![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
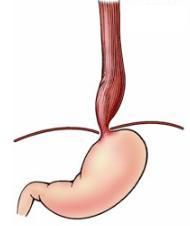
What is this disease chararacterized by inability to completely relax LES, aperistalsis, & Radiographically referred to as bird's beak?
|
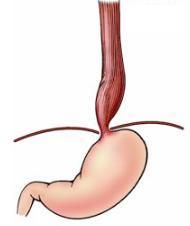
Achalasia
|
|
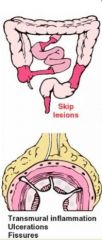
What is this disease? It is characterized by Terminal ilitis, discontinuous, granulomatous inflammation throughout the bowel & contains Skip Lesions.
|
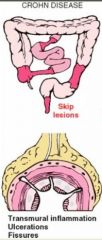
Crohn's Disease
(bowel wall not contained to the tube, so it may get into the uterus or urinary bladder) |
|
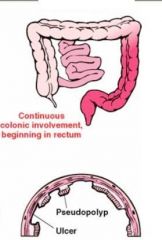
What is this disease? It is characterized by Increased Risk of Colon Cancer, Continuous inflamation, confined to the colon (may have backwash ilitis)
|
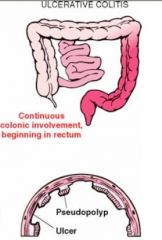
Ulcerative Colitis
(Increased Risk of Colon Cancer) |
|
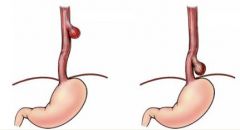
What is this condition?
It is characterized by pouching out of mucosa through the GI tube wall. |

Diverticulum
(in class we referred to this in the intestines, but this is a good picture regardless) Diverticulosis = presence of diverticulae Diverticulitis is inflammation with faecaliths and stasis, risk of perforation and peritonitis |
|
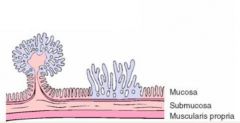
What are these?
|
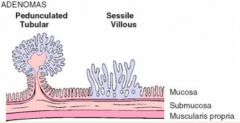
Polyps
Tubular Adenomas* & Villous Adenomas Extensions of the mucosa on all three sides & contains a fibrovascular core Tubular Adenomas have rounded glands and are precancerous (Adenomas are benign however may lead to adenocarcinomas) |
|
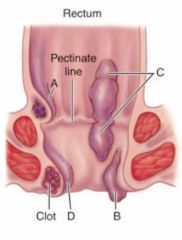
What is this condition and what causes it?
|
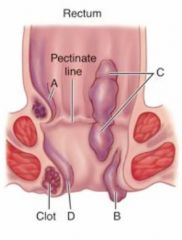
Hemorrhoids
Dilated blood vessels of the rectum Caused by: Pregnancy, sitting, constipation |
|
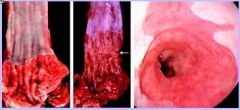
What are these pictures of?
What are the characteristics of the disease? |
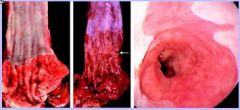
A. is a normal esophagus
B. Barrett's esophagus w/arrow pointing to granular zone C. Barrett's esophagus showing velvety red mucosa, note the pale appearance Characteristics include: 1. Metaplasia- squamous cells are replaced by columnar epithelium better suited to resist injury 2. Complication of reflux 3. Prolonged exposure to irritants |
|
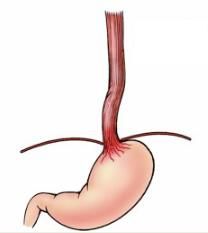
What is this condition and what is it associated with?
|
Mallory-Weiss Tears
(longitudinal tears of the gastroesophageal junction) Usually associated w/violent retching. i.e. alcoholism, bulimia, chemotherapy |
|
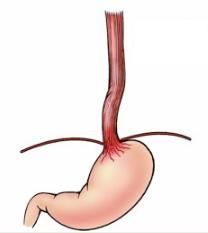
What is this condition and what causes it?
(The esophagus is turned inside out to show condition) |
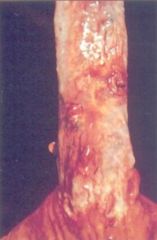
Esophageal Varices
Caused by Dilated vessels due to portal hypertension. Commonly associated w/cirrhosis |
|
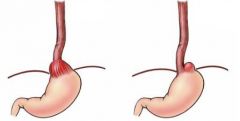
What is this condition?
What is going on in this condition? What are the complications of this condition? |
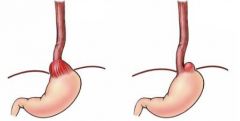
Hiatal Hernia (Sliding & Rolling)
The diaphragmatic leaves separate and the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm, associated w/GERD Complications include: Ulcerations, Perforations, Esophagitis |
|
|
What are the complications of Achalasia?
|
Carcinoma & Candida Esophagitis
|
|
|
What are 2 fairly common esophageal conditions resulting from alcoholism?
|
1. Mallory-Weiss Tears
2. Varices |
|
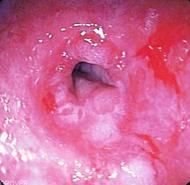
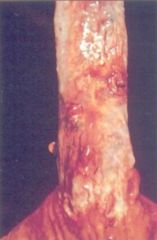
What condition causes scarring and narrowing of the lumen due to ingested caustic substances?
|
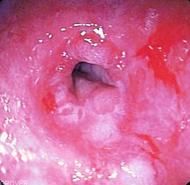
Stricture
|
|
|
What causes Esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus)?
|
1. Primarily Reflux
2. Infections 3. Radiation 4. Crohn's 5. Irritants (tannins, cigarettes, EtOH) |
|
|
What is reflux?
|
Heartburn caused by gastric juices (+ sometimes bile)
|
|
|
What are some causes of reflux?
|
1. Incompentent LES
2. Hiatal Hernia 3. Delayed gastric emptying |
|
|
What are some factors that would predispose you to esophageal carcinoma?
|
1. Drinking very hot tea
2. Tannins in tea 3. Smoking 4. Alcoholism 5. Lack of Green Veggies |
|
|
What is Esophageal Adenocarcinoma?
|
Carcinoma of esophageal glands
(strongly associated w/Barrett's Esophagus) |
|
|
What are the components of acute gastritis?
|
Acute = neutrophils
|
|
|
What are the components of chronic gastritis?
|
Chronic: Lymphocytes, plasma cells, intestinal metaplasia
|
|
|
What is Acute Gastritis?
|
Transient Neutrophilic Inflamation of the Stomach
Causes: NSAIDs, Alcohol, Smoking, Chemotherapy, Sepsis, Burns, Ischemia and shock, Cold (people frozen to death) |
|
|
What is indicative of chronic gastritis?
|
Chronic inflammatory cells above the basement membrane
Mucosal atrophy and epithelial metaplasia Development of carcinoma |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of Chronic Gastritis?
|
H. Pylori*
Autoimmune Alcohol/tobacco Stomach surgery Radiation GVHD |
|
|
What is the #1 causative agent in Peptic Ulcer Disease?
|
H. Pylori
|
|
|
What is a type of absorption disease in the small intestines?
|
Celiac Sprue (loss of Villi so can't absorb food)
|
|
|
What is Ischemic Bowel Disease?
|
Dead necrotic bowel caused by atherosclerosis interupting blood supply
|
|
|
What are some causes of diarrhea?
|
Infection (shigella, salmonella, Giardia, Cryptosporidium in AIDS pts)
Lactose intolerance Pseudomembranous colitis (C-Diff) Antibiotics |
|
|
What are some types of Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
|
Crohn's disease
Ulcerative Colitis Dysentery Collagenous Colitis |
|
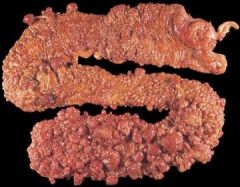
What is the incidence of cancer for people who have Familial Polyposis Coli?
|
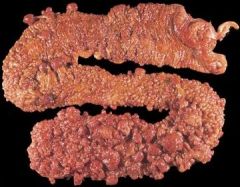
100% incidence of cancer
|
|
|
What is important regarding anemia in male or post-menopausal women?
|
Adenocarcinoma of the Colon
Anemia in male or post-menopausal women is GI malignancy until proven otherwise |
|
|
*What is the normal functions of the Gall Bladder?
|
1. Storage of bile
2. Digestion of fats 3. Excretion of drugs (opiates are excreted through people's bile) |
|
|
What do sickle cell anemia patients all have in addition?
|
Pigmented gall stones
|
|
|
In the Zones of Rappoport, which zone will be killed off first from too much tylenol?
|
Zone III
|
|
|
What causes disruption of the reticulin framework?
|
Cirrhosis
|
|
|
Can Hepatitis B cause hepatocellular carcinoma?
|
Yes
|
|
|
**What are the properties of Hepatitis D?
|
Dane particle
Incompetent virus Needs Hepatitis B coinfection Worse prognosis |
|
|
Who is at risk for hepatitis?
|
Health care workers
IVDA Sex workers Being born of an infected mother |
|
|
What pathology is being described?
Hobnailed liver, long-term inflammation, destruction of the reticulin framework, Regeneration of hepatocytes, Scar tissues, Portal hypertension |
Cirrhosis
|
|
|
What are the causes of Cirrhosis?
|
Alcohol, Infection, Parasitism, alpha 1 antitrypsinase deficiency, hemachomatosis
|
|
|
What are some alcoholic liver diseases?
|
Fatty liver
Alcoholic hepatitis Cirrhosis |
|
|
What is Hemachromatosis?
|
Avid iron absorption
Bronze diabetes (iron deposition in liver, heart, pancreas) |
|
|
What causes derangement of copper metabolism?
|
Wilson Disease
|
|
|
What are the 2 alleles in alpha-1-antitryptinase?
|
PiZZ poor
PiMM good |
|
|
What is Alpha-1-antitryptinase?
|
Protein that neutralizes neutrophil enzymes
(unchecked inflammation) |
|
|
What is the most common liver cancer?
|
Metastasis
|
|
|
**What is the difference between a cyst and a pseudocyst?
|
A cyst is lined by an epithelial membrane, whereas a pseudocyst does not
|
|
|
Who is susceptible to cholesterol stones?
|
Fat
Fertile >40 yrs old Female Fair- white people |
|
|
What is another word for pigment gall stones?
|
Hemoglobinopathies
|
|
|
How do you get pigment stones?
|
1. Hemolytic anemia
2. Breakdown of RBCs 3. Sickle Cell Anemia 4. Trypartate procedure (cholecystectomy, splenectomy, appendectomy) |
|
|
What are the complications of gall stones?
|
1. Biliary colic (cramping pain when eating fatty foods)
2. Impacted stones (jaundice, hepatitis, pancreatitis) 3. Ileus (stuck in the ileocecal valve) |
|
|
What kind of gut flora do gall stones give rise to?
|
Gram negative rods
(stone impactions can lead to bile stasis, stasis leads to bacterial overgrowth) |
|
|
What causes ascending infection in gall stone patients?
|
Cholangitis via gram negative sepsis due to bile stasis
|

