![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
EX1 Category that describes each of the following sedimentary rocks: CONGLOMERATE
a) Clastic b) Chemical c) Bioclastic |
a) Clastic
|
|
|
EX1 Category that describes each of the following sedimentary rocks: SANDSTONE
a) Clastic b) Chemical c) Bioclastic |
a) Clastic
|
|
|
EX1 Category that describes each of the following sedimentary rocks: FLINT/JASPER
a) Clastic b) Chemical c) Bioclastic |
b) Chemical
|
|
|
EX1 Category that describes each of the following sedimentary rocks: SHALE
a) Clastic b) Chemical c) Bioclastic |
d) Clastic
|
|
|
EX1 Metamorphosed limestone is called a(n):
a) Chert b) Dolomite c) Marble |
c) Marble
|
|
|
EX1 Which of the following are minerals:
•animal bone •gold •granite •ice •petroleum •quartz •steel •synthetic diamonds |
gold, ice, quartz
|
|
|
EX1 Which of the following metamorphic rocks are foliated:
•gneiss •marble •quartzite •schist |
gneiss, schist
|
|
|
EX1 What mineral is used in McDonalds 'clay shakes'?
|
Kaolinite
|
|
|
EX1 What is the chemical formula for Tums antacid (calcite):
|
CaCo3
|
|
|
EX1 What mineral is also known as fools gold?
|
Pyrite
|
|
|
EX1 ______ is an example of an oxide mineral.
|
Hematite
|
|
|
EX1 A(n) _______ is an extrusive igneous rock of felsic composition.
|
Rhyolite
|
|
|
EX1 A(n) ________ is an intrusive igneous rock of mafic composition.
|
Gabbro
|
|
|
EX1 How can you identify a nice gneiss?
|
Layering of distinct, minerals including crystals or lathes forced into flat orientations.
|
|
|
EX1 Draw a silica tetrahedra, labeling the atoms appropriately.
|
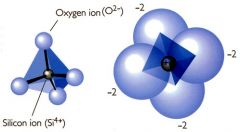
|
|
|
EX1 What does the sequence tell you about ancient sea levels in this area?
sandstone (top) mudstone limestone sandstone coal (bottom) |
Regression and transgression
|
|
|
EX1 Explain what is meant by the 'Method of Multiple Working Hypothesis' and why it is used in geology.
|
To create a variety of hypotheses which can provide information through research instead of focusing on e one idea that can be false.
Used for geology due to constraints of time, cost, and experimentation involving large or deep areas of study of the surface of the earth. |
|

EX1 Your cousin says that it is impossible for this to be granite because it is phanertic which means it was formed underground, how would you respond?
|
Weathering, erosion, and tectonic upheaval has made the pluton surface.
|

