![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lithification |
The process where sediments become rocks
|
|
|
Compaction |
Sediments compressed by weight and overlaying layers |
|
|
Cementation |
Sediments are glued together by national cements, eg silica, calcite, iron oxide |
|
|
Precipitation |
Mineral rich solution precipitates sediemnts that collect at bottom of basin |
|
|
Sediments |
|
|
|
Intrusive Structures |
|
|
|
Batholiths |
|
|
|
Dikes |
|
|
|
Extrusive Structures |
Columnar Jointing |
|
|
Columnar Jointing |
Cooling Lava flow where the exterior cools faster than the interior Exterior in contact with "Cold" air and ground Exterior contracts as cools Exterior will pull away from 5-6 sided colums |
|
|
Magma |
|
|
|
Volatiles |
Dissolved gases in Magma Affects viscoscity and tempurature of magma Most common are H20, CO2, SO2 |
|
|
Partial Melting |
Can make different types of Magma CAused by different melting points causes only some parts to be melted |
|
|
Lava |
Is light a flat coke Molten rock on surface that is losing or lost most of its surface |
|
|
Crystal Form |
External shape taken on whe molecules align in a prefered orienation
Must grow in unrestricted space |
|
|
Mineral System |
Periodic Table is large 4000 identified minerals A handful of well defined mineral familes constitutes over 90% of earth's crust Oxygen makes up 92% of crust, and only abudent element that can be a negatively charged ion |
|
|
Conchoidal Fracture |
|
|
|
Silicate Minerals |
|
|
|
Cleavage |
Tendency for a mineral to break along a preferred plane of weakness in the crystalline structure
Tends to produce smooth surfaces |
|
|
Ion |
Too Few or Many electons |
|
|
Island Silicates/ independent Sillicates |
No Oxygen shared by other tetrahera
Connect with positively charged ions |
|
|
Chain Silicates |
Share two of a tetrahedron's oxygen atoms with adjacent |
|
|
Igneous rocks |
Rocks formed from cooling and cystalations of molten rock
|
|
|
Extrusive cooling |
Fast cooling No visible crystals Like lava from Volcano |
|
|
Intrusive cooling |
Slow Rock is poor conductor of heat |
|
|
Rocks |
Solid Naturally occuring Cohesive aggregate of 2 or more minerals, mineraloids, glass, organic particals or fragments of preexisting rocks |
|
|
Rock Cycle |
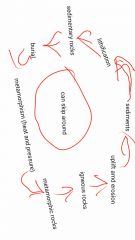
|
|
|
Enviroments of deposition |
The place & manners that sediments are being deposited Each Environment has some control over the creation & deposition of sediments
|
|
|
Fluvial systems |
Sediement size & load determined by water velocity
as water slows, water drops larger sediments |
|
|
Mineral Families |
Sulfides Oxides Carbonates Sulfate Halides Phosphates |
|
|
Sulfides |
Combinations of metals & sulfideiod (S2-) Not abudant, but many valuable for being meatalic ores Decomposses easily incontact with water Pryite, Sphalerite, Galena |
|
|
Oxides |
O2 ions and metal ions Major source for metallic hores Hematite Magnetite |
|
|
Carbonates |
Based on CO3
Calcite Dolomite |
|
|
Sulfate |
Based on (S04) Gypsum Anhydrite |
|
|
Halides |
BAsed on F, Cl, Br, I Soluble in water Tend to be rare Halite=Salt Flurite |
|
|
Phosphates |
Phosphorous Needed for all living things Animals eat plants, Plants get Phosphorous from soil |
|
|
Network Silicates |
Tetrahedra share oxygen atoms in all directions |
|
|
Sheet silicates |
Chains of tetrahedra joined together by covalent bonds
Bonds-> stronger within sheet, weak between sheets |
|
|
Mineral ID Technique |
Luster Hardness Streak color Cleavage Fracture |
|
|
Luster |
Can be Metal or Non MEtalic Metalic luster is always solid, can't have light go though, and has a dark streak, Is heavy
No Metallic lust doesn't look like metal |
|
|
Hardness |
Resistance to being scratched Measured on Mohs scale Finger nails= 2.5 Pennies=3 Glass plates=5.5 |
|
|
Streak |
THe color of the minteral when it is grounded up |
|
|
Color |
Some materials are 1 color Some materals are many Exposure to elements can change the color |
|
|
Intermediate |
Mixture of Mafic and Felsic Minerals Medium colors |
|
|
Igneous composition |
Mafic Felsic Intermediate |
|
|
Pegmatitic |
Crystals caused by intrusive cooling that are 1CM or greater |
|
|
Glassy |
Caused by extrsuing cooling looks like glass |
|
|
Phaneritic |
Crystals caused by intrusive cooling Small 1-2mm |
|
|
Igneous Texture |
Intrusive cooling
Extrusive Cooling
|
|
|
Prophytrite texture |
Caused by 2 stages of cooling. Looks like a chocolate chip cookie THe chips are Phenocrysts THe matrix is the dough |
|
|
Felsic |
Has Silica and potassium fieldspar Light colored-> what, light, gray, pastels |
|
|
Mafic |
Iron & Magnesium
Dark Colored -> Black Brown, blood red |
|
|
Fracture |
Breaking randomly Different from Cleavage |
|
|
Smoking gun Mineral ID |
Acid tests Magnetism Smell Taste |
|
|
Acid Test |
HCL disolves Calcite |
|
|
burial |
Rock layers are forced deeper into the crust.
Altered by lith |
|
|
Saltation |
Paricle bouncing on a windward force Move the dunes Causes windward side light and compact |
|
|
Dunes |
Created when Material is transported by wind
|
|
|
Cross beds |
How to tell the wind directions of a dune Downward direction indicates direction of wind travel |
|
|
Glaciers |
Move Sediments by pushing carring on top or within Ice or freezing to bottom
Can move sediments of all sizes
No layering of sediemnts, but dumps them all in unsorted pile |
|
|
Lacustrine |
Little to no current
|
|
|
Continental shelf |
Shallow ledge jutting out of sea from edge of contient
Deposition from fluvial systms over land
Corals produce calcium carbonate reefs |
|
|
Deep Marine |
Off shelf in deep ocean Some clay settles out, but not much Siliaic ooze-> organisms bearing silica rich shells deposits shells on bottom, building up over time |
|
|
Pressure |
From Techtonic forces & weight & surronding rocks
|
|
|
Parent rock |
Preexisting rock of any type that went though metamorphism to create a new rock |
|
|
Contact metamorphism |
Preexisting rock is touched by magma and associated hydrothermal fluids
Pressure not a factor
Is narrow and local in effect |
|
|
Agents of Metamorphism |
|
|
|
Pyrometamorphism |
Super high temps in a low pressure environments, E.G. lightning strikes |
|
|
Hydrothermal metamorphism |
Chemical Alterations caused by hot fluids can lead to valuable concentration E.G. Cu, Fe, Ni, and Pb |
|
|
Shock Metamorphism |
METEOR SHOCK
High pressure and tempertures in a short amound of time |
|
|
Regional Metamorphism |
Thousands of square miles Burial Dynamothermal |
|
|
Dynamothermal |
Colliding crustal plates will squeeze any rock that happens to get caught between them |
|
|
Tempurature |
Lower limits=400F Upper limit depends on rock, but ends when rock melts
Most take place between 1300-2200 F depending on compositon of rock |
|
|
Metamorphic Rocks |
Rocks that change form in response to a change in envirmontal conditions |
|
|
Metamorphism |
Change in mineral content and/or structure due to directed pressure, heat or contact with hydrothermal fluid |
|
|
Envirornments of depositions |
|
|
|
Swamps |
Stagnant, No Current with little O2 in Water
Little "rocky" sediments Main Sediments are plant debris No current= No decay= Plant materials collects |
|
|
Types of Mineral deposits |
Igneous Rocks
|
|
|
Plate Techtonics |
The theory
|
|
|
Lithosphere |
Made up of upper mantle and crust |
|
|
Continent Drift |
|
|
|
Concentration factor |
The amount of valuable deposits in an area vs the amount of that ore in general |
|
|
Ore deposits |
|
|
|
Cost Factor |
|
|
|
Distribution |
Globally very uneven distribution
|
|
|
Convection cells |
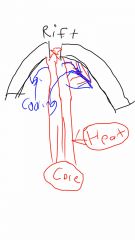
|
|
|
The Driving force |
|
|
|
Seafloor spreading |
|
|
|
wegener motion |
Thought continents moved through the ocean.
Problem is ocean is thicker than continent and the continents would end up at the poles |

