![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
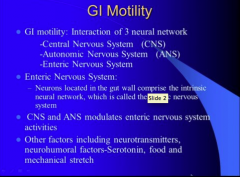
What are the three neural networks of GI motility?
What is the term for neurons located in the gut wall that comprise he intrinsic neural network?
What modulates enteric nervous system activities?
|
|
|
|
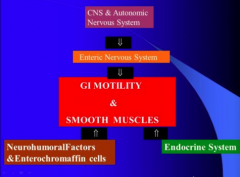
Summarize the effect all the components acting on GI motility |
|
|
|
What does sympathetic do to GI? What does parasympathetic do? |

|
|
|
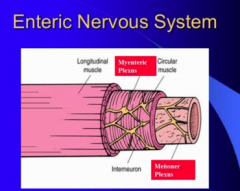
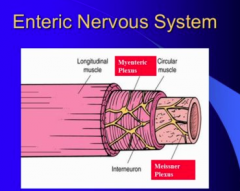
What are the two components of the enteric nervous system?
Which is present between circular and longitudinal muscle layer?
Which is in submucosa |

|
|
|
|
|
|
What does peristalsis result from in ENS? What is the name of these cells?
What are the three components that result in peristalsis
|

|
|
|
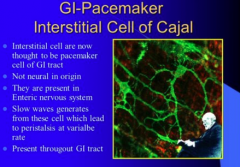
What are the pacemaker cells of GI tract? What type of waves generated from these cells lead to peristalsis?
Where are they present? |
|
|
|
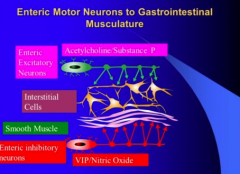
What are the excitatory and inhibitory neurons? Draw the interaction. |
|
|
|
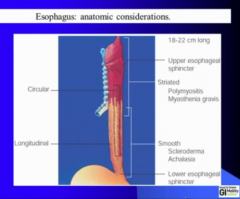
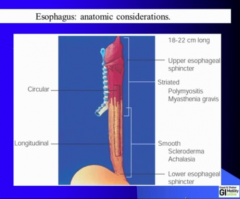
What type of muscle in upper esophageal muscle? What type in body of esophagus? What does the LES allow? What is LES relaxation controlled by? |

|
|
Review
Know where the various disease can impact: Polymyositis, Myasthenia gravis, Scleroderma, Achalasia
Most problems of swallowing come from upper sphincter muscles |
|
|
|
What is primary peristalsis?
What is secondary peristalsis?
What is tertiary peristalsis? |

|
|
|
What is receptive relaxation of fundus? What does the upper part of the stomach handle? What does the lower part handle?
What is the rate of the gastric pacemaker? The antrum empties contents into what? What size are the particles. |

Stomach relaxes as food enters => if not, will have early satiety |
|
|
What are the two patterns of the small bowel? |

|
|
|
What is the fasting pattern (don't care about phases)? |

Migratory motor complex = sweeping function/ house keeping |
|
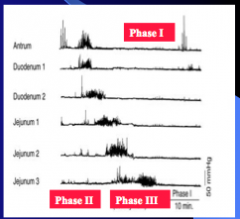
Keeps intestine clean |
Keeps intestine clean |
|
|
What is the fed pattern? What is the purpose? |
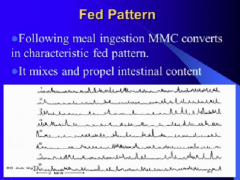
Mixes and propels intestinal content. |
|
|
What is achalasia? What does it mean? It is a failure of what? |

|
|
|
What is the incidence of achalasia? Etiology? Selective loss of what? What will you see on pathology? Infiltration in what regions? |

|
|
|
What is the most common symptom of achalasia? Where is chest pain located? Is heart burn reported? Others? Association with what two diseases? |

|
|
|
What do you need to diagnose achalasia? What is the gold standard for diagnosis? |

|
|
|
What will you see on CXR? |
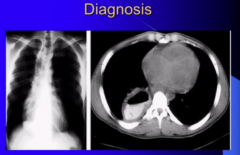
Air and food in dilated esophagus behind silouhette. Classic. |
|
|
What do you perform endoscopy? What are some other causes of dilated esophagus? What do you look for in the stomach? |

|
|
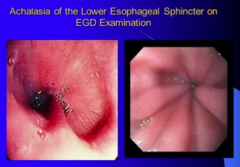
|

|
|
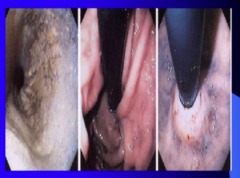
|
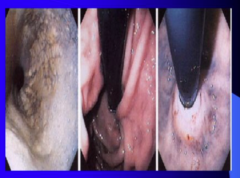
|
|
|
What is s primary screening test with diagnosis accuracy of 95% What is characteristic appearance? What can severe dilatation lead to? What can you see with flurosocapy? |

|
|
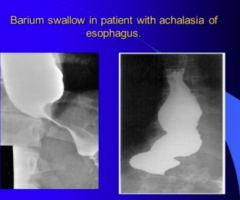
What is this? |
Bird beak appearance |
|
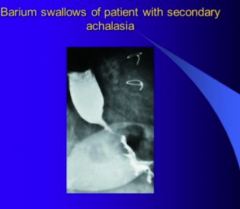
What is this? |
Pseudoachasia = tumor which leads to narrowing stricture |
|
|
What is manometry? What does it measure? |

|
|
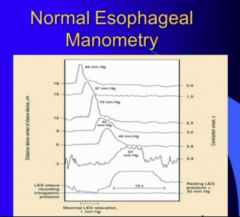
Can see good pressure generated all the way down. Stepladder pattern |
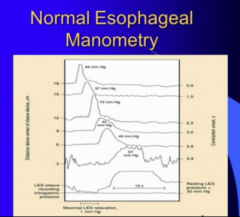
If achalasia = no peristalsis |
|
|
What are the two criteria to diagnosis achasia? |

|
|
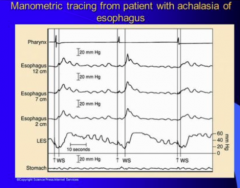
What is missing here? |
No good peristalsis |
|
|
Again what are two two criteria? |
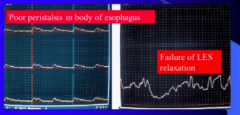
|
|
|
What are two medical treatments for ACH? What about endoscopic treatments? (2)
Which is the best treatment? |
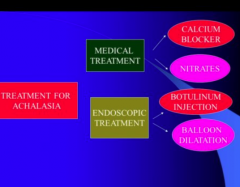
|
|
|
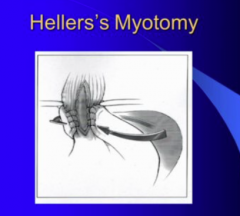
What is the surgical treatment for ACH? |
Heller's myotomy |
|
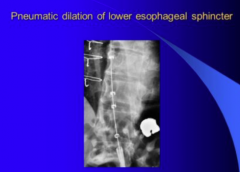
Balloon treatment |
Incise LES (laproscopy) Cut to muscle and only leave submucosa => risk of inability to swallow, will also have reflux => need to do incomplete wrap, wrap LES with gastric cardia tissue to have enough pressure in the area that refill doesn't happen and lets food pass through. |
|
|
What are the three complications of achalasia? Increase risk of which type of cancer? |

|
|
|
What are some diseases associated with achalasia-like motility disorders?
(Cancer, trypanosoma infection, old people, calcium, neuro...) |

|
|
|
What are motility disorders characterized by?
What are three abnormal patterns? |

Hypertensive LES is not Achalasia because they will have normal peristalsis but high pressure |
|
|
What is diffuse esophageal spasm? |

|
|
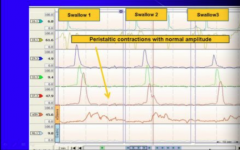
How do you know this is diffuse esophageal spasm? |
Multiple high peaks Prolonged duration contractions |
|
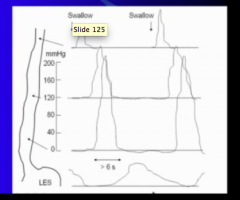
What is nutcracker esophagus? How do you know this it the condition? |
Hypercontracting esophagus Increased distal peristaltic amplitude and duration |
|
|
Long standing acid reflux = more than 5 years duration Weight loss, problems with swallowing, family history, anemia.
What should you do with all these patients? |
Evaulate by specialist => endoscopy, etc. Many patients with achalasia take 4-5 years before a diagnosis. |

