![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
HYPOTHESIS |

A hypothesis is the "if" part (antecedent) of a conditional statement.
|
|
|
CONCLUSION |
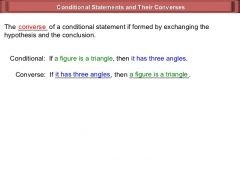
The part of a conditional statement after then.
|
|
|
BI-CONDITIONAL |

A biconditional statement is defined to be true whenever both parts have the same truth value.
|
|
|
LAW OF DETACHMENT |

In mathematical logic, the Law of Detachment says that if the following two statements are true: (1) If p, then q. (2) p. Then we can derive a third true statement: (3) q.
|
|
|
LAW OF SYGOLLISM |

In mathematical logic, the Law of Detachment says that if the following two statements are true: (1) If p, then q. (2) p. Then we can derive a third true statement: (3) q.
|
|
|
RULER POSTULATE |

Ruler Postulate Summary. On a number line, every point can be paired with a number and every number can be paired with a point. The number associated with a point A on a number line is called its coordinate. The distance between two point A and B is denoted by AB.
|
|
|
SEGMENT ADDITION POSTULATE |
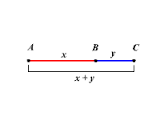
The segment addition postulate is a fairly obvious-seeming postulate which states that: If a point B lies on a line segment , then . That is, the distance from one endpoint to the other is the sum of the distances from the middle point to either endpoint.
|
|
|
PROTRACTOR POSTULATE |
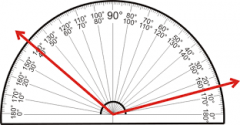
The Protractor Postulate. Printer Friendly. Postulate: The Protractor Postulate. Given line AB and a point O on line AB. Consider rays OA and OB, as well as all the other rays that can be drawn, with O as an endpoint, on one side of line AB.
|
|
|
ANGLE ADDITION POSTULATE |
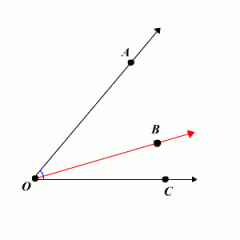
The angle addition postulate states that if B is in the interior of AOC, then. That is, the measure of the larger angle is the sum of the measures of the two smaller ones.
|

