![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is metamorphism? |
Change in mineralogy, possibly in composition or texture, without the rock melting |
|
|
What is metamorphism a result of? |
Increased pressure (depth & stress) Temperature Water (fluids) |
|
|
Metamorphism happens under ____ conditions (non-melting) |
subsolidus |
|
|
The composition of the protoliths help determine: |
the final composition limestone ----> marble mudstone ----> slate |
|
|
Of the things that make metamorphism happen, which is the most important?
|
Temperature |
|
|
Weathered rock sequences Clay (7 diff. rocks) Quartz sand (3 rocks) Limey ooze (3 rocks) |
Clay -- (lithification)-> shale --(metamorphism)--> slate --> phyllite --> schist --> gneiss --> magma Quartz sand --> sandstone --> quartzite limey ooze --> limestone --> marble |
|
|
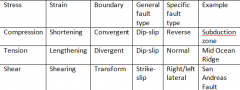
Stress: Strain: ____ causes ____ |
Stress: pressure Strain: the change that is made Pressure caused deformation |
|
|
What can deformed rocks tell us? (6) |
What stresses caused it Direction of stress due to orientation Magnitudes of stress Plate tectonic motions and direction of continents Buried structures can hold petroleum Can predict future movement (earthquake predictions) |
|
|
|
|
|
3 types of deformation 1. 2. (bonds are what?) 3. (bonds are what?) |
Elastic: reversible, non-permanent, returns to original shape when stress is removed Plastic: ductile, bonds are breaking but rock is still cohesive, permanent Brittle: nonconhesive, bonds are breaking all at once and release energy, permanent |
|
|
5 conditions for brittle vs ductile behavior |
Temperature (higher=ductile) Water (more=ductile) Confining pressure (more depth=ductile) Strain (slow=ductile) Mineralogy (weak minerals like micas versus hard ones like quartz) |
|
|
Anticlines versus synclines Where is petroleum usually found? |
Anticlines /\
Synclines \/ Petroleum found in anticlines |
|
|
Way to find absolute age of rock
|
Radioactivity |
|
|
Radioactivity definition |
The nuclei of certain unstable atoms spontaneously break apart (decay) at a constant rate and new atoms are created (daughters) along with radiation and heat |
|
|
Half-life |
the time it takes for half of the parent atoms to decay into stable daughter atoms |
|
|
What are earthquakes a result of? When are there no earthquakes? |
Periodic (sudden) releases of strain energy that accumulated in elastic rocks When rocks form plastically (no strain buildup) |
|
|
Where are the dangerous locations for earthquakes? Not dangerous? |
Convergent and transform Divergent is not so dangerous, because rock is weak under tension so there's no buildup |
|
|
Frequency and strength of earthquakes in: Divergent zones Convergent/Transform |
Frequent and small, no time to buildup energy Infrequent and large, because energy builds up |
|
|
Types of Seismic waves 1. 2. |
Body and surface |
|
|
2 types of body waves |
Compression: fastest, primary P-waves, travel through solid, land and air Shear waves: slower, secondary S-waves, travels only through solids |
|
|
Measuring earthquakes: Richter scale: more important than richter scale: |
magnitude is related to amplitude of pen squiggle But more important is the amount of energy released, 30X from M1 to M2 |
|
|
Tsunami: It is not: At ___ and ___ boundaries, but not ____ |
"harbor wave" is NOT a tidal wave At convergent and divergent, but not transform (because there is no water displacement at the transform boundaries) |
|
|
Rock density ____ as depth increases ---> seismic velocity _____ |
increases increases (waves are faster deeper underground) |
|
|
Velocity ____ in ductile mantle Why? |
Slows The magma allows for plate movements, making mantle ductile and less dense |
|
|
Waves and Core S waves ____ at core because P waves ____ at core because |
stop (can't travel through liquid) slow, then speed up because the core is solid (more dense) |
|
|
How do we know how big the core is? |
Use s-waves Some parts of the earth don't get the s-waves, so you know there's something blocking them |
|
|
Shadowzone |
area where are no seismic waves |
|
|
How do we know the inner core is solid? |
P-waves were coming out of the other side of earth faster than they should have been (there's a dense solid making the velocity faster in the middle of the earth) |
|
|
What kind of magnet is the earth's inner core? |
Dipole |
|
|
What is true north? |
The North Star (polaris) which is the earth's axis Diff. than magnetic earth, which is a little lower |
|
|
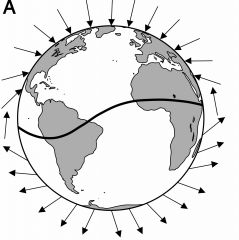
Magnetic field lines - what do they look like surrounding the earth? |
|
|
|
Evidence of plate tectonic theory (6) |
Fit of continents Rock layers (records) similar Correlation of rock types (surface and deep) Continuation of mountains across oceans Glacial direction flow Fossil records |
|
|
A Wegener
|
Continental drift hypothesis: continents are not together now, therefore they must have drifted People rejected his idea because there was no viable mechanism on how it could work |

