![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define: Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
|
BENIGN
1) Molar Pregnancies --> complete (classic) and incomplete (partial) moles MALIGNANT 2) Persistent moles 3) choriocarcinoma 4) placental site trophoblastic tumors |
|
|
Which group of people have the highest rate of molar pregnancy?
|
Asian women, especially from Japan
|
|
|
Name some of the risk factors associated with molar pregnany
|
1) extremes of age
2) history of GTD 3) nulliparity |
|
|
Define: complete mole
|
fertilization of an 'enucleate ovum' or *empty egg* by a sperm that then replicates with itself, making it *entirely paternally derived*
|
|
|
Will fetal tissue be present in complete moles or incomplete moles?
|
fetal tissue will be present in *incomplete moles.* Remember that incomplete moles are the ones with an extra paternal set, and so have both maternal and paternal genes.
|
|
|
Trophoblastic proliferatoin is characteristic of a partial or complete mole?
|
Complete! trophoblastic proliferation is characteristic of complete moles and associated w/ diffuse swelling of chorionic villi called "hydropic degeneration."
-Mole appears grape-like -Absence of fetus villi |
|
|
high hCG levels: complete or incomplete?
|
high hCG levels --> complete!
hCG>100,000 mIU/mL |
|
|
Discuss the biochemistry of hCG, and what other central systems it can affect
|
hCG has an alpha subunit that is also found in LH, FSH, and TSH
-FSH/TSH stimulation --> theca lutein cysts -TSH stimulation --> hyperthyroidism |
|
|
Describe what the villi look like in a complete mole vs. normal vs. partial mole
|
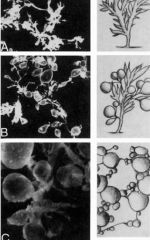
A) normal chorionic villi
B) partial mole w/ normal villi mixed w/ swollen ones C) complete mole, swollen vesicular villi |
|
|
Most common symptom of molar pregnancy?
|
irregular, heavy vaginal bleeding during early pregnancy
|
|
|
Grape-like molar clusters in the vagina or cervical os are most representative of?
|
Complete mole
|
|
|
absence of feta heart sounds and uterine size greater than gestational age with grape like molar clusters and theca lutein cysts is indicative of?
|
complete mole
|
|
|
Tx: complete molar pregnancy
|
Immediately remove the mole w/ a D and C. Give the mom Rhogam if she is Rh negative.
|
|
|
A woman is s/p D and C for a complete mole. How should she be monitored to ensure that she has had a complete resolution of the disease?
|
Serial beta-hCG titers
|
|
|
Pathogenesis: Partial/incomplete mole
|
Fromed when a normal ovum is fertilized by 2 sperm simultaneously, resulting in a *triploid karyotype* w/ 69 chromosomes (69XXY)
|
|
|
Discuss the hCG levels in a partial or incomplete mole
|
They are normal or only mildly elevated because there is more cytotrophoblast
|
|
|
Will there be a fetus with an incomplete mole?
|
Yes! amniotic fluid, fetal heart rate, and fetus can all be present. Often there is an overwhleming number of abnormalities and they spontaneously abort in a few weeks.
|
|
|
Compare the diagnosis times of partial to complete mole
|
Partial: diagnosis comes w/ vaginal bleeding from miscariage/incomplete abortion in late first trimester
Complete: more severe sx, earlier in pregnancy |
|
|
Tx: partial mole
Followup: partial mole |
D and C
serial hCG levels |
|
|
What are the three types of malignant GTD?
-how can we further classify these types? |
-invasive or persistent mole
-choriocarcinoma -PSTT (placental site trophoblastic tumors) 1) metastatic vs. nonmetastatic 2) IF METASTATIC: good prognosis vs. bad prognosis |
|
|
How is malignant GTD treated?
|
chemotherapy -- it is *extremely sensitive to it!*
|
|
|
What is a persistent mole?
-how to identify? |
A mole that occurs after the evacuation of a molar pregnancy.
-identified as a plateau'd hCG after molar tx |
|
|
Define: Choriocarcinoma
-sx |
rare form of GTD, necrotizing tumor that occurs weeks-years after any gestation type
-pts present with mets to lungs, vagina, liver, brain, kidney |
|
|
Define: PSTT
|
extremely rare tumor that arise at placental implantation site characterized by
-absence of villi -proliferation of cytoptrophoblasts -chronic low hCG levels |

