![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Principle of uniformitarianism |
Principles of geology have not changed over time, laws we see today have been applied throughout history "The present is the key to the past" |
|
|
|
Are Earths processes fast of slow? |
Slow |
|
|
|
What part of Earths surface makes up the crust/tectonic plats? |
Lithosphere "Lithospheric plates" |
|
|
|
Are continents stable? |
No, they move |
|
|
|
Explain tectonic plate recycling |
Material can be recycles into Earths interior and new material comes up around plate edges |
|
|
|
What causes natural disasters? |
The movement of the tectonic plates |
|
|
|
How are bonds formed? |
Using electrical charges |
|
|
|
What makes up an atom |

Protons, neutrons, and electrons |
|
|
|
What is an ion? |
An element missing an electron |
|
|
|
Sizes of molecules |

|
|
|
|
Who was the first geologist? |
William smith |
|
|
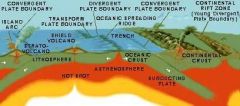
|
Read the map |
|
|
|
Name the types of bonds from strong to weak |
Covalent (electron shared by ions) Ionic (electrostatic attraction) Metallic (electron not bound to individual nucleus) |
|
|
|
What is the problem with elements subbing for one another? |
They won't have balanced charges |
|
|
|
Ionic bond |
Electrostatic attraction Example: graphite breaks up onto paper |
|
|
|
Metallic bond |
Electron not bound to individual nucleus Example: conductors like aluminum and copper |
|
|
|
What are the 6 defining characteristics of a mineral? |
1 solid 2 definite chemical composition 3 occurs naturally 4 inorganic 5 highly ordered arrangement of atoms=crystal structure 6 electrical charges must be balanced in the mineral |
|
|
|
How are crystals formed? |
They are formed in the arrangement that atoms attach to the nucleus Ions get through by diffusion |
|
|
|
In order to identify a mineral what two things are needed? |
Chemical composition Specific crystal structure |
|
|
|
Poly morph |
Minerals that have the same chemical composition but different chemical structures Example: diamond and graphite are both made of carbon but have different chemical structures |
|
|
|
Name three rocks that are not true minerals and why |
Glass, obsidian, coal They lack a crystal structure |
|
|
|
What is Earths crust made of? |
#1 oxygen #2 silicone #3 aluminum #4 iron #5 calcium |
|
|
|
Silicate mineral |
Most abundant group of rock-forming minerals Made of carbon so they can bond in many different ways |
|
|
|
What is a silicated mineral's typical components? |
Magma Sediments Granites |
|
|
|
Single-chain silicates |
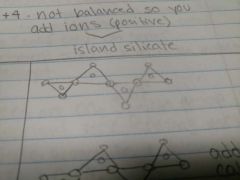
Add different elements to balance out the mineral |
|
|
|
Double-chain silicates |
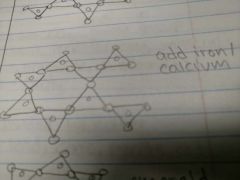
Typically add iron and calcium |
|
|
|
Ring silicates |
The silicates that make gemstones such as emeralds, ring have lots of space to tuck weird things in |
|
|
|
Silicate sheets |
A bunch of double chain silicates bonded together Example: muscovite and biotite sheets are one molecule thick |
|
|
|
Tetrahedra-framework silicates |
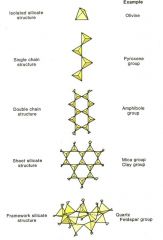
Quartz and feldspar |
|
|
|
Plagioclase feldspar |
Undergoes chemical substitution that is temperature dependent NaAlSi3O8>CaAl2Si2O8 |
|
|
|
Carbonates |
Need a CO3 or CO-2 anion group |
|
|
|
Name three major carbonates |
Calcite Aragonite Dolomite |
|
|
|
Sulfides |
Metals bonded with sulfer |
|
|
|
Name three sulfides |
Lead, zinc, pyrite |
|
|
|
Environmental interlude |
Consequences for mining in the environment Example: mining nickel-copper sulfides may lead to acid mine drainage in rainy River and BWCAW |
|
|
|
Halides |
Metal element bonded with Chlorine, Flourine, or bromine |
|
|
|
Silicone has a charge of what? |
+4 |
|
|
|
What electrical charge does oxygen carry? |
-2 |
|
|
|
Solid solution series |
Change in chemical composition (elements subbing for one another) |
|
|
|
Stability depends on |
Temperature Pressure |
|
|
|
Recrystallization happens when |
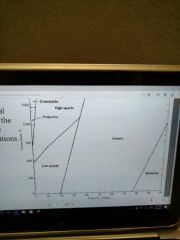
The temperature and pressure change causing the mineral to recrystallize into a form that is stable under those conditions |

|
|
|
Silicate minerals form in what arrangement |

Tetrahedral |
|
|
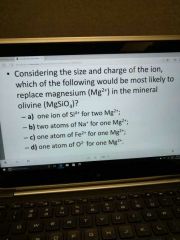
|
C |
|

