZ, NTS and the GI tract - Enhances gastric emptying, which is believed to minimize stasis that precedes vomiting **** |
Metoclopramide
|
|
|
Clinical Use:
- Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting – High dose - Radiation-induced nausea and vomiting –High dose Post operative nausea and vomiting – Low dose-->Doesn’t work |
Metoclopramide
|
|
|
Would metoclopramide be
useful for motion sickness? |
No
Doesn't effect M or H1 receptors |
|
|
Adverse Effects:
**CNS effects** **Extrapyramidal reactions** - Blocks D2 receptors in the CNS - Especially with high doses - TARDIVE DYSKINESIA ****** |
Metoclopramide
|
|
|
A patient on high dose Metoclopramide for N/V is complaining of clumsiness and tripping. What's going on?
*** |
**Extrapyramidal reactions**
- Blocks D2 receptors in the CNS - Especially with high doses - TARDIVE DYSKINESIA |
|
|
"-setron"
|
5-HT3 Blockers
**Block Serotonin Receptors** |
|
|
Class of Drugs?:
Ondansetron Granisetron Dolasetron Palonosetron |
5-HT3 Blockers
(block serotonin receptors) |
|
|
Where are 5-HT3 receptors located?
|
NTS, CTZ and Gut
|
|
|
Clinical Use:
- Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting - Prevents acute NV (within 24 h) - Little effect on delayed NV (1-5 days) when used as monotherapy |
5-HT3 Blockers
|
|
|
Treats Acute NV associated with chemotherapy
|
5-HT3 Blockers
|
|
|
Treats delayed NV associated with chemotherapy
|
Aprepitant
**Substance P** |
|
|
Adverse Effect:
- Prolongs QT Interval |
5-HT3 Blockers
|
|
|
What is the advantage of using
ondansetron vs. metoclopramide in a patient with Chemotherapy NV? |
Unlike metoclopramide, ondansetron doesn't block D2 (dopamine) receptors.
LESS CNS SIDE EFFECTS!! |
|
|
Substance P/neurokinin 1(NK1)
receptor antagonists used for acute and delayed NV associated with Chemotherapy Also used for PONV |
Aprepitant
|
|
|
Corticosteroid to treat CINV and PONV
|
Dexamethasone
|
|
|
This drug:
- Combined with other agents (e.g. 5-HT3 antagonist or high dose metoclopramide) to improve efficacy in preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting - Monotherapy or combination therapy for delayed chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting - Post operative nausea and vomiting |
Dexamethasone
|
|
|
What class of drug is Dronabinol?
|
Cannabinoids
|
|
|
Clinical Use:
- Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting **Not adequately controlled by other drugs** |
Dronabinol
(Cannabinoids) |
|
|
Adverse Effects:
Dysphoria Hallucinations Sedation Vertigo Dry mouth Disorientation |
Dronabinol
(Cannabinoids) |
|
|
Another Summary!!
Yaaayy! |
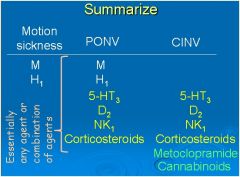
|
|
|
A 47-year-old male is being treated with methotrexate for cancer. What would be the best preventative therapy for his nausea and vomiting?
A. D2 antagonist (eg prochlorperazine) B. 5HT3 antagonist (eg palonosetron) C. M blocker (eg scopolamine) D. NK1 antagonist (eg aprepitant) E. Metoclopramide F. Dexamethasone |

|
|
|
A 47-year-old male is being treated with methotrexate for cancer. What would be the best preventative therapy for his nausea and vomiting?
Answer: Dexamethasone What if this drug was contraindicated for some reason. What would you use? A. D2 antagonist (eg prochlorperazine) B. M blocker (eg scopolamine) C. NK1 antagonist (eg aprepitant) D. Metoclopramide E. H1 blocker (eg dimenhydrinate) |
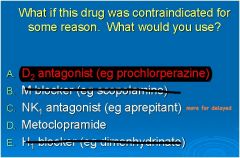
|
|
|
A 47-year-old male is being treated with cyclophosphamide for cancer. What would be the best preventative combination therapy for his nausea and vomiting?
(select all that apply) A. D2 antagonist (eg prochlorperazine) B. Palonosetron (5HT3 antagonist) C. M blocker (eg scopolamine) D. NK1 antagonist (eg aprepitant) E. Metoclopramide F. Dexamethasone |

|
|
|
A 47-year-old male is being treated with cisplatin for cancer. What would be the best preventative combination therapy for his nausea and vomiting?
(select all that apply) A. D2 antagonist (prochlorperazine) B. 5HT3 antagonist (ondansetron) C. M blocker (eg scopolamine) D. NK1 antagonist (eg aprepitant) E. Metoclopramide F. Dexamethasone |
B. 5HT3 antagonist (ondansetron)
D. NK1 antagonist (eg aprepitant) F. Dexamethasone (Remember, Cisplatin has a HIGH emetogenic potential) |
|
|
You are using the following drug combo to treat NV in a Chemo patient on cisplatin:
5HT3 antagonist, NK1 antagonist, Dexamethasone The drug combo is not working well enough. What can you do to help control his nausea and vomiting? (select all that apply) A. Add D2 antagonist (eg prochlorperazine) B. Add M blocker (eg scopolamine) C. Add H1 blocker (eg dimenhydrinate) D. Add cannabinoid (eg dronabinol) E. Switch from ondansetron to high dose metoclopramide |
Add D2 antagonist
Add cannabinoid Switch from ondansetron to high dose metoclopramide |
|
|
What is Gastroparesis?
|
Gastric emptying is delayed in the
absence of mechanical obstruction |
|
|
What effect does serotonin have on gut motility? What about dopamine?
|
Serotonin (binds 5-HT4) enhances the release of ACh by neurons which stimulates gut motility
Dopamine inhibits ACh release and thus decreases gut motility |
|
|
How will metoclopramide
affect gut motility? |
It blocks Dopamine receptors which keeps them from inhibiting gut motility
It also enhances activated 5-HT4 receptors which enhance gut motility by allowing more ACh release from neurons (High Dose metoclopramide can INHIBIT 5-HT3 receptors!!) |
|
|
Gastroparesis is a complication of_____
|
Diabetes
|

