![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Latitude |
Horizontal lines on map/globe. Must have N or S following number |
|
|
Longitude |
Vertical lines on the map/globe. Must have E or W following number |
|
|
How to take a half life |
Divide both sides by initial amount
|
|
|
Valley |
Low lying land bordered by higher ground |
|
|
Hill |
Round elevation of land |
|
|
Ridge |
Linear elevation of land |
|
|
Saddle |
Low point in a ridge line of hills |
|
|
Contour line |
Line on a map that connects points of equal elevation above sea level |
|
|
Close spaced contour lines |
Indicate steep slopes |
|
|
Widely spaced contour lines |
Indicate more gently slopes |
|
|
Tick marks (hashes) on contour lines |
distinguish depressions from hills |
|
|
Contour interval |
The amount elevation that exists between each contour line |
|
|
Relief |
The difference in elevation between two or more points using contour lines |
|
|
How to find relief? |
Total relief = highest elevation - lowest elevation |
|
|
Gradient |
Measure of the steepness of a slope between two points |
|
|
How to find gradient |
Vertical elevation from A to B / Horizontal distance from A to B |
|
|
Stress |
Deformation. Leads to strain |
|
|
Compression: Push together |
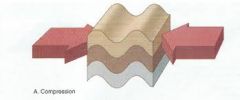
Shortening |
|
|
Tension: Pull apart |
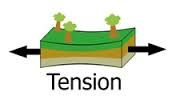
Stretching |
|
|
Shear: Sliding past each other |
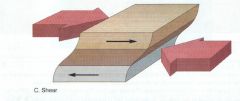
Shearing |
|
|
Strike |
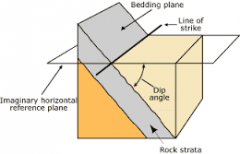
Compass direction of a rock unit measured parallel to the intersection of that unit with a horizontal plane |
|
|
Dip |
The angle between the horizontal plane and the planar surface being measured Dip is always perpendicular to strike |
|
|
Plunge |
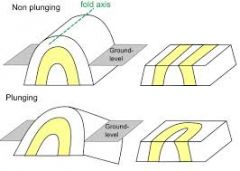
The angle between the fold axis and the horizontal |
|
|
Trend |
The direction that the axis is inclined downward |
|
|
Dome |
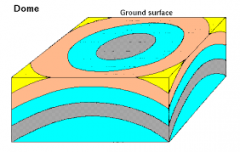
Oldest rocks are in the center |
|
|
Basin |
Youngest rocks are in the center |
|
|
Arc upward |
Oldest rocks in center |
|
|
Arc downward |
Youngest rocks in center |
|
|
Geologic cross section |
Representations of vertical slices through the earth used to clarify or interpret geologic relationships with or without accompanying maps |
|
|
Focus/hypocenter |
Underground origin of the earthquake, point of initial breakage and movement along a fault |
|
|
Epicenter |
The location on the surface of the earth directly above the focus/hypocenter |
|
|
Divergent boundaries |
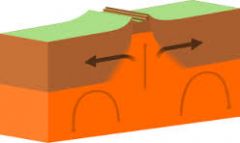
Tensional forces |
|
|
Transform boundaries |
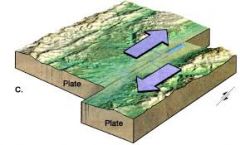
Shear forces |
|
|
Convergent boundaries |
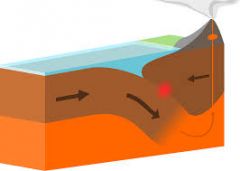
Compressional |
|
|
Body waves |
Travel outward from the focus in all directions through Earth's interior (P and S waves) |
|
|
Surface waves |
Travel along Earth's surface away from the epicenter |
|
|
P-waves |
Compressional (push-pull) body waves in which rock vibrates back and forth parallel to the direction of wave propagation Tavel through solid and fluids |
|
|
S-waves |
Shearing (transverse) body wave in which rock vibrates "up & down" perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. NOT transmitted through liquids |
|
|
Lag time |
Peak discharge (the time when the river reaches its highest flow) because it takes time to reach the river |
|
|
Triangulation |
Need three points |
|
|
Perennial stream |
Flow throughout the year |
|
|
Braided channels |
Created when the discharge of water cannot transport its load decrease in stream velocity leads to sediment being deposited on the bottom of the channel The bars separated the channel into several smaller channels creating a braided appearance. |
|
|
Meandering channel |
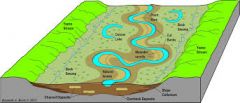
Erosion occurs on the outer edge of a meander (cutbank) Deposition occurs along the inner edge of the meander (point bar) Meandering causes the stream to migrate over time. |
|
|
Stream terrace |
Horizontal surface on either side of a stream channel above the stream level and modern floodplain |
|
|
Stream gradient |
The steepness of slope of a stream along a selected length. (influences velocity distribution) |
|
|
Gradient |
Change in elevation / distance |
|
|
base level |
The lowest level that a stream can erode |
|
|
Absolute base level |
Ocean |
|
|
Local base level |
Lake |
|
|
Porosity |
Rocks contain pore spaces that fill with water |
|
|
Permeability |
Permeable bedrock makes the best aquifer |
|
|
Aquifer |
Subsurface rock strata that can store and transport water |
|
|
Water table |
Top of the saturated zone |
|
|
Karst Topography |
Distinctive topography that indicated dissolution of underlying soluble rock, generally limestone |
|
|
Lithology of Karst |
Limestone dissolves because rainwater is slightly acidic (HCL) reacts with calcite (which makes up limestone) |
|
|
Springs |
Places where water flows naturally from the ground from spaces in bedrock |
|
|
Perched water table |
Above and separated from main water table by an unsaturated zone |
|
|
Confining bed |
Impermeable bedrock preventing the flow of water |
|
|
Oxford lake system |
|
|
|
Tributary |
A stream that flows into a larger stream or other body of water |
|
|
Flood plane |
The land area bordering a river that is subject to flooding |
|
|
Drainage basin |
The entire area of land that is drained by one stream or an entire stream sytem |
|
|
Drainage divides |
linear boundaries that separate one drainage basin from another |
|
|
Free atic zone |
|
|
|
Confined aquifer |
an aquifer that is sandwiched between confined beds |
|
|
Unconfined aquifers |
An aquifer that does not have a confining bed above it - often exposed at the surface of the Earth |
|
|
Moroane of a mountain |
|
|
|
Superposition |
Within a sequence of undisturbed sedimentary orvolcanic rocks, oldest rocks are at the bottom and youngest at the top |
|
|
Continuity |
layers of sediment initially extend laterally inall directions |
|
|
Horizontally |
layers of sediment are originally depositedhorizontally |

