![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
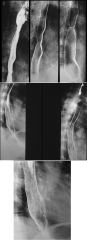
BARRETT’S ESOPHAGUS
Columnar metaplasia 2-10% of Reflux Esophagitis 8-10% develop adenocarcinoma |
|
|
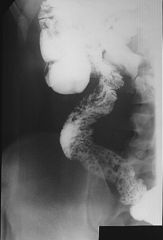
CROHNS DISEASE
90+% Involvement of TI DDX: Yersinia Tb Lymphoma |
|
|
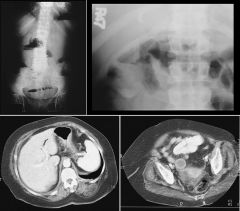
GALLSTONE ILEUS
|
|
|
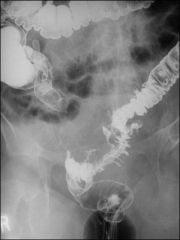
DIVERTICULITIS
inflammation of pericolonic fat (98%) diverticula (84%) bowel wall thickening of 4-12 mm (70%) abscess (47%) fluid +/- air of peritonitis (16%); fistula (14%); obstruction (12%); intramural sinus tract (9%); ureteral obstruction (7%) |
|
|
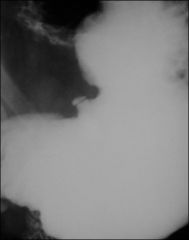
BENIGN GASTRIC ULCER
projection beyond luminal contour depth > width smooth fading of gastric folds lesser curvature (not reliable) concomitant duodenal ulcers Hampton’s line (1-mm lucent line) persistent pooling of barium in crater |
|
|
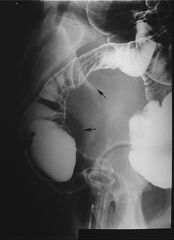
ENDOMETRIOSIS
Involves bowel 15-20% Extramucosal mass effect at rectosigmoid junction Tx: Hormonal therapy, Resection Usually asymptomatic |
|
|
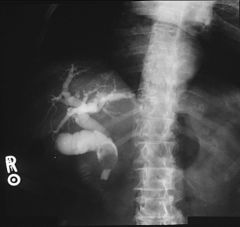
MIRIZZI SYNDROME
|
|
|
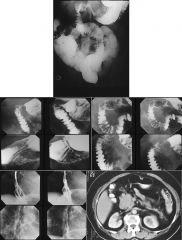
ZOLLINGER-ELLISON
Gastrinoma: 60% malignant Multiple ulcers of stomach + duodenum Tx: gastrectomy 10% ectopic (stomach, duodenum, splenic hilum) 50% of Z-E ==> MEN-1 |
|
|
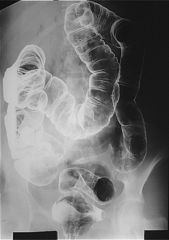
FAMILIAL POLYPOSIS COLI
autosomal dominant (33% sporadic) adenomas ==> colon Ca absent at birth adenomas develop in teenagers associations: desmoid tumors SB adhesions POLYPOSIS SYNDROMES Inher Malig Type familial polyposis coli AD + adenoma Gardner syndrome AD + " Turcot syndrome AR CNS " Peutz-Jeghers syndrome AD + hamartoma Cowden syndrome AD ? " juvenile polyposis coli ? - inflamm Cronkhite-Canada syndrome NR - " |
|
|
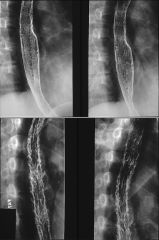
CANDIDA ESOPHAGITIS
Immunocompromised Odynophagia “Shaggy” esophagus: Suggest AIDS |
|
|
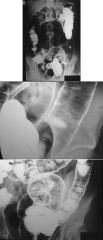
CROHNS DISEASE
Crohn disease ulcerative colitis Location right side left side Ulcers deep shallow Contraction no yes Ileocecal valve thickened gaping Fistulae yes no Eccentricity yes no Carcinoma slight increase marked increase Megacolon unusual yes |
|
|
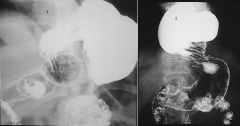
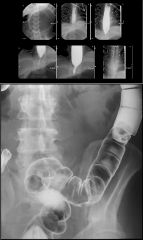
GASTRIC VOLVULUS
Organoaxial rare in kids associated with large hiatus hernia rotation along long axis of stomach Mesenteroaxial antrum lies above cardia (i.e., rotation around line connecting greater and lesser curvature) form seen in neonates obstruction at pylorus or GE junction usually acute associated with eventration of LEFT hemidiaphragm or diaphragmatic hernia |
|
|
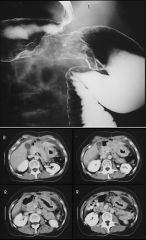
POLYP
ADENOMATOUS POLYP Villous Cancer Risk: <1 cm = 10% >2 cm = 54% Tubular (More Common) Cancer Risk: <1 cm = 1% >2 cm = 34% |
|
|
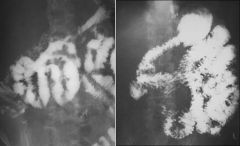
GASTRIC CARCINOMA
GASTRIC NARROWING neoplastic carcinoma (linitis plastica) lymphoma metastases inflammatory caustic radiotherapy granulomatous disease: Crohn disease, TB, sarcoidosis eosinophilic enteritis GASTRIC CARCINOMA location: 60% lesser curvature 30% GE junction 10% greater curvature probability of malignancy of an ulcer: fundus 90% greater curvature 70% lesser curvature 10-15% 3rd most common GI malignancy (after colorectal + pancreas) 95% adenocarcinoma (rarely squamous cell or adenoacanthoma) predisposing factors: pernicious anemia (2X risk) chronic atrophic gastritis adenomatous + villous polyp (7-27% are malignant) gastrojejunostomy |
|
|
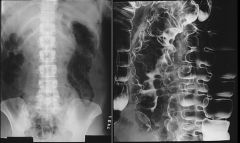
BOWEL WALL THICKENING
hemorrhage edema ischemia sprue malabsorption hypoproteinemia Whipple disease amyloidosis Henoch-Schonlein syndrome abetalipoproteinemia Crohn disease |
|
|
PNEUMOTOSIS CYSTOIDES COLI
complication: assymptomatic large pneumoperitoneum (may persist for months/years) |
|
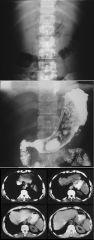
|
GASTRIC LYMPHOMA
Secondary Involvement Primary NHL MALT- H. Pylori |
|
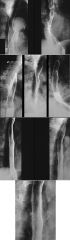
|
GLYCOGENIC ACANTHOSIS
benign (no malignant potential) degenerative accumulation of glycogen in squamous epithelium multiple small 1-3mm mucosal nodules in mid to distal esophagus Asymptomatic |
|
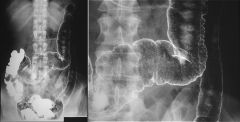
|
ULCERATIVE COLITIS
acute fine mucosal granularity "double tracking" = longitudinal submucosal ulcers "collar button" ulcers "thumbprinting" = symmetric thickening of colonic folds pseudopolyps = islands of edematous mucosa and granulation tissue subacute inflammatory polyps (sessile) coarse granular mucosa chronic "lead pipe" colon = rigidity + symmetrical narrowing of lumen "burnt-out colon" = distensible colon without haustral markings filiform polyposis = postinflammatory polyps (10-20%) complications: toxic megacolon colon Ca (1-16%) strictures (10%) |
|
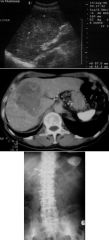
|
ANGIOSARCOMA
THOROTRAST previously used contrast agent accumulated in RE system liver spleen lymph nodes thorium emits alpha particles associated with: hepatobiliary Ca (Angiosarcoma) leukemia aplastic anemia dense liver and spleen "bone within a bone" |
|
|
BUDD-CHIARI
etiology: thrombus (OCs, dehydration, septicemia, polycythemia vera, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria) congenital (web in hepatic v. or IVC) tumor or other mass (eg, hydatid cyst) sickle cell anemia trauma findings: HM ascites esophageal varices "hot" caudate lobe |
|
|
AMIODARONE TOXICITY
Ddx: Dense Liver hemochromatosis hemosiderosis Wilson disease Thorotrast amiodarone gold (for RA) thallium overdose glycogen storage diseases |
|
|
CARCINOID
"rule of one-third" 1/3 of GI carcinoid in SB 1/3 ==> mets 1/3 have 2nd malignancy 1/3 multiple 90% from distal ileum or appendix 90% of appendicial tumors desmoplastic reaction ==> kinking + angulation of SB angio: intensely vascular lesions |
|
|
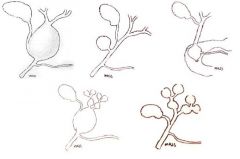
CHOLEDOCHAL CYST I
|
|
|
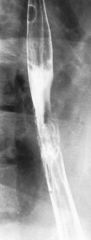
DOXY ESOPHAGITIS
|
|
|
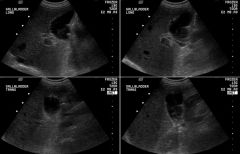
EMPHYSEMATOUS CHOLECYSTITIS
males (3:1), esp. diabetics usually acalculous high mortality |
|
|
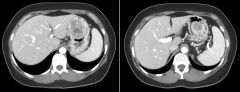
GIST
|
|
|
HCC
|
|
|
INSULINOMA
Usually solitary 85% benign Hypervascular |
|
|
INTUSSUSCEPTION
75% in kids <2 y/o ileocolic (75%), ileo-ileocolic (15%) 90% idiopathic leading point: lymphoid tissue (possibly increased 2' to enteritis) in older kids + adults (ileo- or colocolic) Meckel diverticulum Peyer's patches lymphoma large mesenteric nodes duplications polyps "currant jelly" stools "coiled spring" on BE ** transient intussusception: a/w sprue |
|
|
CHOLEDOCHOLITHIASIS
|
|
|
MESENTERIC PANNICULITIS
Ddx Neoplasm: Met, Carcinoid, Sarcoma or desmoid tumor Inflammatory: pancreatitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and extra-abdominal fat necrosis (ie, Weber-Christian disease), mesenteric adenitis, acquired immune deficiency syndrome, Whipple's disease, sprue, sarcoidosis, or tuberculosis |
|
|
SBO
|
|
|
SMA SYNDROME
Partial obstruction of third part of duodenum by superior mesenteric artery (SMA) Seen with: marked weight loss anorexia nervosa total body casting X-ray: distension of proximal duodenum classically disappears when prone |
|
|
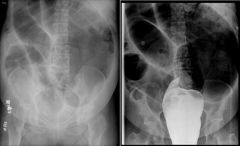
SPRUE
gluten enteropathy celiac disease (kids), nontropical sprue (adults) hypersensitivity to gluten tx: remove gluten from diet tropical sprue clinically & radiologically similar to nontropical sprue tx: folate, B-12, antibiotics a/w ** transient intussusception esophageal Ca () + small bowel Ca (QUESTIONABLE!!) diffuse intestinal lymphoma (rare; except in Middle East) |
|
|
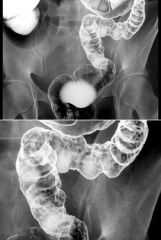
UC
|
|
|
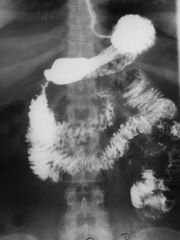
SIGMOID VOLVULUS
|
|
|
GIARDIASIS
Nonspecific findings Thickening, distortion and spasm of the duodenum and the proximal jejunum rapid transit of barium segmentation and increased luminal fluid due to hypersecretion and hypermotility, simulating sprue. |
|
|
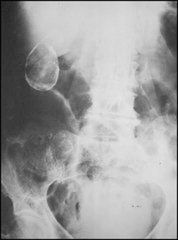
PORCELAIN GALLBLADDER
0.6-0.8% of cholecystectomy patients 80% female 10-20% develop gallbladder Ca 90% associated with gallstones |

