![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
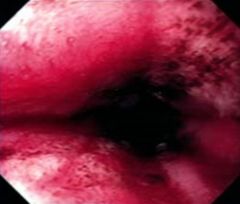
This was seen on endoscopy of a patient with reflux symptoms. What is this an example of? What are the complications/ risks of this disorder? |
Esophageal Erosions
Complications:
|
|
|
What factors (esophageal and gastric) contribute to GERD? |
|
|
|
What medications are used for the treatment of GERD? |
|
|
|
What lifestyle changes are recommended for the treatment of GERD? |
|
|
|
What surgical treatments are used for the treatment of GERD? |
Fundoplication (aka. "wrap")
Linx Bracelet
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Eosinophilic Esophagitis? |
|
|
|
What endoscopic findings are features of Eosinophilic Esophagitis? |
|
|
|
How is Eosinophilic Esophagitis diagnosed? |
Biopsy
|
|
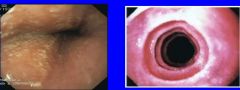
What endoscopic findings can be seen in these images? What disease/ disorder are these findings consistent with? |
Left: white plaques (shiny raised bumps) Right: concentric rings
Consistent with Eosinophilic Esophagitis |
|
|
What site is most commonly injured by ingestion of a strong acid? What type of damage (necrosis) results? |
Stomach injured more than esophagus Coagulative Necrosis |
|
|
What site is most commonly injured by ingestion of a strong alkalis (base)? What type of damage (necrosis) results? |
Esophagus injured more than stomach Liquifactive Necrosis |
|
|
What complications are associated with the ingestion of caustic substances (acids or bases)? |
|
|
|
What is achalasia? |
|
|
|
What age range(s) does achalasia typically present? |
20-40 yo |
|
|
What symptoms are most commonly associated with achalasia? |
|
|
|
What is a "bird beak deformity" on barium swallow practically pathogneumonic for? |
Achalasia |
|
|
How is achalasia diagnosed? |
|
|
|
What disease present with achalasia (cause secondary achalasia)? |
|
|
|
How is achalasia treated? |
|
|
|
A patient presents with chest pain and dysphagia. Examination via endoscopy with biopsy, pH test, and barium swallow are normal allowing you to eliminate GERD, eosinophillic esophagitis, and achalasia. What types of disorders (category and specific disorders) should be at the top of your differential? |
Spastic Motor Disorders
Upper Esophageal Sphincter Disorder |
|
|
How do you differentiate between the different Spastic Motor Disorders (what would you do to generate a specific diagnosis)? |
Esophageal Manometry |
|
|
What findings on manometry would you expect to see in a patient with Diffuse Esophageal Spasm? |
|
|
|
What findings on manometry would you expect to see in a patient with Nut Cracker Esophagus? |
|
|
|
What findings on manometry would you expect to see in a patient with Hypertensive LES? |
|
|
|
What findings on manometry would you expect to see in a patient with Ineffective Esophageal Motility? |
30% of contractions are non-peristaltic or low amplitude |
|
|
How are patients with Spastic Motor Disorders treated? |
|
|
|
What systemic diseases can affect the esophagus? |
|
|
|
What factor predisposes an individual to infectious esophagitis? |
Immunocompromised State:
|
|
|
When biopsying a patient with infectious esophagitis what is the most important area to biopsy? Why? |
The leading edge of the ulcer
|
|
|
How does Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the esophagus typically present? |
|

