![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Line |
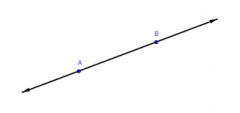
A straight one-dimensional figure that extends infinitely in both directions |
|
|
Plane |
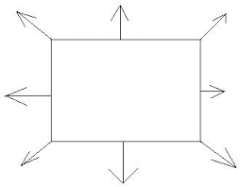
A flat surface that extends infinitely in all directions |
|
|
Collinear |
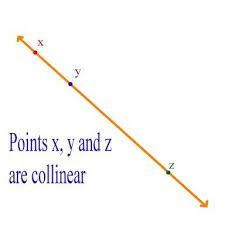
Points that lie in the same plane |
|
|
Coplanar |
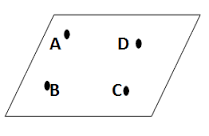
Points that lie in the same plane |
|
|
Line Segment |
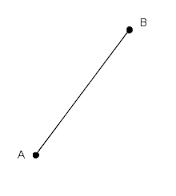
Part of a line that has two points |
|
|
Distance Formula- What it's used for and the formula |
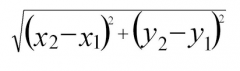
Finding the distance between the endpoints |
|
|
Ray |
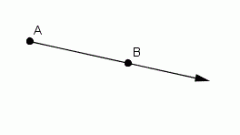
A line with a single endpoint that extends infinitely in one direction |
|
|
Midpoint Formula- what it's used for and the formula |
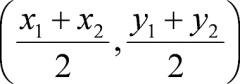
Finding the midpoint of a segment |
|
|
Acute Angle |
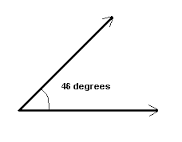
An angle that equals less than 90 degrees |
|
|
Obtuse Angle |
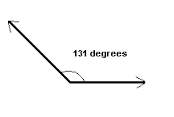
An angle that equals more than 90 degrees |
|
|
Right Angle |
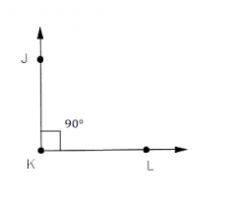
An angle that equals 90 degrees |
|
|
Bisector |
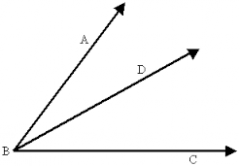
A line that divides something into two equal parts |
|
|
Supplementary angles |
![Two angles with the sum of 180 degrees ([non]adjacent)](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/17/94/87/20179487_m.png)
Two angles with the sum of 180 degrees ([non]adjacent) |
|
|
Complimentary angles |
![Two angles with the sum of 90 degrees ([non]adjacent)](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/23/01/06/20230106_m.png)
Two angles with the sum of 90 degrees ([non]adjacent) |
|
|
Perpendicular angles |
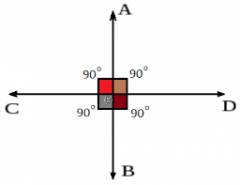
Lines that are at right angles to each other |
|
|
Adjacent angles |
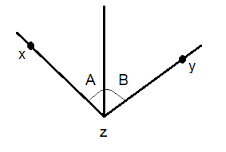
Share a common side, has a common vertex, and no common interior points |
|
|
Linear Pair |
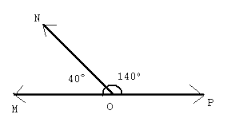
Adjacent angles that form opposite rays |
|
|
Vertical Angles |
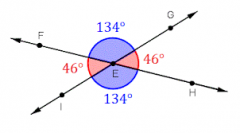
Nonadjacent angles that are formed by two intersecting lines (are congruent) |
|
|
Polygon |
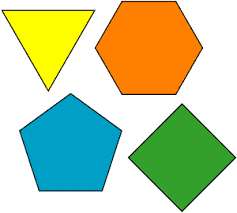
A closed figure that is formed by sides and is named by its vertices (in consecutive order) |
|
|
Equilateral |
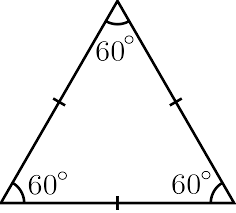
All congruent sides |
|
|
Equiangular |

All angles are congruent |
|
|
Regular Polygon |
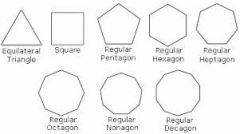
Both equiangular and equilateral |
|
|
Circle |
A 3-dimensional object shaped like a ball |
|
|
Square |
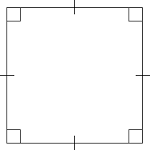
A solid figure with many plane faces |
|
|
Rectangle |
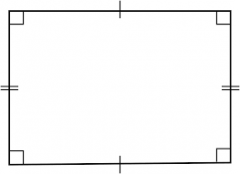
A polyhedron whose faces are identical regular polygons |
|
|
Trapezoid |
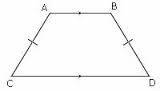
A solid object with two identical ends and flat sides |
|
|
Triangle |
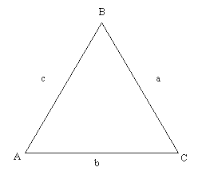
A polyhedron formed by connecting a polygonal base and a point |
|
|
Parallelogram |
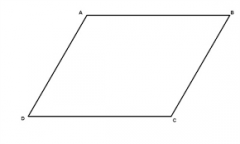
A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides |
|
|
Regular Polygon |
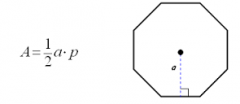
A=1/2aP |
|
|
Pythagorean Theorem |
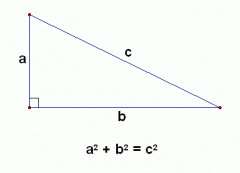
a^2+b^2=c^2 |
|
|
Polyhedron |
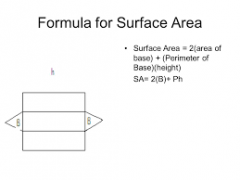
V=Bh T=Ph+2B |
|
|
Regular Polyhedron |
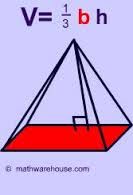
V=1/3Bh T=1/2 P(slanted height)l+B |
|
|
Prism |
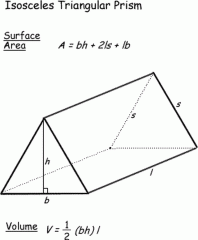
V=(pi)r^2h T=2(pi)rh+2(pi)r^2 |
|
|
Pyramid |
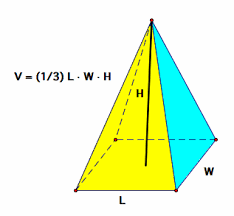
V=1/3(pi)r^2h T=(pi)r(slanted height)l+(pi)r^2 |
|
|
Cylinder |
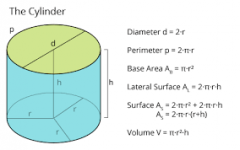
V=4/3(pi)r^3 T=4(pi)r^2 |
|
|
Circle |
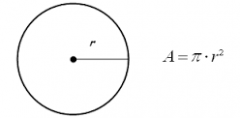
A=(pi)r^2 |
|
|
Square |
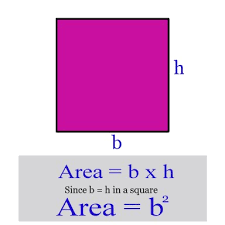
A=s^2 |
|
|
Rectangle |
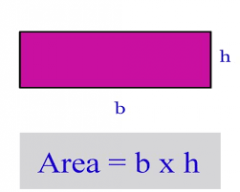
A=bh |
|
|
Trapezoid |
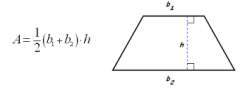
A=1/2(b1+b2)h |
|
|
Parallelogram |
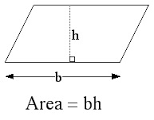
A=bh |
|
|
Regular Polygon |
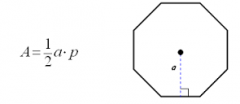
A=1/2aP |
|
|
Triangle |
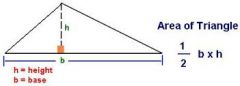
A=bh/2 or A=1/2bh |

