![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
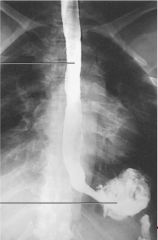
|
Reflux Esophagitis (GERD)
|
|
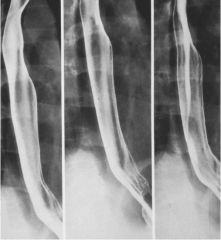
|
Reflux Esophagitis (GERD)
|
|
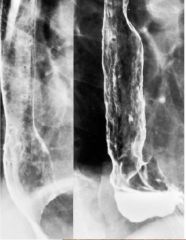
|
Reflux Esophagitis (GERD)
|
|
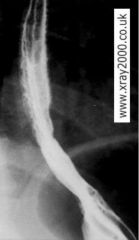
|
Reflux Esophagitis (GERD)
|
|
|
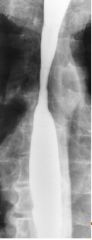
Barrett's Esophagus
|
|
|
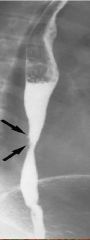
Barrett's Esophagus
|
|
|
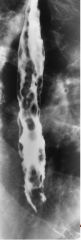
Esophageal Varices
|

