![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
194 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the NANB viral heps technically?
|
C, E, G, SEN, TTT, maybe others
|
|
|
What is the most common type of new pathogen? Why?
Emerging pathogen: 3 examples? Re-emerging pathogens: 3 examples? |
Virus - simpler/smaller genome, quicker adaptations
new, never before seen pathogen Ebola, Chikungunya virus, Granulobacter bethesdensis in CGD patients previously seen pathogens, thought gone: Influenza H5N1 avian flu, measles, Ecoli O157:H7 (spinach), salmonella (peanut butter) |
|
|
Common features of viral hepatitis?
Lab findings? |
RUQ abd pain, nausea, anorexia, fatigue, fever, jaundice, hepatomegaly
elevated liver enzymes, bilirubin in blood/urine, Alk Phos, LDH |
|
|
4 m/o infant presents with watery diarrhea, vomiting x 24 h. no PO intake, appears dehydrated:
Morphology? Which group most common? Why is its habitat unique? |
Rotavirus
dsRNA, Reoviridae A more common in temperate climates, circulates in winter months |
|
|
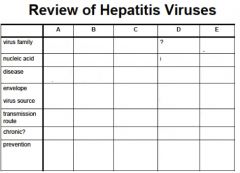
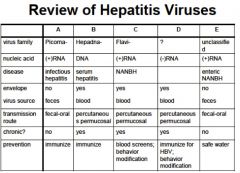
HAV:
1. Family of viruses? 2. stable or unstable in environment? 3. acute, chronic infection? asymptomatic, symptomatic? 4. Transmission? Where? 5. single outbreak or community? 6. Vaccine? Who gets which kind? |
1. picornaviridae, +ssRNA, one serotype worldwide (enterovirus group)
2. stable in environment 3. acute, asymptomatic infections in kids, adults quick onset "infectious hepatitis" 4. fecal-oral, crowded, poor hygiene 5. community outbreaks 6. inactive vaccine for children. killed vaccine for the military, travelers to endemic regions, high risk groups. of infection. |
|
|
List from CDC of re-emerging pathogens? (5)
|
• Staphylococcus aureus
• Clostridium difficile • Enterovirus 71 • Group A Streptococcus • Mumps virus |
|
|
Hep A pathogenesis? (incubation as well)
definitive dx of acute infection? definitive dx of past infection? Tx of HAV? |
intestine --> hepatocytes (replication) --> feces- incubation- 30 days
acute infection, >14 y/o anti-HAV IgM - acute infection anti-HAV IgG - past infection no antiviral tx, vaccinations, children @ 1 y/o, travelers |
|
|
What two bacterias cause a syndrome clinically indistuishable from typhoid fever?
|
camplylobacter fetus
yersinia enterocolitica |
|
|
HBV:
1. Family? 2. Transmission? 3. How is the liver damaged? 4. When do clinical signs show up? 5. Who gets the active vaccine? 6. Who gets the passive vaccine? |
1. hepaDNA viridae, enveloped (partially) dsDNA
2. blood/semen, to liver 3. Damage to liver cells is immune mediated (due to release of toxic substances from infiltrating mononuclear cell and cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs) 4. When liver damage ensues clinical signs occur 5. children, infants, high-risk 6. health care workers |
|
|
3 reasons why re-emerging pathogens come back?
|
develop resistance
decline in vaccination rates re-assortment from other species |
|
|
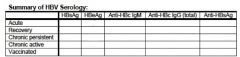
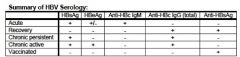
Hep B:
General serum marker of infection: why? Recovery/immunity to HBV by itself vs found with other Abs: Marker of acute infection: Marker of past/chronic infection: active replication: |
general: HBsAg- surface is what body sees first "s"
Recovery/immunity: anti-HBsAb (alone = vaccination) (with other Ab's = recovery) acute: anti-HBc IgM chronic: anti-HBc IgG active replication: HBeAg, HBV-DNA |
|
|
What age group is most commonly affected?
What makes Rotavirus so hardy? What binds to glycolipids on the membrane of villus epithelial cells? |
6-24 mo.
no membrane, can remain for days on surfaces, wide pH survival, relatively resistant to cleaning/disinfectants capsid |
|
|
Serum findings in active infections of Hep B?
Serum findings in recovery? Serum findings in chronic persistent? Chronic active? |
HBsAg, anti-HBcAg IgM
anti-HBsAg, anti-HBcAg IgG HBsAg, anti-HBcAg IgG, anti-HBeAg HBsAg+, HBeAg, HBcAg IgG, DNA Pol. |
|
|
What are the criteria for viral eradication?
|
1. humans critical for transmission (no non‐human reservoir)
2. sensitive and specific diagnostic tools exist 3. effective intervention is available |
|
|
Which hepatitis often co-infects with Hep B?
What type of virus? risk group? Serologic dx? Which ones are more likely in chronic vs acute? |
Hep D
ssRNA, unclassified IVDA's and partners anti-HDV IgM (high in chronic) also found in acute, anti-HDV IgG (late in acute), HDV Ag |
|
|
H. pylori was officially "discovered" by:
How? Habitat? |
Marshall, Warren
Marshall ate a H. pylori cx - exhibited symptoms of gastritis exclusively human gastric mucosa |
|
|
Hep C:
Family, type of virus? animal reservoir? Transmission? 90% of who will get this? commonly causes _________ infections. leading cause of ______________. |
Flavivirus, +ssRNA
humans, chimps injection, needle stick, sexual, 90%- drug users chronic liver transplantation |
|
|
What gives the influenza A virus the ability to replicate?
Markers found in blood? |
8 strands, which allows for many changes
HA- hemagglutanin NA- neuraminidase |
|
|
What are the "serum transmitted" Hep viruses?
|
B and D
|
|
|
S/S of Rotavirus?
Pattern of when occuring and where? Mortality from what? malabsorption of what? |
smelly poops, fever, nausea, diarrhea, watery diarrhea WITHOUT LEUKOCYTES, fever
- circulates in winter months "winter diarrhea" starts SW in Autumn, ends NE in Spring dehydration fat, lactose |
|
|
HBV Ag or anti found from (acute infection)...
a. 4-24 weeks b. 6-32 weeks c. 32+ weeks d. 6+ weeks |
a. HBsAg
b. IgM anti-ABc c. Anti-Hbs d. Total anti- HBc |
|
|
What is antigenic drift? What pressures it?
What is antigenic shift? Which drift/shift is pandemic? |
point mutations in serotype - antigens pressure (in mammals)
whole gene change/rearrangement - species jumping (shift) H1N1 |
|
|
Factors that promote progression/severity of Hep C:
Ability to clear virus depends on ______ response. |
EtOH, age, HIV, male, HBV
T-cell (CD4, CD8) |
|
|
What are the three types of clinical "manifestation" labels for salmonella...
|
1. Enteritis
2. Septicemia 3. Enteric fever- |
|
|
Which hepatitis is not person-person transmitted?
Type of virus? Related to what virus? Best way to prevent Hep E infection? |
Hep E
NANB hep virus ,non-eveloped RNA genome similar to Calciviruses watch for contaminated H2O |
|
|
T/F: H5N1 is easily transmitted person-person.
_________ has high death rates in sub-Saharan Africa due to low vaccination. 199 people infected in 2006 with _________ from eating bad spinach: |
F
Measles E. coli O157:H7 |
|
|
Name the type of virus for the following...
a. AKA infectious hepatitis b. replicates via RNA intermediate c. High risk sexual drug abusers |
a. HAV- Hep A
b. HBV- Hep B b. HDV- Hep D |
|
|
What virus can cause either respiratory or GI diseases?
Morphology? transmission? Where does it attack? |
adenovirus
dsDNA, non-enveloped droplets, fecal-oral, poorly chlorinated H2O, attacks mucoepithelial cells of conjunctiva, repiratory tract, GI, GU, leads to decreased absorption of Na and H20 |
|
|
Types of HBV chronic infections?
Incubation period? More likely to develop chronic infection at what age? |
Chronic persistent- can still transmit but not symptomatic
Chronic active- symptomatic hepatitis - 100 days (about) - 0-5 yrs old |
|
|
Recently this virus has been seen on the rise with 8,383 cases in California in 2010...
|
Pertussis
|
|
|
For Acute HBV infections at what times would you see...
a. HBeAg b. Anti- HBe |
a. 4-12 weeks
b. 12+ weeks |
|
|
What causes amoebic dysentery?
Most common dissemination? S/S of acute and chronic? What stage is often ingested? |
Entamoeba histolytica
Liver abscess acute: dysentery, abd pain, mucosal necrosis chronic: acute S/S, + quadrinucleate cysts in feces cysts |
|
|
1. needs HBV as a helper to code its surface protein
2. Worrisome of mortalities in pregos |
1. Hep D
2. hep E |
|
|
What should you not use on O157:H7 patients? (2)
Bacteria found in Hershey's chocolate in Canada, 2006: One major complication from Salmonella poisoning? Which emerging pathogen has the mosquito as a vector? |
Abx, anti-diarrheals
Salmonella Reiter's syndrome (can't see, can't pee, can't go out with me) Chikungunya virus |
|
|
How does Hep D create Super-infection vs. coinfection...
Which is usually acute vs. chronic? |
Co-infection usually acute- D got while getting B
Super- usually chronic after already having B you get D |
|
|
People on a cruise develop GI symptoms with abd cramps, main symptom is vomiting, also diarrhea, malaise, HA. Disease lasted for 2-3 days:
what age groups does it affect more? any blood/leukocytes in stool? |
caliciviruses - Norwalk virus, Norwalk-like
adults, children > 4 y/o No blood or leukocytes |
|
|
For superinfection of HDV how do you prevent?
How do you cure/prevent coinfection |
stop shitty behavior to prevent developing super infection
- Coinfection if you cure B you cure D |
|
|
What type of virus is chikungunya and what family is it?
What is it similar to? Symptoms? Vector? |
Alpha virus- Togaviridae family
(+)ssRNA genome - joint pain, rash, other similar viral reactions Joint pain |
|
|
What serology studies find for Hep E?
|
anti- HEV IgG, anti HEV IgM, viral detection
|
|
|
Which clinical manifestation of salmonella am I describing...
a. risk higher in pediatric, geriatric and immunocompromised gets in blood b. 6-48 hrs after ingestion, nausea, abdominal cramp, vomiting, non-bloody diarrhea (last 2 days-1 week) c. 10-14 days after ingestion, rose spots d. most common |
a. septicemia
b. enteritis c. enteric fever d. enteritis |
|
|
What is the diagnostic process for HCV?
|
1. anti- HCV first with ELISA
2. Confirm with RIBA test for RNA specific for Hep C 3. HCV PCR qualitative- (reverse transcriptase) to find out if presentand quantitative to find out how much present |
|
|
Bacteria only seen in chronic granulomatous disease CGD patients, used for vinegar production, Gram(-) rod:
|
Granulobacter bethesdensis
|
|
|
|
|
|
Where are caliciviruses often found?
Most common transmission? What causes "winter vomiting disease"? How do you dx? |
water - shellfish, contaminated food, lakes
contaminated food Noroviruses by exclusion, R/O everything else, cup like hollows under microscope, Amplification of the viral genome from stool samples by RT-PCR is the mainstay of diagnosis |
|
|
1.1 Slutty Drugged Waitress Test show:
– HAV IgG: positive – HAV IgM: negative – HBsAg: positive – Anti-HBsAg: negative – Anti-HBcAg IgM: positive – HBeAg: positive – Anti-HBeAg: negative – Anti-HCV: negative |
Start with A's and then go C and then B
HAV IgG- not active then skip B See- Anti-HCV neg so no Hep C See "M" for HBV meaning she has acute infection, then others are used to confirm... but keep CHRONIC IN MIND IF PERSON IS DIRTY WHORE |
|
|
35 y/o, traveled to Bangladesh, fever, diarrhea, G(-) rod, non-lactose, motile, H2S+:
30 y/o, sudden onset fever,abd pain, watery diarrhea; eaten crabs, diffuse abd tenderness: |
Salmonella typhi
V. parahemolyticus, halophilic species (high salt) |
|
|
1.2 Six month follow up of slutty waitress with normal liver enzymes
– HBsAg: positive – Anti-HBsAg: negative – Total Anti-HBcAg: positive – Anti-HBcAg IgM: negative – HBeAg: negative – Anti-HBeAg: postive |
more like chronic peristent not active, but can still transmit infections
|
|
|
H.pylori
Infections are associated with _______ conditions in childhood. ______% of the developed world is colonized. ___ out of 10 peptic ulcers due to H. pylori infection |
crowded, low socioeconomic status
70-90% 9/10 |
|
|
1.3 Two years later of dirty waitress:
– HAV: IgG positive --HAV IgM: negative – HBsAg: positive -Anti HBsAg: negative – Total Anti-HBcAg: positive – Anti-HBcAg IgM: negative – HBeAg: positive – HBV DNA: positive – Anti-HDV IgM: positive – Anti-HCV: negative |
now she has D most likely superinfection
|
|
|
25 y/o on vacation in Mexico; abrupt watery diarrhea, abd cramps, fever/chills; no RBC's, WBC's, parasites in stool:
20 y/o, extensive purpuric rash, oliguria, weakness; bloody diarrhea, RBC's, no parasites, ate a hamburger: |
ETEC, probably EAEC
EHEC, E. coli O157:H7 |
|
|
|
|
|
What pathogens cause enteric disease in AIDS patients/immunosuppressed?
37 y/o homosexual male, vomiting, diarrhea, cramping, abd pain, no blood in stool, no leukocytes, intranuclear inclusions with halo: |
CMV, HSV, HIV
CMV |
|
|
30 y/o in hospital, watery diarrhea, abd pain, N/V; on ampicillin 5 d.
What else might you see? |
C. difficile
Pseudomembranous colitis |
|
|
This bacteria is motile non-lactose fermenter, H2S+,
|
salmonella
|
|
|
19 y/o, abd cramps, bloody diarrhea, afrbile, ate undercooked chicken, occult blood +, G- S-shaped rods, microaerophilic:
15 y/o, ate fried rice, cramping/vomiting: |
C. jejuni
B. cereus, type I (emetic, heat stable) |
|
|
What groups are most at risk for CMV infection?
transmission of CMV? |
high income - 50%
low income - 85% homosexuals - 95% sexual, urine contact, transfusion/transplantation |
|
|
E. histolytica:
Characteristic histology finding? Diagnostic requirement? Treatment? |
NO cysts, trophozoites + RBC's
3 stool tests - trophozoites + RBC's mild: iodoquinol,paromomycin moderate: Met, tinidazole Severe/extraintestinal: *Met*, dehydroemetine |
|
|
Review:
DsRNA, 10-11 segments, non-enveloped: domestic/wild animals, outbreaks in closed environments - camps, cruises, schools: - look like a star in electron microscope, cause diarrhea in kids <5 yrs |
Rotavirus
Norwalk virus astrovirus |
|
|
Growth on MacConkey usually means?
If it is clear growth vs. pink? |
Growth is usually G-
If clear it mean non-lactose fermenting |
|
|
serotypes 40,41 associated with diarrhea in infants:
most common cause of viral GE in industrialized countries, "winter vomiting disease": "summer diarrhea", often community outbreaks: |
Adenovirus
Norovirus Norwalk virus |
|
|
Morphology of H. pylori?
Converts urease to __________. Pathology? |
G-, microaerophilic, spiral/corkscrew shape, up to 7 flagella
ammonia, CO2 local tissue/mucosal injury, increased gastrin, HCl |
|
|
affects immunocompromised, highest risk in homosexuals and low-income:
vaccine approved in 2006, mortality due to dehydration: |
CMV
Rotavirus |
|
|
Gram-negative bacilli, non-motile, non-lactose fermenter, survives in cytoplasm
Transmission? |
Shigella
- 4 F's: food, fingers, feces, flies |
|
|
What viruses may be seen in healthy GI tracts without infection?
|
CMV, HSV, HIV
|
|
|
Giardiasis:
Organism? Prevalence is high with _________. Acute S/S? Treatment? |
Giardia intestinalis- "beaver fever"- not "Beiber fever" man if i ever saw t aht kid i would just punch him
poor water sanitation explosive diarrhea, abd pain, smelly farts, greasy stools DOC is Metronidazole, Oral rehydration |
|
|
Which are the main viruses associated with gastroenteritis?
|
1. Caliciviruses
2. Rotaviruses 3. Adenoviruses 4. Astroviruses 5. SRSV (Small round structured) aka norwalk like |
|
|
What are the two most common in US groups of shigella?
What is exotoxin? How many cause infection? |
S. Flexneri (Group B)
S. sonnei (group D) - shiga toxin- 10-20 bacilli can cause |
|
|
watery diarrhea also results from viral protein (NSP4) enterotoxin activity
– causes excess chloride secretion |
Rotavirus
|
|
|
What is the preferred habitat of H. pylori?
|
exclusively human gastric mucosa (but can survive outside humans in feces and drinking water)
|
|
|
most important cause of gastroenteritis in infants and young children
|
Rotavirus
|
|
|
Where do Shigella attach and penetrate?
Some of the strands produce enterotoxin... what does this do with the shiga (exotoxin) toxin? |
GI epithelial and M cells by using the host cells actin for transport
- cleave ribosomal RNA- causes host cell death and tissue destruction |
|
|
Diagnosis of Rotavirus?
|
Viral antigen (VP6) detection from stool most common
– ELISA – rapid antigen detection - Group A rotaviruses can be cultured in monkey kidney cells |
|
|
Spore forming protozoa: *SPORE IN NAME*
Organisms? S/S? Transmission? Who is mostly affected? |
Cryptosporidium, Isospora/Cyclospora, Microsporidia
S/S: acute diarrhea in normal, chronic in immunocompromised Transmission: fecal-oral Usually affects immunocompromised - well hydrated "Flagyl"- metronidazole |
|
|
ROTA means?
2nd most common viral cause of gastroenteritis (all ages) |
Right Out The Anus
adenovirus |
|
|
Shigella
1. incubation period 2. symptoms |
1. 36-72 hours
2. non-specific symptoms: fever (39°C), cramping abdominal pain, watery diarrhea after 48 hours, dysentery (bloody, mucous containing, small volume stools, pain upon defecation) ~2 days later |
|
|
Incubation period: 8 to 10 days
• Transmission: Fecal-oral, fomite • Signs: diarrhea for 5-12 days • Population children, neonates |
adenovirus
|
|
|
What bug is a major cause of chronic gastritis and duodenal ulcers?
|
H. pylori
|
|
|
Incubation period: Less than 24 hours
• Transmission: Fecal-oral, Community outbreak respiratory? • Signs: Fever, nausea, (diarrhea sometimes) • Duration: ~3 days • Age effected: Adults & older children • Seasonal?: most common in summer |
Norwalk/Calciviruses (taxonomy is fucked up)
|
|
|
Difference between shigella and plesiomonas?
|
Plesiomonas oxidase positive
– Shigella is oxidase negative |
|
|
A 37-year -old homosexual male with AIDS has vomiting, diarrhea, and severe cramping abdominal pain. What are the causes of vomiting and diarrhea in an immune compromised patient?
Bacteria, Virus, Parasite, Fungi possible? |
– Bacteria- Shigella, Salmonella, Campylo, Mycobacterium
– Viruses- CMV, HSV, HIV – Parasites- Cryptosporidia, microsporidia, isopora, giardia - Fungi- Candida esophagitis |
|
|
Cryptosporidiosis:
Infects what hosts? S/S of Isospora and Cyclospora? Lab Dx for these organisms? Tx for C. parvum? Iso/Cyclo? |
Crypto - cattle, livestock, *dogs*
Iso/Cyclo S/S: flu-like symptoms Lab Dx: modified acid-fast stain Tx for C. parvum: none, need to maintain immunity Tx for Iso/Cyclo: Bactrim |
|
|
HIV pt.
– no blood in stool – no fecal leukocytes – stool cultures did not reveal any bacterial pathogens – O&P exam negative – stool was negative for Adeno & Rotavirus antigen |
some kind of virus, think CMV just cause he is a HIVite
|
|
|
Gram-negative, slender, curved or comma-shaped, microaerophillic, motile rods
|
campylobacter (jejuni) most common
|
|
|
You find a bug that is gram negative, microaerophilic, spiral/corkscrew shaped, has 7 flagella, and produces urease.... what do you think it is?
|
H. pylori
|
|
|
Leading cause of bacterial diarrheal illness in US
1. Incubation 2. What causes overt disease of it? 3. most common manifestation of this? |
Campylobacter
1. 3-5 days after ingestions 2. if penetrates mucous layer and invades GI epithelial cells 3. watery diarrhea |
|
|
Most common human helminthic infection?
Route of infection? Manifestations? DOC for Ascaris? |
Ascaris lumbricoides
Ingestion, penetrate alveolar wall, ascend bronchi --> throat, swallowed appendicitis, eosinophilic pneumonitis (Loeffler's Syndrome) Albendazole |
|
|
What special media and techniques are required to detect campylobacter?
|
Campy-BAP and Skirrow media
|
|
|
What are the 2 biggest virulence factors of H. pylori?
What are the main tests used to diagnose? |
1.flagella and urease
2. rapid urease test, urea breath test, ELISA, stomach biopsy and culture |
|
|
Aerobic gram negative found in domestic and farm animals presents often as appendicitis in the winter
|
yersinia enterocolitica
|
|
|
Hookworm found in US?
Route of infection? S/S? DOC? |
Necator americanus
filariform larva --> skin --> lungs --> swallowed --> intestine --> maturation, eggs in feces +anemia, malnutrition, edema DOC: infants - pyrantel pamoate, adults - meben/alben |
|
|
This bacteria grows at 4 C and causes painful enlargement of mesenteric lymph
nodes - daycare outbreats |
yersinia enterocolitica
|
|
|
Strains of H. pylori producing expressing what gene and what toxin cause more intense tissue inflammation and induce IL-8 production?
|
1. Vacuolating cytotoxin (VacA)
2. Cytotoxin-associated gene (CagA) |
|
|
ACT enterotoxin, mostly immunocompromised with water habitats
|
Aeromonas hydrophila
|
|
|
Which helminth completes its entire life cycle in humans?
(Strong with the force this one is) Two life cycles? S/S? DOC? |
Strongyloides stercoralis
Free-living - fecal oral Parasitic - skin --> lungs --> throat --> swallowed S/S: ground itch, pneumonitis, ulcers DOC: albendazole, ivermectin |
|
|
SSDC agar?
|
yersinia enterocolitica
|
|
|
What is the method of choice for diagnosing H. pylori infection?
Breath test? |
urease test
Breath test is C14 unless prego than C13 |
|
|
small, curved Gram-negative rods with a
single flagellum, activates adenylate cyclase to increase cAMP |
V. Cholerae
|
|
|
Whipworm:
2nd most common US whipworm? Route of infection? Egg shape? DOC? |
Trichuris trichiura
fecal-oral Egg: barrel shape, 2 polar plugs DOC: mebendazole, albendazole |
|
|
How is V. Cholerae transmitted?
Colonizes what? What toxins does it produce? |
contaminated water or food (usually shellfish, crabs)
- small bowel - cholera enterotoxin, mucinase, and endotoxin |
|
|
What do normal flora of the GI tract do?
|
maintain health and normal function:
1. synthesize vit K 2. aid in nutrient absorption 3. conversion of bile pigments to bile acids 4. prevent colonization by pathogens |
|
|
Caused by toxin; most often occurs in underdeveloped nations; commonly associated with consumption of raw oysters; comma shaped
|
V. cholerae
|
|
|
Pinworms:
Organism? Why is this worm's habitat unique? Route of infection? Dx? (Got any tape)? DOC? |
Enterobius vermicularis
common in temperate regions, NOT TROPICAL ROI: eggs hatch in perianal region, larva into GI tract Dx: tape on ass, find eggs DOC: albendazole |
|
|
This bacteria produces an exotoxin that activates adenylate cyclase in the crypt cells. The increase in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) activates Cl- secretory channels. Consequently, sodium and water accompany Cl- into the lumen, which results in an osmotic diarrhea.
|
V. cholerae
|
|
|
T of F. GI tract is sterile at birth.
|
True
organisms introduced in food, breast milk, etc |
|
|
abrupt watery diarrhea "rice water" stools... of this bacterial toxin,
|
V. cholerae
|
|
|
Roundworms: (pets)
Commonly found in what animals? Usually affects what organ? Tx? Prevention? |
Dogs, cats
eye is usually affected (toxocara) Tx: Albendazole, mebendazole Prevention: treat pets, cover sandboxes, cook crustaceans well |
|
|
What type of media do you need for vibrio cholera?
|
TCBS (thiosulfate- citrate bile salt-sucrose)
- cholera will show yellow and others (vibro only) will show green |
|
|
major cause of chronic gastritis and duodenal ulcer
|
H.pylori
|
|
|
halophilic (salt-loving) and grows in
marine environments – commonly found in raw or undercooked shellfish • more common in Japan |
V. parahaemolyticus
|
|
|
Trematodes - Flatworms
3 Schistosomiasis species? Where are they found? Larval stage in what animals? What organs do they like? DOC? |
mansoni - S. America, Arabia, Africa
haemotobium - Africa, India japonicum - Asia fresh water snails M - liver portal system, H - bladder, K - sup. mesenteric veins DOC - Praziquantel |
|
|
What are the five E.coli's?
E- entero |
toxigenic, pathogenic, hemorrhagic, invasive, aggregative
1. ETEC: Enterotoxigenic 2. EPEC: Enteropathogenic 3. EHEC: Enterohemorrhagic 4. EIEC: Enteroinvasive 5. EaggEC: Enteroaggregative (or EAEC) |
|
|
H. Pylori
Shape? Virulence factors? Flagella? How do they work? |
a. microaerophilic- spiral/corkscrew shape
b. flagella and urease c. 7 d. grow on surface of gastric epithelium cells, in the mucus layer |
|
|
What are the five E.coli's?
E- entero |
toxigenic, pathogenic, hemorrhagic, invasive, aggregative
1. ETEC: Enterotoxigenic 2. EPEC: Enteropathogenic 3. EHEC: Enterohemorrhagic 4. EIEC: Enteroinvasive 5. EaggEC: Enteroaggregative (or EAEC) |
|
|
Tapeworms:
Host for: T. solium, T saginata, D. latum: body structure? Route of infection? S/S? DOC? |
T. solium: pigs
T. saginata: cattle D. latum: fish scolex, proglottids + eggs ROI: under-cooked meat S/S: usually none, sometimes appendicitis, B12 deficiency DOC: Praziquantel |
|
|
What is the key to noting its an infection from bacteria in diarrhea?
|
fecal leukocytes with "left shift" meaning neutrophils PMNs are present
|
|
|
Explain how urease helps H. Pylori live in stomach
How do you diagnose? |
converts urea to ammonia and CO2
- >5% bacterial total protein = rapid urease test- looking for enzyme |
|
|
Cholera-like toxin, *T*raveler's diarrhea:
adheres to small bowel, common in (Pint-sized) children: Shiga-like toxin, O157:H7, inflammatory colitis: |
ETEC
EPEC EHEC |
|
|
Echinococcus:
Unique about life cycle? Characteristic manifestation? |
Humans aren't really involved in life cycle, but can ingest the adult organism and be infected
Hydatid cysts |
|
|
What are the many inflammatory gastroenteritis pathogens (8)?
|
– Salmonella sp.
– Shigella sp – Vibrio parahaemolyticus – EIEC - EHEC – Campylobacter sp. – Yersinia enterocolitica – Francisella tularensis |
|
|
Other than urease and flagella what are four other virulence factors of H. Pylori?
|
1. phospholipases (breakdown host membranes)
2. adhesins (hook on) 3. protease- breaks down mucus layer 3. CagA (cytotoxin Associated Gene)- 4. VacA combined with CagA can cause intense tissue inflamation and IL-8 production |
|
|
Shiga-like, but no toxin, invades colonic epithelium:
in colonic mucosa, +toxin, prolonged watery diarrhea: Which ones are non-inflammatory/non invasive? (PAT) InvAsive, inflammatory? |
EIEC
EAEC EPEC, EAEC, ETEC EIEC, EHEC |
|
|
Balantidiosis:
Organism? Route of infection? What animal has 20-100% prevalence? |
Balantidium coli
ingestion of cysts Pigs |
|
|
Which of the bacterial causes of diarrhea is a lactose fermenting?
|
E. coli
|
|
|
Which cytokine is super involved with H.pylori infections?
|
IL-8
|
|
|
Salmonella sp.
habitat? What pet is common? |
Gram-negative rods, motile facultative anaerobes, non-lactose fermenting
S. typhi- humans GI rest of Salmonells intestines of animals - turtles (reptiles) |
|
|
What helminth can migrate to your CNS and cause calcified cysts?
|
Cysticercosis-brain
caused by T. solium |
|
|
SHIga-like?
Montezuma's Revenge? ETEC affects what cell pathways? What does that cause? |
EHEC, EIEC
EAEC more adenylate-cAMP, cGMP more Cl- release, H2O follows |
|
|
Pt. comes in to the clinic after he went crazy and ate his dog's poo about 15 years ago and felt he should confess... you feel a mass on his liver. turns out he's got them all over his liver... Dx? Tx?
|
Dx: Echinococcus granulosus (hydatidosis)
Tx: surgical removal of hydatid cysts, give Praziquantel w/ albendazole or meb) |
|
|
What's unique about EPEC's attachment to the cell? (Princess on a Pedestal)
3 stages: stick to mucosa, biofilm formation, cytotoxin, intestinal cell damage: |
attaching and effacing - EPEC injects tir receptor, binds to intimin, rearranges actin in the cell --> pedestal, bacteria on top
EAEC |
|
|
Pt. presents w/ severe bloody diarrhea and RUQ pain after coming back from swimming tour in third-world countries. Stool sample reveals cysts w/ 4 nuclei and trophozoites containing RBC's. Dx? Tx?
|
Dx: E. histolytica (amebiasis)
Tx: Metronidazole followed by paromomycin |
|
|
Normally salmonella enteridis infections show what symptoms? What cells do they invade?
What symptoms does salmonella typhi (or paratyphi) show ? |
Enteridis- fever, abdominal pain, and diarrhea
• invades intestinal epithelial cells – inflammatory diarrhea Typhi- fever, nonproductive cough, bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, skin develops small rose-colored macules (rose spots) |
|
|
Pt. presents w/ foul-smelling EXPLOSIVE diarrhea, bloating. Hx reveals he went hiking a week ago and drank from the beautiful streams. Dx? Tx?
|
Dx: Giardiasis
Tx: Metronidazole or Tinidazole |
|
|
Has 3 stages: mucosal adherence, *biofilm*, cytotoxin/intestinal cell damage
Why is pathogenic E. coli pink on MacConkey's agar? What E. coli are related to S(HI)gella? |
EAEC
lactose fermenter EHEC, EIEC |
|
|
Immunocompromised Pt. presents w/ severe watery diarrhea after visiting a local farm to pet the animals. Stool sample reveals cysts on acid-fast stain. Dx? Tx?
|
Dx: cryptosporidium
Tx: symptomatic |
|
|
Since this type of bacteria is sensitive to gastric acid how does it invade?
|
- attach to gastric epithelial cells in small intestine and colon
--->bacterial type III secretory system to inject bacterial proteins into host cells - eventually makes tunnel from bacterial cell to cause bacteria to flood in |
|
|
Pt. presents w/ appendicitis and eosinophilic pneumonitis. They got back from a tropical year-long trip. Stool sample reveals ovoid eggs. Nothing else remarkable. Dx? Tx?
|
Dx: Ascaris lumbricoides
Tx: Albendazole or Mebendazole |
|
|
EHEC usually affects what systems?
Complications? (E-*H*-E-C) Which bacteria do you AVOID ABX use? Why? |
large bowel - necrosis, neutrophils
kidneys - shiga toxin hemorrhagic colitis, HUS EHEC - kills bacteria --> more toxin released |
|
|
8-yr-old female presents w/ diarrhea, wt loss, anemia, distended abdomen, and itchy rash on planter surface of L foot. Stool sample reveals some eggs. Dx? Tx?
|
Dx: Hookworm (Necator americanus)... be careful as larvae look like strongyloides
Tx: Albendazole or Mebendazole |
|
|
What are the three non invasive Ecolis
What does that mean? |
do not see fecal WBCs
• ETEC • EPEC • EAggEC |
|
|
Pt. presents w/ steatorrhea, vomiting, malabsorption syndrome, skin lesion on foot. Stool sample was negative, but enterotest (string test) was positive. Dx? Tx?
|
Dx: Strongyloides stercoralis
Tx: Ivermectin po |
|
|
What are the 2 invasive E. Coli's
|
• EIEC
• EHEC |
|
|
10-yr-old male presents w/ slightly bloody diarrhea, lower abdominal pain, tenesmus, and rectal prolapse. Stool sample reveals barrel-shaped eggs. Dx? Tx?
|
Dx: whipworm (trichuris trichuria)
Tx: Mebendazole |
|
|
Name E.coli with each...
a. traveler's diarrhea b. No toxin produced; adheres to apical surface, flattens villi, prevents absorption, c. elaboration of cytotoxin which damages interstinal cells d. infants < 6 months |
a. ETEC
b. EPEC c. EAggEC d. EPEC |
|
|
7-yr-old male presents w/ "my booty itch at night". You pull out the scotch tape b/c you suspect what? Tx?
|
Dx: Pinworms (enterobius vermicularis)
Tx: Mebendazole |
|
|
What is the difference between the labile and stabile toxins of ETEC?
|
a. LT- A in cytoplasm ADP-ribosylates GTP-binding protein,
stimulates adenylate cyclase-cAMP system b. ST- binding stimulates intracellular cGMP levels, stimulates chloride ion secretion and/or inhibition of NaCl adsorption |
|
|
Little child presents w/ unilateral cataracts and retinitis. He enjoys playing w/ "scruffy the dog" all day everyday during the summer and sharing food with him. Found some eggs in the stool. Dx? Tx?
|
Dx: Toxocara canis (or cati)
Tx: Albendazole or Mebendazole |
|
|
Name the E. Coli with
a. Tir and Intimin – causes actin re-arrangement and pedestal formation b. Typically, food-borne transmission (e.g., uncooked hamburger); (O157:H7) c. avoid antibiotics with this type |
a. EPEC
b. EHEC c. EHEC |
|
|
Which Schistosoma species lives in your venous plexuses of the bladder?
|
S. hematobium
|
|
|
To isolate EHEC what are the special tests in addition to MacConkey plates?
|
1. Sorbitol must be included in the medium- inability to ferment sucrose
2. ELISA detection of Shiga Toxins 1 and 2 (Verotoxins) in stool specimens |
|
|
Which schistosoma species lives in your portal system of the liver and small venules of the colon and lower ileum?
|
S. mansoni
|
|
|
This bacteria major risk in maternal infection during pregnancy
– neonatal sepsis and meningitis follow amniotic fluid infection |
listeria monocytogenes
|
|
|
Which schistosoma species lives in your superior mesenteric veins draining the SI?
|
japonicum
|
|
|
Pt. presents w/ inflammation of spleen and liver, fever, chills, abd pain. He just got back from spending a year in the carribean. Stool revealed eggs w/ an obliquely oriented "tail." Dx? Tx?
|
Dx: schistosomiasis (mansoni)
Tx: Praziquantel |
|
|
Carrier state common in tropical countries often without disease
• Causes dysentery and GI bleeding in susceptible hosts • May mimic GI carcinoma -perforate mucosa and disseminate widely |
Entamoeba histolytica
|
|
|
This is mostly found in the SE US and can penetrate the foot. How much blood does it drink?
What positive can we come up with on these? What sign may we see in myocardium? |
hookworm - Necator Americanus
- drinks .2ml of blood causes anemia - secrete anticoagulant and do not reproduce inside - "tiger stripes" in myocardium |
|
|
What is the flag sign in hair and what bug is it associated with?
|
- due to anemia possibly caused by necator Americanus (hook worm)
|
|
|
What type of worm do you do the "scotch tape" test for?
|
Pinworm (enterobius vermicularis)
|
|
|
most common cause of epileptic seizures from people that come from tropics
|
cysticercosis
|
|
|
"Beaver Fever" with severe non‐invasive diarrhea after drinking water fresh from rocky mountain stream
|
Giardia lamblia
|
|
|
Larvae hatch in the gut, then migrate through tissue to the lung – are swallowed, then mature in the gut
• Eggs are passed through in the feces, where they may infect another human via fecal‐oral contamination |
Ascaris lumbricoides- intestinal round worms
|
|
|
larvae hatch in small intestine and make way into the cecum where they live as adults which may cause anal- prolapse
|
Whipworm – Trichuris trichiuria
|
|
|
Brain cysts and seizures think...
|
taenia solium (cysticercosis)
|
|
|
Liver cysts think
|
echinococcus granulosus
|
|
|
Portal hypertension thinking (parasite)
hematuria, bladder cancer |
schistosoma mansoni
schistosoma haematobium |
|
|
Microcytic anemia
|
necator americanus
|
|
|
Perianal pruritus
|
enterobius
|
|
|
Name the three parasites that migrate to lungs are coughed up and swallowed into the GI to grow to adults...
How does each of the three cause problems? Diagnosed? |
1. Ascaris lumbricoides (egg/eosinophils in feces)- eggs injected
2. Necator Americanus (eggs eosinophil in feces)- larvae penetrate skin 3. Strongyloides stercorous (filiarform passed)- larvae penetrate skin |
|
|
Normal flora in the GI tract synthesize _________ and help to convert ______. May also enhance. _____
Describe bacterial interference. 3 common pathogens of acute infectious diarrhea: |
Vitamin K, bile pigments --> acids, mucus production
normal flora compete w/ pathogens for nutrients in GI Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter |
|
|
3 mechanisms of bacterial pathogenicity in GI:
Why is intoxication unique? What organism associated with Antibio-associated diarrhea? |
intoxication, infection, antibio-associated
don't need to ingest bacteria- just toxin, no fecal leukocytes found C. diff |
|
|
Intoxication: 4 major organisms?
Inflammatory response or not? Which bacteria is anaerobic? |
– Clostridium perfringens
– Clostridium botulinum – Staphylococcus aureus – Bacillus cereus NOT inflammatory C. perfringens |
|
|
1. anaerobic, G+, spore forming bacilli, boxcar shaped:
2. Transmission? 3. Problem? 4. enterotoxin targets what? |
1. C. perfringens
2. meats, gravy, some vegetables 3. -part of normal flora as well 4. ion transport into intestine, which causes membrane to be more permeable, water follows, leaky membranes |
|
|
1. How many organisms of C. perfringens are pathogenic?
2. S/S of clostridium intox? 3. characteristic on anaerobic blood agar? |
1. > 10^5 food or 10^6 organisms/g stool
2. watery diarrhea, cramping <24 h, NO FEVER 3. zone of double hemolysis |
|
|
1. anaerobic, G+, spore forming rods, from home-canned vegetables/products, honey:
2. Virulence factor? 3. Action of toxin? |
1. C. botulinum
2. Botulinum toxin (neurotoxin) 3. prevents Ach release, muscle contraction failure, flaccid paralysis |
|
|
1. What C. botulinum antigens are pathogenic? (4)
2. ____ protects against stomach acids, and ____ blocks Ach release. 3. S/S when does it manifest?? |
1. A,B (bind),E,F
2. B - stomach, A - blocks Ach release 3. (1-2 days to travel to target center.) blurred vision, dry mouth, constipation, abd pain, flaccid paralysis |
|
|
1. Most common cause of intoxication in U.S.?
2. morphology? 3. virulence factor? 4. What kinds of food? |
1. S. aureus
2. G+ cocci in "grape" clusters 3. heat-stable enterotoxin 4. Creamfilled deserts, mayonnaise, dairy products, high salted foods |
|
|
Where does S. aureus bind to?
S/S? Most potent membrane damaging toxin in S. aureus? |
emetic reflex center --> projectile vomiting
vomiting, little/no diarrhea, NO FEVER, symptoms p 1-4 h. ingestion alpha-toxin |
|
|
aerobic G+ spore forming bacilli, central spores:
Major food associated with B. cereus: |
Bacillus cereus
rice- think chinese buffets |
|
|
Two types of toxins for B. cereus? Where do they act?
Which B. cereus toxin is heat-stable, which is heat-labile? |
emetic eneterotoxin (Type I)- 2-3 hrs after ingestion
diarrheal enterotoxin (Type II) - intestinal epithelium - stimulates adenylate cyclase/cAMP --> fluid accumulation (10-14 hrs after) I - stable, II - labile |
|
|
1. Treatment for intoxication reactions generally?
2. How do you treat botulism, why is it different? |
1. supportive care - fluids, hydration, electrolytes
2. - botulism differs because it is neural toxin. -monitor cardiac, respiratory - antitoxin (A,B,E) |
|
|
describe how bacteria cause diarrhea by infection
|
pathogenesis due to:
– colonization and/or – toxin production and/or – tissue invasion |
|
|
most implicated food products are meats & gravy dishes
– sometimes vegetables |
c. botulinum
|
|
|
8 antigenic types of S. aureus enterotoxin?
|
– SEA, B, C1-3, D, E, H
|
|
|
Bacteria associated w/ Dairy
|
Campylobacter, salmonella
|
|
|
Bacteria associated w/Eggs
|
Salmonella
|
|
|
Bacteria associated w/Meats
|
C. perfringens, B. Cereus, Campylobacter, Salmonella
|
|
|
Bacteria associated w/Ground Beef
|
EHEC
|
|
|
Bacteria associated w/poultry
|
campylobacter
|
|
|
Bacteria associated w/ pork
|
C. perfringens, yersinia enterocolitica
|
|
|
Bacteria/ virus associated w/ seafood
|
astrovirus and vibrio sp
|
|
|
Bacteria/ virus associated w/ oysters
|
calicivirus and vibrio
|
|
|
Bacteria associated w/ veggies
|
C. perfringens
|
|
|
Bacteria associated w/ mayo, salads with highly processed foods and cream puffs
|
Staph aureus
|
|
|
Bacteria associated w/ Rice Starch
|
Starch/Rice- B. Cereus enterotoxin I (Heat stabile)
|
|
|
Bacteria associated w/ Canned foods, honey, for children under 1
|
C. Botulinum
|

