![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Etiological of intra-hepatic jaundice ?
(Characteristics) |
-Viral hepatitis ( ALT > AST)
-Autoimmune hepatitis (Anti LKM1/smooth muscle)
-Primary biliary cirrhosis (Anti mitochondrial)
-Haemachromatosis (↑ Ferritin/iron)
-Dx |
|
|
etiology of post-hepatic jaundice ?
(Characteristics) |
Gallstones
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (UC, P-ANCA)
Pancreatic/cholangio CA (painless palpable gallbladder) |
|
|
With Alcoholic liver dx , what do LFT show? |
AST >> ALT |
|
|
With viral hepatitis , what do the LFT's show ? |
ALT >> AST |
|
|
What is the progression of alcoholic liver disease ?
(Characteristics) |
1. Hepatic steatosis (Fat within hepatocytes)
2. Alcoholic hepatitis ( Kupffer/stellate cells, Mallory bodies, Neutrophils)
3. Alcoholic Cirrhosis (Nodules + bands of fibrosis) |
|
|
What are mallory bodies ? |
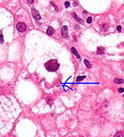
eosinophilic inclusions (Curly rope appearance) |
|
|
What are other causes of hepatic steatosis ? |
NASH
Reye's Syndrome |
|
|
What is Non-alcoholic hepatosteatosis |
Obesity/Metabolic syndrome induced hepatic steatosis |
|
|
What is acute liver failure caused by ? |
V-Budd chiari, HELLP I- HAV, Ascending cholangitis N-Hepatocellular CA Dx- Paracetamol OD , Isoniazid I- C-α-antitrypsin deficiency, Wilson's dx A-Primary biliary cirrhosis , Autoimmune hepatitis T-Alcohol E-
|
|
|
What is fulminant hepatic failure |
Acute liver failure + encephalopathy |
|
|
What do stellate cells do ? |
Secrete collagen -> fibrosis |
|
|
What are causes of cirrhosis ? |
-Alcohol, NAFLD
-HBV/HCV
-Autoimmune hepatitis/primary biliary cirrhosis
-Hemochromatosis
-Wilson's
-Dx |
|
|
What are S/S of cirrhosis |
-Clubbing -Dupuytren's contracture
-Portal HTN -> esophageal varices, caput medusa , Hepatorenal syndrome
-Estrogen -> palmar erythema, spider naevi , gynecomastia
-Vit K deficiency -> Hemorrhage
-Hypoalbuminemia -> Ascites, leuconychia
-↓ detoxification -> Encephalopathy , cerebral oedema, jaundice |
|
|
What is hepatorenal syndrome ? |
Portal HTN --> dilatation of splanchnic vessels + vasoconstriction to renal arteries |
|
|
What are the complications of liver failure ?
Rx |
-Encephalopathy -Rx Lactulose -cerebal oedema - Rx Mannitol
-Ascites - Rx Fluid/salt restriction, diuretics
-Hemorrhage - Rx Vitamin K
-Esophageal varices -Rx- Vasopressin + nitroglycerin, TIPS
-Hypoglycemia - Rx Gluclose 100mL 10%
-Infection |
|
|
For primary biliary cirrhosis , describe
What is it? Antibodies S/S
Complication |
Autoimmune against intrahepatic bile ducts
Anti mitochondrial
S/S: ↑ AST/ALT & ALP , jaundice
Granuloma
Complication: SICCA syndrome , Hepatocellular CA |
|
|
For primary sclerosing cholangitis , describe
What is it ? Antibodies S/S
Associated condition
Complication |
Autoimmune against extra-hepatic bile ducts
P-ANCA
S/S: obstructive jaundice , ↑ALP
Associated w/ UC
Complication : cholangiocarcinoma |
|
|
What antibodies are associated with autoimmune hepatitis ? |
Anti LMK1/ Smooth muscle /ANA |
|
|
What is nutmeg liver ?
Caused by ?
Complication |
Congestion of blood in liver
Caused by: Right CHF
Complication: Cardiac cirrhosis |
|
|
How is Wilson's disease inherited ? |
Autosomal recessive |
|
|
What is the pathophysiology behind Wilsons dx? |
Defect in copper secretion from hepatocytes --> Copper accumulates in liver & not released in circulation |
|
|
For Wilson's, describe the
S/S |
(CNS + eyes + liver)
-Kayser-Fleischer rings -Cirrhosis -Basal ganglia deposition -> dyskinesias
-Fanconi's syndrome |
|
|
What is Fanconi's syndrome ? |
No reabsorption @ proximal tubules of kidneys
-Rickets -Renal tubular acidosis -hypokalemia -polyuria/polydipsia |
|
|
For wilson's how would you
Ix Rx
|
Ix: low Ceruloplasmin, increased 24 hr urinary copper
(low copper in blood!)
Rx: Penicillamine
|
|
|
What is hemachromatosis ? |
Increase Fe uptake by gut --> Iron deposition in tissues |
|
|
Where is iron usually stored ? |
Macrophages |
|
|
Secondary hemachromatosis is caused by what ? |
Multiple blood transfusions |
|
|
What are the S/S of hemachromatosis ? |
(Skin , pancreas, liver, heart, gonads)
Bronze DM ( bronze skin + DM)
Cirrhosis
restrictive heart failure
Impotence |
|
|
For hemachromatosis , how would you
Ix? Rx? Complication |
Ix: Increased Ferritin & decreased TIBC , Increased iron
Rx: Phlebotomy , desferoxamine
Complication: hepatocellular CA |
|
|
What are the risk factors for hepatocellular CA ? |
Cirrhosis - Viral, autoimmune , hemachromatosis/Wilson's
Alfatoxins ( Aspergillus infection) |
|
|
What does hepatocellular CA secrete ? |
EPO -> Polycythemia
AFP (Tumor marker) |
|
|
How does hepatocellular CA metastasize? |
Hematogenous |
|
|
Rank the Hepatitis's according to which is the commonest |
A (commonest) < B < C (rarest) |
|
|
Hepatitis is also caused by what other viruses ? |
EBV
CMV |
|
|
What LFT results indicate a viral hepatitis ? |
ALT >> AST |
|
|
For HAV , describe it's
Transmission Carrier status Incubation period |
Fecal-oral
Asymptomatic Alone ( no carrier) Acute |
|
|
For HBV describe it's
Transmission Carrier status Incubation period |
Transmitted: -Parenteral -Vertical -Sexual
Carrier Chronic |
|
|
For HCV describe it's
Transmission Carrier status Incubation period |
Parenteral transmission
Carrier Chronic |
|
|
Vaccinations are available for which hepatitis viruses ? |
HAV
HBV |
|
|
Which Hepatitis virus causes fulminant hepatitis in pregnant women ? |
HEV |
|
|
Which types of hepatitis viruses carry a risk of cirrhosis/hepatocellular CA ? |
HBV
HCV |
|
|
How do you Rx HBV ? |
IFN-a |
|
|
How do you Rx HCV? |
IFN-a + Ribaviron |
|
|
What are the characteristics of HDV ?
Incubation period |
Requires co-infection w/ HBV
If superinfection --> short incubation period If Co-infection -> Chronic incubation |
|
|
for HEV
transmission Who is it found in ? Characteristics |
Fecal oral
In Expectant mothers Epidemics |
|
|
For an acute HBV infection, describe which viral markers would be present
HbSAg Anti-HBs HBe-Ag Anti-HBe Anti-HBc |
HbSAg
HBe-Ag
Anti-HBc (IgM) |
|
|
For the window period of hepatitis infection, describe which viral markers would be present
HbSAg Anti-HBs HBe-Ag Anti-HBe Anti-HBc |
Anti-HBc |
|
|
For an chronic HBV infection with high infectivity, describe which viral markers would be present
HbSAg Anti-HBs HBe-Ag Anti-HBe Anti-HBc |
HbSAg
HBe-Ag
Anti-HBc (IgG) |
|
|
For an chronic HBV infection with low infectivity , describe which viral markers would be present
HbSAg Anti-HBs HBe-Ag Anti-HBe Anti-HBc |
HbSAg
Anti-HBe
Anti-HBc (IgG) |
|
|
For a person that has recovered from HBV, describe which viral markers would be present
HbSAg Anti-HBs HBe-Ag Anti-HBe Anti-HBc |
Anti-HBs
Anti-HBe
Anti-HBc (IgG) |
|
|
For who has been vaccinated against HBV, describe which viral markers would be present
HbSAg Anti-HBs HBe-Ag Anti-HBe Anti-HBc |
Anti-HBs |
|
|
Describe the spermatic coverings and their origins |
Transversalis fascia --> internal spermatic fascia
Internal oblique muscle -> cremaster muscle
External oblique aponeurosis -> external spermatic fascia |
|
|
Where is the deep inguinal canal located ? |
1/2 b/w ASIS & pubic symphysis |
|
|
What make up the walls of the inguinal canal ? |
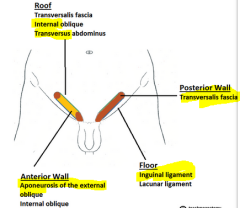
(MALT)
Muscle (sup). Aponeurosis (ant.) Ligament (Inf. ) Transversalis fascia (post.) |
|
|
What is Hesselbach's triangle ?
Describe it's borders |
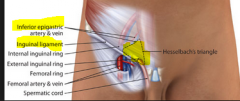
Area of direct hernias
Inferior epigastric vessels Inguinal ligament Lateral rectus abdominus
|
|
|
What are the types of hernias
(Characteristics) |
-Indirect inguinal ( Young men + lateral to inf. epigastric vessels)
-Direct inguinal ( Elderly men + medial to inf. epigastric vessels)
-Femoral hernia (women + inferomedial to pubic tubercle) |
|
|
Which hernia enters through hesselbach's triangle ? |
Direct inguinal hernia |
|
|
which hernia has the highest risk of strangulation ? |
Femoral > Direct inguinal > indirect inguinal |
|
|
Which hernia is common in children ? |
Indirect inguinal hernia |
|
|
If there is a child < 1 yr with an indirect inguinal hernia , how would you manage this ? |
Surgery |
|
|
What are other types of hernias ? |
-True umbilical (congenital - Rx if > 3 yrs)
-Incisional
-Paraumbilical (superior to umbilicus)
-epigastric hernia ( epigastric reigon - through linea alba) |
|
|
What are the normal function of hemorrhoids ? |
Control defecation |
|
|
For hemorrhoids, describe
Risk factors S/S
Rx: |
Risk factors: Constipation, pregnancy , portal HTN
S/S: Itchy lump , tenesmus
Rx: Avoid straining/constipation, Banding, Scleropathy, hemorrhoidectomy |
|
|
How do you grade hemorrhoids? |
1. Above pectinate line 2. Below pectinate line 3. spontaneous external 4. Permanently external |
|
|
What is a piloanal sinus? |
infection of a hair follicle @ anus |
|
|
What is pruritus ani? |
Itch around anus |
|
|
What is perianal hidradenitis suppurativa ? |
clusters of inflamed apocrine sweat glands |
|
|
What are the characteristics of Whipple's disease |
PAS+ve granules
Malabsorption Arthralgia Hyperpigmentation Photosensitivity
Pericarditis |

