![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Organisms that make botulism |
Bacteria Clostridium botulinum and other Clostriums (baratii, butyricum, argentinense) |
|
|
|
Root of word botulism |
Latin: botulism-> sausage |
|
|
|
Pediatric vs adult botulism inoculatilm |
Peds: bacterial growth in gut Adult: ingestion of toxin from food Other: wound botulism and aerosolized terrorism |
|
|
|
Main population that gets wounds botulism |
IV drug users |
|
|
|
Spore factors: temp, ph Toxin stability |
Survive 100c for hours, 120 less than 30 mins. Germinate pH>4.5, NaCl<3.5%, low nitrite Produce toxin >27c (one strain down to 5c (E) Toxin: destroyed 80c for 30 mins, 100c for 10 mins |
|
|
|
Food smell if contaminated |
A and B: putrified smell and appearance due to proteolytic E: normal due to sacchrolytic |
|
|
|
Toxin path in gut |
Bound to hemagglutinin and other proteins to get past stomach. Alkaline intestines favours release and absorption Symptoms usually within 1 day, but up to 7 days |
|
|
|
Bacteria path in gut and risk factors |
Alkaline stomach of infants and people on ppis, hx of bypass doesnt kill it. Immature gut flora allows replication. Symptoms 1-2 months |
|
|
|
Toxin structure |
Single polypeptide 900 dalton's Gets cleaved to 150 dalton active piece that has a heavy 100 dalton chain and 50 dalton light chain |
|
|
|
Mechanism of toxin |
Heavy chain facilitates entry into.presynaptic cholinergic neurons in peripheral system Light chain cleaves SNARE proteins responsible for exocytosis of acetylcholine |
|
|
|
Differences between toxin subtypes |
All cleave different SNARE proteins, likely given variable toxicity |
|
|
|
Other effects of BoNT |
At high [ ] can impair release of norepi and serotonin centrally |
|
|
|
Does botulism affect central acetylcholine neurons? |
No. |
|
|
|
Which proteins does each botulism subtype target? |
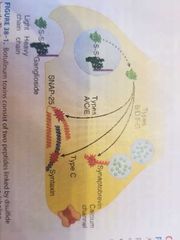
|
All SNARE proteins |
|
|
Botulism s/s |
Early: nausea, vomiting, abdo distension and pain Usually within 24 hours: weakness starting in facial nerves down, blurred vision, horizontal nystagmus, inability to accommodate Constipation from smooth muscle effect Anticholinergic effects EXCEPT the tachycardia and AMS Dysarthria, dysphonia (nasally) Decreased to abscent reflexes Hypotension and brady Normal sensation and MS |
|
|
|
Botulism vs GBS vs Miller Fisher Variant |

|
|
|
|
Presentation of infant botulism |
<1 year Constipation, feeble cry, difficulty feeding, decreased tone (mainly neck and arms, floppy baby). Mydriasis, ophthalmoplegia, diminished gag, poor sphincter tone Usually gradual due to gradual absorption |
|
|
|
Risk factors doe infant botulism |
Breast feeding (formula get colonized by protective organisms). Children of people who work with soil (construction, farming, nurseries, plumbers) Deficiencies in immune systems |
|
|
|
Risks of botulinum antitoxin |
Equine derived: so serum sickness(9-17%), hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis (2%) |
|
|
|
Pre-treatment for botulinum antitoxin |
Histamine blockers Steroids |
|
|
|
How does botulinum antitoxin work? |
Binds to UNBOUND butulism toxin. DOES NOT FIX ALREADY AFFECTED MUSCLES |
|
|
|
Botulism antitoxin for infant botulism? |
Different from the other one BabyBIG, human derived IG. |
|
|
|
Antitoxin definition |
Antibody or antibody fragment against a toxin |
|
|
|
Toxoid definition |
Inactivated form of a bacterial toxin |
|
|
|
Current heptavalent botulism antitoxin is produced how? |
Immunizing horses for months with toxoids. Pooling horses Ig from different stereotypes of antitoxin. Pepsin enzymatic cleavage to despeciate achieving 98% FAB and only 2% intact. |
|
|
|
Differences between FAB and intact Ig? |
FAB is despeciated and so less immunogenic. Less likely to get serum sickness or anaphylactic reactions. FAB has shorter half life due to improved renal clearance and uptake by vascular endothelium and surrounding tissues |
|
|
|
Dose of heptavalent botulism antitoxin? |
1 vial is 10-100x the amount needed for typical food borne illness. A second vial can be needed to due nonlinear interactions and ongoing absorption of toxin, or in cases of colonization. |
|
|
|
Pharmacokinetics and dynamic of babying botulism antitoxin |
Half life of 28 days. Can neutralize 20-500x the normal oral dose of botulism out to 20 days (20x). Thus. One infusion generally enough to treat |
|
|
|
BabyBIG botulism antitoxin efficacy |
Only against A and B now, need heptavalent Ig for others |
|
|
|
Adverse effects of babyBIG botulism antitoxin |
None reported, but lots theoretical Main: loss of live vaccine efficacy within 3 months Main:IgA deficient patient may develop immune response to subsequent IgA containing products. Other: Trali, hemolytic anemia, aseptic meningitis |
|
|
|
Heptavalent BAT botulism antitoxin dosing |
Adult: 1 vial at a very slow rate increased every 30 mins Children: weight based as a calculated percentage of adult dose Infant: 10% of adult dose. |
|
|
|
BabyBIG botulism antitoxin dosing |
1.5ml/kg. 0.5ml/kg/hour x 15 mins then 1 ml/kg/hour until done. |
|

