![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three common forms of peptic ulcers? |
-H. Pylori associated |
|
|
What is H. pylori? |
-it is a spiral shaped, pH sensitive, gram negative bacteria |
|
|
How do NSAIDs cause ulcers? |
They cause direct irritation of gastric mucosa and inhibitprostaglandin synthesis |
|
|
How does stress cause mucosal damage? |
-mucosal ischemia |
|
|
Compare/contrast the three forms of peptic ulcers.
|
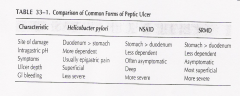
|
|
|
What are some complications associated with peptic ulcerdisease? |
Bleeding (d/t artery erosion, 50% of upper GI bleeds) -perforation – obstruction (d/t scarring, edema) |
|
|
What is the acid producing cell in the stomach?
|
the parietal cell
|
|
|
Where do proton pump inhibitors work?
|
on the K+/H+ ATPase proton pump, blocking hydrogen ion release (the final pathway)
|
|
|
What kid of receptors on the parietal cell do medications to treat peptic ulcer disease work on?
|
-ATPase -gastrin-cholecystokinin-B receptor -histamine receptor -muscarinic receptor -enterochromaffin-like cell -somatostatin receptor |
|
|
List some histamine-2 receptor antagonists. |
Cimetidine – ranitidine – famotidine – nizatidine |
|
|
List some proton pump inhibitors. |
Omeprazole –esomeprazole – lansorazole – rabeprazole –pantoprazole |
|
|
What are some miscellaneous agents used to treat PUD? |
Antacids: hydroxide salts of aluminum and magnesium (neutralize acid in the stomach) |
|
|
What is the MOA of H2 antagonists? |
They bind to and block the H2 receptors located on theparietal cell |
|
|
What are some adverse effects of H2 antagonists? |
They are generally well tolerated. |
|
|
Describe Cimetidine. |
Available PO or IV. OTC. |
|
|
|
Available PO, IV, OTC. |
|
|
Describe ranitidine. |
Available PO, IV OTC. |
|
|
What is the MOA of PPIs? |
Proton pump is the final common pathway in acid secretion. |
|
|
What are some adverse effects of PPIs? |
Overall well tolerated |
|
|
What are some adverse effects of long term use of PPIs? |
May decrease B12 absorption – hypomagnesemia (muscle spasms,arrhythmias, tremors, seizures) - gastric tumors |
|
|
Which PPI is most likely to inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes? |
Omeprazole |
|
|
What PPI may require dosage adjustment if there is liverfailure? |
All of them but especially lansoprazole |
|
|
What is the MOA of Sucralfate? |
Binds electrostatically to positively charged proteinmolecules in the ulcer crater ( forms a protective barrier) |
|
|
What are the adverse effects of sucralfate? |
Constipation, hypophosphatemia, aluminum toxicity in renalfailure pts due to aluminum |
|
|
Where does each class of drugs for treatment of PUD work? |
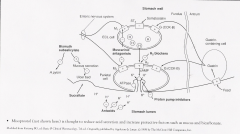
|
|
|
How do you treat H. pylori? |
Combination regimen |
|
|
What is the first line regimen recommended for H. pyloritreatment? |
Carithromycin-based triple therapy: |
|
|
What is the Bismuth quadruple therapy? |
Second line treatment for H. pylori. **not tolerated well** |
|
|
What is a third option for H. pylori treatment? |
PPI BID + amox BID x5d then PPI BID + clarit BID +tinidazole x 5 d |
|
|
What is the treatment for active duodenal/gastric ulcers? |
-conventional tx with H2 receptor antag, sucralfate orantacids (heals 90% duodenal ulcer at 8 weeks) |
|
|
What are some things that play a part in refractory ulcers? |
Poor pt compliance – antimicrobial resistance – smoking –nsaid use – gastric acid hypersecretion – H2 receptor antag tolerance |
|
|
How do you treat refractory ulcers (sx still there at 8weeks –duodenal – or 12 weeks - gastric? |
Test for H.pylori |
|
|
Who needs maintenance therapy for PUD and how do you do it? |
Pts with frequent recurrences |
|
|
How do you treat NSAID induced ulcers? |
Stop the NSAID |
|
|
What is misoprostol? |
Synthetic prostaglandin E analog |
|
|
What is used for prophylaxis of NSAID induced ulcers? |
Misoprostol |
|
|
What is used for prophylaxis of stress ulcers? |
H2 antagonists or PPIs |
|
|
Describe the pathophysiology of nausea and vomiting. |
Triggered by afferent impulses to the vomiting center whichis located in the medulla |
|
|
What kind of neurotransmitter receptors are located in thevomiting center, CTZ and GI tract? |
Cholinergic – serotonergic – histaminic – dopaminergic –opiate |
|
|
What are some locally-mediated etiologies of N/V? |
Bowel obstruction – ulcers – surgery – drugs (irritation ofGI mucosa) |
|
|
What are some centrally-mediated etiologies of N/V? |
Drugs (CTZ stimulation: antineoplastic agents, ipecac,opioids, general anesthetics) Anticipatory |
|
|
How common is post-op nausea/vomiting? |
20-30% in general surgical population |
|
|
What are some adverse effects of post-op nausea/vomiting? |
Patient distress/morbidity: wound dehiscence, esophagealrupture, aspiration, dehydration, increased ICP, pneumothorax |
|
|
What are some risk factors for PONV? |
Female (3x males) - history of PONV or motion sickness –nonsmoker – younger age (<50) - general vs regional anesthesia – inhalationanesthetics and nitrous – intra or post op opioid analgesics – duration ofsurgery/anesthesia (30mins increases risk 60%) - type of surgery (lap, gyne,abdominal) |
|
|
List some anti-dopaminergics. |
Butyrophenones – droperidol, haloperidol |
|
|
List some antihistaminic/anticholinergic used for PONV |
Promethazine – diphenhydramine – dimenhydrinate – meclizine– hydroxyzine – scopolamine |
|
|
List some serotonin antagonists. |
Dolasetron – granisetron – ondansetron – palonosetron |
|
|
List a benzodiazepine used for PONV. |
Lorazepam |
|
|
List a corticosteroid used for PONV. |
Dexamethaxone |
|
|
List a neurokinin-1 receptor (substance P) antagonist usedfor PONV. |
Aprepitant – expensive but may last longer, give 40mg w/in 3hrs of induction |
|
|
What is the MOA of antidopaminergic agents? |
Dopamine-receptor antagonism at the CTZ |
|
|
What are some adverse effects of antidopaminergic agents? |
Extrapyramidal effects – dysphoria – sedation – hypotension– QT prolongation and torsades |
|
|
What is the MOA of serotonin receptor antagonists? |
They bind to and block serotonin receptors involved in theemetic pathway |
|
|
What are some adverse effects of serotonin receptorantagonists? |
Headache, lightheadedness, constipation |
|
|
How does dexamethasone work to help PONV? |
Exact mechanism unknown |
|
|
What anti-emetics would you give at induction? |
Aprepitant – dexamethasone – palonosetron |
|
|
Which anti-emetics would you give at end of surgery? |
Droperidol – ephedrine – granisetron – ondansetron –dolasetron |
|
|
Which anti-emetic would you give the prior evening or 2hours before? |
Scopolamine |
|
|
What are some strategies to reduce baseline risk for PONV? |
Avoidance of general anesthesia by using regional |
|
|
What is the PONV risk if a patient has 0 risk factors? 1? 2?3? 4? Treatment? |
Low 10% ---> wait and see |
|
|
Which medications do you not readminister for PONV? |
Dexamethasone or scopolamine |

