![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
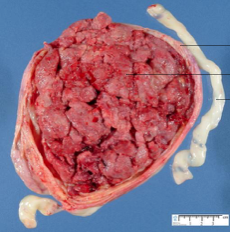
|
normal placenta, maternal side |
|
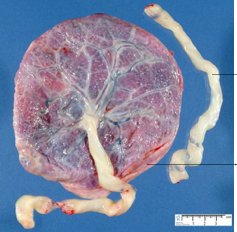
|
normal placenta, fetal side |
|
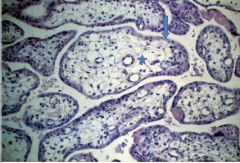
|
2nd trimester placenta - fewer fetal blood vessels |
|
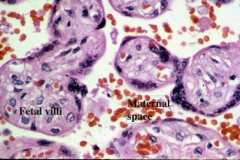
|
mature term placenta - more vascular, smaller villi, syncytial knots |
|
|
most common medical diseases in placenta |
intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), chorioamnionitis |
|
|
gross anomalies of placenta |
accessory lobe, multiple lobes, cysts, vascular lesion |
|
|
gross anomalies of umbilical cord |
marginal or membranous insertion, trauma/hematoma, true & false knots, 2 vessel (single artery) cord |
|
|
gross anomalies of membranes |
circumvallate duplication, web, adhesions, bands, meconium stains |
|
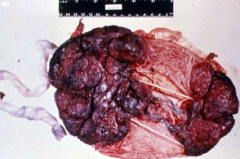
|
accessory lobe (bipartite placenta) - cause = chorion fails to involute |
|
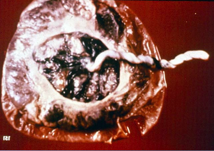
|
circumvallate placenta: membranes too central in disk |
|

|
amniotic band: insert b/t placenta & limbs or face of fetus - can cause craniofacial defects, amputations |
|
|
causes of umbilical cord knots |
multiple gestations, polyhydramnios, extra-long cord |
|
|
disorders of early pregnancy |
spontaneous abortion & ectopic pregnancy |
|
|
disorders of late pregnancy |
twin placentas, abnormalities of placental implantation, placental infections, (pre)eclampsia |
|
|
spontaneous abortion causes |
fetal: chromosomal abnormality
maternal: hematogenous infection, endocrine (DM), structural, vascular (eclampsia) |
|
|
spontaneous abortion presentation & Dx |
sx = abnormal hemorrhage; HCG, U/S, D&C |
|
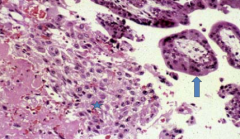
|
spontaneous abortion w/ immature placenta - extravillous trophoblast & chorionic villi |
|
|
ectopic pregnancy |
fallopian tube is MC site; RF = PID, scarring, previous surgery, endometriosis |
|
|
acute chorioamnionitis |
infection spread 2 ways: ascending (most common) or transplacental/hematogenous route suspect group b strep, listeria |
|
|
normal umbilical cord |
inserts in central area of placenta; two arteries + one vein |
|

|
chorioamnionitis - gross |
|

|
acute chorioamnionitis - microscopic |
|
|
grading of acute chorioamnionitis |
1 = below chorion 2= into chorion and subamnion 3 = into amnion &/or funisitis |
|
|
placenta abruptio |
premature separation of placenta; cause = retroplacental clot; sx = painful bleeding a/w DIC RF = smoking, cocaine |
|
|
monoamniotic monochorionic twins |
one large baby + one small baby |
|
|
monochorionic twins |
generally identical - share one placenta |
|
|
dichorionic twin |
fraternal or identical - two separate placentas |
|
|
placenta accreta |
fusion of placenta to the myometrium (no decidual layer) |
|
|
placenta accreta risk factors |
adhesions, scar tissue, infection |
|
|
placenta accreta complications |
hemorrhage, uterine tear, massive post-partum bleeding |
|
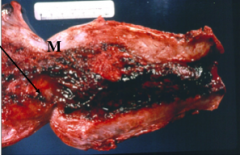
|
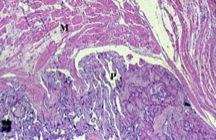
placenta accreta - gross |
|
|
placenta accreta - microscopic |
|
|
(Pre)eclampsia |
systemic syndrome due to abnormal maternal endothelial function sx = HTN, proteinuria, edema (+ seizures) |
|
|
pathophysiology of preeclampsia |
obstruction of spiral arterioles leads to decr. uteroplacental perfusion -> incr. VC and decr. VD -> systemic HTN, DIC -> proteinuria and decr. GFR, seizures & coma, abnormal LFTs, ischemia and fibrin thrombi |
|
|
HELLP |
hemolytic anemia + elevated liver enzymes + Low platelets; variant of pre-eclampsia |
|
|
eclampsia Rx |
terminate pregnancy - delivery or medical abortion |
|
|
microscopic picture of preeclampsia/IUGR |
weigh less, >2cm central infarctions; decidual atherosis, hyaline necrosis, fibrin thrombi, vascular narrowing, occlusion; syncytial knots, thick syncytial BM |
|

|
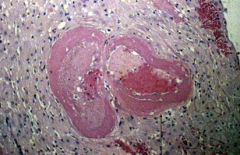
placental infarction |
|
|
decidual vascular atherosis in preeclampsia |
|
|
gestational trophoblastic tumors |
rare neoplasms of trophoblasts; can follow any gestational event; all have increased hCG; risk of choriocarcinoma, responds to chemo |
|
|
complete hydatidiform mole formation |
fertilization of an empty ovum by two sperms or one sperm that undergoes duplication |
|
|
partial hydatidiform mole formation |
two sperm fertilize a single ovum (69 chromosomes) |
|

|
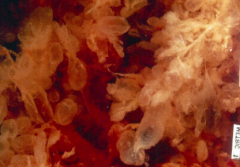
complete hydatidiform mole - gross |
|
|
complete mole - hydropic villi (grape-like) |
|
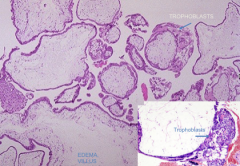
|
complete mole - see huge edematous villi + over-proliferating trophoblasts |
|

|
partial mole - gross - remnants of fetal tissue + slightly hydropic villi |
|
|
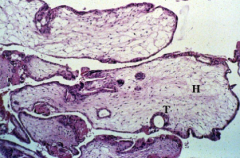
partial mole - microscopic |
|
|
gestational choriocarcinoma |
malignant neoplasia of trophoblasts; incr. hCG; no villi; better prognosis than germ cell tumor (chemosensitive) |
|

|
choriocarcinoma - microscopic |
|
|
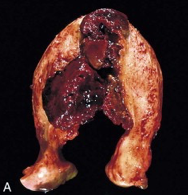
gestational choriocarcinoma - hemorrhagic mass invading uterine wall |
|
|
placental site trophoblastic tumor |
only intermediate trophoblasts (HPL+, CK+, CD10+), vascular invasion, very rare |

