![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
168 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The Earth is a |
unique, evolving system. |
|
|
Geology helps you understand |
physical science |
|
|
____ _____ explains many Earth processes |
Plate tectonics |
|
|
The Earth is a |
very old planet |
|
|
_________ and _________ processes drive geologic phenomena |
Internal; external |
|
|
__________ _________ affect our environment. |
Geologic phenomena |
|
|
Physical aspects of the Earth system are linked to |
life processes |
|
|
Science comes from ______________ and people make ________ _____________ |
observation; scientific discoveries. |
|
|
The earth is one of _____ planets (____ ____________ and ____ ____ or ___ ______) orbiting our sun, which is one of _____ ________ ________ stars of the revolving, spiral shaped ______ ____ galaxy. Hundreds of billions of _______ speckle the visible universe. |
eight; four terrestrial, four gas, ice giants, three hundred billion, Milky Way, galaxies |
|
|
According to the ___ ____ ______, a cataclysmic explosion at _____ ___ formed the universe, which has been _________ ever since. _____ formed during the Big Bang collected into nebulae, which due to _________, collapsed into ______ _____, the first stars. |
Big Bang Theory; 13.7 GA; expanding; Atoms; gravity; dense balls. |
|
|
___________ ____________ formed in stars and supernovas added to gases in ___________ from which new generations of stars formed. Planets formed from ______ of ____ and ___ ________ the stars. As they formed, planets differentiated, with ______ _________ sinking to the center. |
Heavier elements; nebulae; rings; dust; ice orbiting; denser materials |
|
|
The Earth produces a ________ _____ that deflects solar wind. An atmosphere of __ and __ gas surrounds the planet. Oceans cover __% of the surface, and the land the remainder. The difference between the highest and lowest points is only about ___% of the radius. |
magnetic field; N2; O2; 70; 0.3 |
|
|
The Earth consists of many materials, the most common of which is ________ rock. Studies, including analysis of earthquake waves show that the Earth can be divided into three layers---the _____, the ______, and the ____. Temperature and pressure increase with _____. |
silicate; crust; mantle; core; depth |
|
|
Earth's outermost layer, the _____, is very ____. Oceanic and continental crust differ in ___________. Most of Earth's mass lies in the ______. A ________ core lies at this planet's center. The crust and outermost mantle together comprise the _____ ___________. |
crust; thin; composition; mantle; metallic; rigid lithosphere |
|
|
_______ argued that the continents were once merged into a supercontinent called Pangaea that later broke up to produce smaller continents that _______ apart. The ________ ______ of __________, as well as the ____________ of _______ _______ _____, _______, and ____ _____ all make better sense if Pangaea existed. |
Wegener; drifted; matching shapes; coastlines; distribution; ancient climate belts; fossils; rock units |
|
|
Study of ______________ indicates that the continents have moved relative to the Earth's ________ _____. Each continent has a different apparent _____ ______ ____, which is only possible if the continents move ("drift") relative to each other. |
paleomagnetism; magnetic poles; polar wander path |
|
|
New studies of the seafloor led to the proposal of ________ _________. New seafloor forms at ___-_____ ______ and then moves away from the axis, so ocean basins can get wider with time. Old ocean floor _____ back into the mantle by __________. As ocean basins grow or shrink, __________ _____. |
seafloor spreading; mid-ocean ridges; sinks; subduction; continents drift |
|
|
______ ________ _________ form because reversals of the Earth's magnetic polarity take place while ________ _________ occurs. The discovery of these _________, as well as documentation that the seafloor gets _____ away from the ridge axis, proved that the seafloor spreading hypothesis is _______. |
Marine magnetic anomalies; seafloor spreading; anomalies; older; correct |
|
|
Earth's lithosphere is divided into about ______ places that move relative to each other. Geologists recognize three different types of plate boundaries (_________, __________, and _________) based on relative motion across the boundary. Plate boundaries are determined by _______ _____. |
twenty; divergent; convergent; transform |
|
|
Seafloor spreading occurs at _________ _____ boundaries, defined by mid-ocean ridges. New oceanic crust solidifies from ________ _____ along the ridge axis. As plates move away from the axis, they ____, and the ____________ mantle forms and thickens. |
divergent plate; basaltic magma; cool; lithospheric |
|
|
At a __________ _____ boundary, an oceanic plate _____ into the mantle beneath the edge of another plate. A ________ ___ and a ______ delineate such plate boundaries, and ___________ happen along the contract between the ___ places as well as in the downgoing slab. |
convergent plate; sinks; volcanic arc; trench; two |
|
|
At _________ _____ boundaries, one plate slips ________ past another. Most transform boundaries link of segments of ___-_____ ______, but some, such as the ___ _______ _____, cut across continental crust. |
transform plate; sideways; mid-ocean ridges; San Andreas Fault |
|
|
A ______ _________ marks the point where three plate boundaries join. A hot spot is a place where _________ may be due to _______ at the top of a mantle plume. As a plate moves over a plume, a ___-____ _____ develops. |
triple junction; volcanism; melting; hot-spot track |
|
|
Rifting can split a continent __ ____ and can lead to the formation of a new _________ _____ boundary. When two buoyant _______ ______, such as continents and island arcs, collide, a ________ ____ forms and __________ eventually ceases. |
in two; divergent plate; crustal blocks; mountain belt; subduction |
|
|
Plates move at _ to __ cm/yr. Relative motion specifies the rate that a plate moves ________ to its ________, whereas absolute motion specifies the rate that a plate moves ________ to a _____ _____ beneath the plate. ___ ____________ can detect relative plate motions directly. |
1; 15; relative; neighbor; relative; fixed point; GPS measurement |
|
|
Minerals are ______ with a ___________ structure (an _______ ___________ of _____ inside) and a _________ ________ _______. They form by _______ _________ in the Earth system. |
solids; crystalline; orderly arrangement; atoms; definable chemical formula; natural processes |
|
|
The crystal structure of minerals is defined by a _______ _________ ___________ of _____ that has ________. Minerals can form by ______________ of a ____, by _____________ from a _____ ________ or a ___, or by _____________ of _____ in a _____. |
regular geometric arrangement; atoms; symmetry; solidification; melt; precipitation; water solution; gas; rearrangement; atoms; solid |
|
|
The characteristics of minerals (such as _____, ______, ______, _______ ______, ________, ________ _______, ________, _________, and ________ with ____) are a manifestation of the _______ _________ and ________ ___________ of minerals. |
color; streak; luster; crystal shapes; hardness; specific gravity; cleavage; magnetism; reaction; acid; crystal structure; chemical composition |
|
|
The _____ known minerals can be organized into a relatively small number of classes based on ________ ______. Most minerals are _________, which contain _______-______ __________ arranged in various ways. |
4000; chemical makeup; silicates; silicon-oxygen tetrahedra. |
|
|
Gemstones are particularly ____ and ________ minerals. The gems or jewels found in jewelry have been _______ using a lap-- the _____ are not _______ _______ _____ or ________ ________. The fire of a jewel comes from the way it ________ _____ internally. |
rare; beautiful; faceted; facets; natural crystal facets; cleavage surfaces; reflects light |
|
|
Molten rock underground is called _____, whereas molten rock that has come out of a vent at the Earth's surface is ____. Solidification of magma produces _________ rocks. Solidification of lava, either __ _____ or on the _______, or as _________ ______ __ ___ ___, produces _________ _______ rocks. |
magma; lava; intrusive; in flows; surface; fragments cooled in the air; extrusive igneous |
|
|
The Earth is ___ inside. Even so, the crust and mantle are _____, except in special places where pre-existing solid rock undergoes _______. _______ can be triggered by a ________ in ________, ________ of _________ and/or _________ of ___ _____ from ______ _____. Geologists classify magma based on its ___________. |
hot; solid; melting; melting; decrease; pressure; addition; volatiles; injection; hot magma; deeper below; composition |
|
|
Magma rises because it's _______ and because of ________ due to overlying rocks. The rate of melt movement is affected by _________, which depends on ___________ and ___________. When molten rocks enters a ______ environment, it _______. The rate of cooling depends on the ___________ and _____ of the magma body. |
buoyant; pressure; viscosity; composition; temperature; cooler; freezes; environment; shape |
|
|
Molten rock can extrude either as a ___ ____ or as ___________ ______. Intrusions underground __________ igneous rock with ____ ____. ________ ________ (sills and dykes) are ___-____ intrusions. Blob-shaped intrustions are ____. Huge ____________ consist of many plutons. |
lava flow; pyroclastic debris; juxtapose; wall rock; Tabular intrusions; wall-like; plutons; batholiths |
|
|
Igneous rocks come in a variety of ___. Mafic rocks tend to be ________ than felsic rocks. Textures of igneous rocks vary from _____, to ____-_______, to _____-_______. Geologists classify and assign names to igneous rocks based on ________ and _________. |
colors; darker; glassy; fine-grained, coarse-grained; texture; composition |
|
|
The formation of igneous rocks can be understood in the context of _____-_________ ______. ____ ________ due to release of fluids from subducting slabs produces melts at __________ _______. Melting at ___ _____ is probably due to ____________ of ______ _____________ also triggers melting beneath _____ and ___-_____ ______. _________ of ___ ______-_______ _____ into the crust at _____ and __________ _______ causes melting of the _____. |
plate-tectonics; theory; Flux melting; convergent margins; hot spots; decompression rising asthenosphere; rifts; mid-ocean ridges; Injection; hot mantle-derived magma; rifts; convergent margins; crust |
|
|
* The universe is _________. -The other galaxies are all moving _____ from us. -We're not the ______ of the universe -Shows that everything originated from one _____ |
expanding; away; center; point |
|
|
*Looking at the absorption spectra of the star -we know what it ______ look like -we see we have the _____ _______ but not in the right place. |
should; right pattern |
|
|
*Where do matter and energy come from? -________ _________ formed within a few seconds. After three minutes, __ and __, __, _ were all created by ______. - only works up until atomic number __ (____) -Gravity collected ______ and made _____. -__________ released enough energy to make atomic elements with numbers larger than __. |
Hydrogen atoms; He; Be; Li; B; fusion; 26; Iron; gravity; stars; Supernovas; 26 |
|
|
*Sun formed
-_________ ______ (gravitational) -Energy in the planets meets at the ____ |
potential energy; core
|
|
|
Something smashed into the Earth and broke a piece off and that's the ____. |
Moon |
|
|
Volcanoes spew out _________, |
volatiles |
|
|
We have to wait until its ____ enough to have liquid water. |
cool |
|
|
The Earth system includes the __________, _________ (anything _____), ___________ (all _____ on Earth), and ___________ (all of the stuff made out of ____) [___ what we mean when we say lithosphere in Geology] |
atmosphere, biosphere; alive; hydrosphere; water; lithosphere; rock; not |
|
|
The continents all ___ ________. |
fit together |
|
|
There is not the same amount of __________ on Earth. |
elevations |
|
|
We know more about the _______ of ____ than our own seafloor. |
surface; Mars |
|
|
___ __ up is space. |
100 km |
|
|
Ocean floors are _-_ km deep |
4; 5 |
|
|
The Earth is ______. |
differentiated. |
|
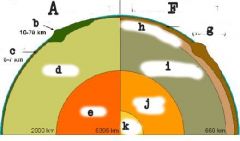
|
Compositional Layers; Continental; Oceanic; Mantle; Core; Mechanical Layers; lithosphere; aesthenosphere; mesosphere; outer core; inner core |
|
|
The boundary between crust and mantle is called the ____. |
Moho |
|
|
The difference in the layers is their _______ ___________. |
chemical composition |
|
|
Mechanical difference in layers is in their _________ (how it flows) |
viscosity |
|
|
*Iron is the ________ element that we have a lot of. -Most of the iron is in the _____ ____. -Most trace elements occur in the _____.
|
heaviest; inner core; crust |
|
|
Seismic waves react ____________ in the crust and the mantle. |
differently |
|
|
_____ and _____ are too simple. |
Solid; liquid |
|
|
There are different levels of __________. Water is the _____ viscous. The ______ the viscosity, the ____ is flows. |
viscosity; least; higher; less |
|
|
The word "__________" is not really used. |
mesosphere |
|
|
*Plate tectonics -______ are ___________ that is moving over an ______________ that is able to flow. -Crust and ____________ ______ -The crust for the continents is _______. -Plates move apart at ___-______ ______. --where new, ___ ______ is erupting. ----becoming _______ crust -__________ ________ when plates collide. |
Plates; lithosphere; asthenosphere; lithospheric mantle; thicker; mid-ocean ridges; hot mantle; oceanic; convergent boundary |
|
|
Igneous rocks are ______ _____ that cooled down |
molten rocks |
|
|
The old oceanic crust got |
subducted |
|
|
*Continental Crust is ____ _____ -It's like a __________ ______. -Continents ___ __________, _______ _______ _________, etc. |
less dense; floatation device; get stretched; pushed back together |
|
|
*Why is the Earth doing this? -Earth is making the ____ ______ rock rise. -Earth is a physical system trying to achieve ________. -Plate tectonics is the Earth's way of ________ _____ ____. -________ |
less dense; coolness; cooling itself off; convecting |
|
|
*What defines a unit of plate? -__________ - __________ ________ the ____ -_______ is moving as a _____ piece. |
Boundary; motion between; plates; plate; solid |
|
|
Some plates are entirely _______, others are made of both _______ and _______ ________. |
oceanic; oceanic; continental; lithosphere |
|
|
Active continental margins are |
plate boundaries |
|
|
_____ _____ are not plate boundaries |
passive margins |
|
|
Earthquakes occur in________ _________ that define tectonic plate boundaries. |
seismic belts |
|
|
Three types of plate boudaries -Divergent: -convergent: -transform: |
plates move away, plates move toward, plate move past |
|
|
When continental lithosphere ______ and __, the upper crust breaks by _______. Upwelling asthenosphere initiates ___________. Rifting may _____ a _______ in ___. |
stretches, thins; faulting; volcanism; split; continent; two |
|
|
The East African rift is an _____ ____. The Red Sea started as a rift, but it evolved into a _______ _______ _______, the rift axis became a ___-____ _______. |
active rift; narrow ocean basin; mid-ocean ridge |
|
|
A _______ ___________ exists beneath the ridge axis. Molten rock that flows out onto the seafloor produces ______ _________. _______ ________ inject ______ the magma chamber. _________ forms at depth. |
magma chamber; pillow basalt; Basalt dikes; above; Gabbro |
|
|
____ still happen along the plates. |
Earthquakes |
|
|
The further away we get from the edges, the ____________ the Earthquakes are. |
deeper |
|
|
Continental collision starts _________ subduction. |
After |
|
|
Continental crust is ___ _________ to subduct, so ______ ________ develop. |
too buoyant; mountain ranges |
|
|
Sinking lithosphere is ____ going into the core, but is being ________ into the lower mantle. |
not; reabsorbed |
|
|
Hot material is ______ __, _________, and is _______ to the ______. |
coming up; crystallizes; pushed; sides |
|
|
______ is not exactly the boundary. |
Trench |
|
|
________ ________ scraped up |
Accretionary Prism |
|
|
In some cases, a volcanic island arc develops on a ______ ________ of ______ ________ that had split away from the main continent |
small fragment; continental crust |
|
|
*Transform faults -happen a ton as part of the __-______ ________ -The mid-ocean ridge is much _________ than the deeper _______ _______. The ridge is offset along its length by transform fault _____ ________. -Some transform boundaries ___ continental crust. For example, across the ___ _________ _________, the Pacific plate moves _________ relative to the ____ __________ _______. |
mid-ocean ridges; shallower; abysmal plains; fracture zones; San Andreas Fault; northwest; North American plate |
|
|
*Hot Spots -Geologists recognize numerous hot-spot tracks ______ the _______. -Probably a consequence of ______ ________ -Coming at least from ______ in the ________ -_______ of material -a chain of _______ ___________ forms -Hawaii --Islands ______ in age with distance from the present hot spot. --_____________ _________.
|
around; world; mantle plume; deep; mantle; extinct volcanoes; increase; energetically favorable |
|
|
*How did we figure plate tectonics out? -_______ ___________ (1925) -Continents look like _______ _______ -_______ -_________ leave a telltale signature -________ belts -_________ belts -He had no idea ___ they moved from each other -Looked at ______ |
Alfred Wegener; puzzle pieces; fossils; glaciers; mountain; climate; how; magnetism |
|
|
*Paleomagnetism -The Geomagnetic Field has both _______ and _____ --_______ --________ -Rocks can acquire _______ --Cools and iron grains _____ with Earth's field --________ wherever they are -Geomagnetic pole _______ a bit (points mostly north) -________ variation -Geomagnetic field ________ every so often --___________ ________ -had to have a ton of ______ to figure this out --_____
|
magnitude; direction; inclination; declination; magnetization; align; frozen; wanders; paleosecular; reverses; symmetric pattern; boats; WWII |
|
|
*Eight elements make up __% of the Earth's crust -mostly ______ -Order of elements by amount --_________ |
90; oxygen; Oxsialfecanakmg |
|
|
*Oxygen is the only _____ (negatively charged) -_______ - a lot of times, we're gonna put _______ with oxygen because there's a lot of _______ -_____________- a fundamental building block of ______ _______, the most common type of minerals |
anion; tetrahedron; silicon; silicon; silicatetetrahedron; silicate minerals |
|
|
_______ __________ constitute almost the entire crust and mantle of the Earth. |
Silicate Minerals |
|
|
*Silicate minerals with isolated tetrahedral __ ____ _______ any oxygens. Instead, they are bonded together by their _________. -Examples include ______ and _____ -Acts as though it were its own ______ -Important to understand that properties we can observe are ________ into the _____ of what they are. |
do not share; cations; olivines; garnets; anion; woven; fabric |
|
|
* In single-chain silicates, ___ of the _____ _____ ________ are bonded together. The Si:O ration is _:_. -example: _______ |
two; three basal oxygens; 1; 3; pyroxenes |
|
|
Double-chain silicates are like __ ____ _____ that share oxygens where tetrahedral _____ yielding an Si:O ratio of _:_ -example: _______ |
two single chains; touch; 2;7 |
|
|
*______ ___________ share oxygens along the ______ of the tetrahedral, but not the oxygen at the ___ of the tetrahedral. The Si:O ratio is _:__ -Examples: _____ and _______ _________ |
Sheet silicates; base; top; 4; 11; micas; clay minerals |
|
|
In framework silicates, all of the oxygens are ________ between _________ _____________, yielding an Si:O ratio of _:_ -most ____ packed -Examples: _______ and _______- |
shared; adjacent tetrahedral; 1;2; densely; quartz; feldspar |
|
|
___________ ________ is mostly silicate minerals |
Oceanic crust |
|
|
Silicate minerals are classified by the |
anion |
|
|
*__________ -__________ __________ bonded to oxygen --Ex. _________, __________, and ______ -________: metal cation bonded to a sulfide anion --Examples: ______, ____________, and _________ -________: metal cation bonded to a sulfate anionic group --Many of these form by ______ of _______ --ex:__________ (______) and ___________ (__________) -_________: 2nd to right column --Ex: _________ and _________ --tend to make ________ --breaks into _____ -_________ --ex: ______ and __________ --This is where the ________ in rocks go -_________ --example: _______ |
Oxides; metal cations; magnetite; hematite; rutile; sulfides; pyrite; galena; sphalerite; sulfates; evaporation; seawater; gypsum; hydrated; anhydrite; dehydrated; Hallides; halite; fluorite; salts; cubes; carbonates; calcite; dolamite; carbon; phosphates; apatite |
|
|
Pure masses of a single metal or non-metal |
native elements |
|
|
Name 4 native elements |
copper, gold, silver, sulfur |
|
|
Darrelhenryite
|
new species of tourmaline named after a professor at LSU |
|
|
The types of minerals we find in the crust are ____________ than the ones in the mantle. |
different |
|
|
Volcanoes can be due to ______ of the plate. |
Subduction |
|
|
All things are |
spatially related. |
|
|
Crystals develop _________ from a central seed and grow to ______ ____________ ________. Existing crystals may act as _________, ________ growth in one or more directions |
outward; fill existing space; obstacles; restricting |
|
|
little bits (clasts) cemented together |
clastic rocks |
|
|
example of a clastic rock |
sandstone |
|
|
individual mineral crystals that grew up together |
crystalline rock |
|
|
example of crystalline rock |
granite |
|
|
come from magma or melt that is crystallizing |
igneous rocks |
|
|
bits of rock that broke off or eroded away cemented together |
sedimentary rock |
|
|
________ forms as a sedimentary rock. |
NOthing |
|
|
Come from temperature or pressure changes, used to be a different rock |
metamorphic rocks |
|
|
All rocks are born as ____ ______. |
igneous rocks. |
|
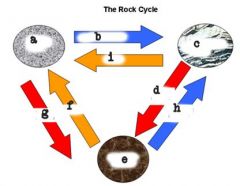
|
Igneous Rocks; weathering and erosion; sedimentary rocks; heat and pressure; metamorphic rocks; melting; heat and pressure; weathering and erosion; melting |
|
|
Igneous rocks with really big grain size |
phanatic |
|
|
igneous rocks with tiny grains |
aphanatic |
|
|
igneous rocks with a mix of grain size |
porphyritic |
|
|
*Crystalline igneous rocks are classified by ______ and ________
|
texture; composition |
|
|
Composition of igneous rocks |
felsic, intermediate, mafic, ultra mafic |
|
|
texture of igneous rocks |
fine, coarse, glassy |
|
|
*Glassy textures are most common in _______ __________ _________
|
felsic igneous rocks |
|
|
frothy felsic rock full of vesicles that floats |
pumice |
|
|
glassy volcanic rock that fractures conchoidally |
obsidian |
|
|
glassy, vesticular mafic rock |
scorcia |
|
|
_________ ___________ are affected by how fast or slow they cool |
different textures |
|
|
Melts are mostly _______. -___________ -Trace elements --used as ______ later on -Volatiles are also in melts --anything that can be a ___ ---H2O, CO2, SO2, N, He -Can be from _ to __% |
silica; AlFeCaNaKMg; evidence; gas; 0; 15 |
|
|
If you have a lot of silica, your melt will be ______. |
Felsic; Fe=Iron; Sic=Silica |
|
|
If you have a middle amount of silica, your melt will be |
intermediate |
|
|
If you have very little silica, your melt will be _________ |
mafic; ma=magnesium, fic=iron |
|
|
If you've got a lot of Mg and Fe, your melt will be |
ultramafic |
|
|
Very low amounts of silica is still about |
40% |
|
|
realm where igneous rocks solidify above ground |
extrusive |
|
|
extrusive igneous rock |
basalt |
|
|
realm where igneous rocks solidify below ground |
intrusive |
|
|
Large grains took a _____ time to form |
long |
|
|
Two minerals in oceanic crust |
gabbro and basalt |
|
|
two minerals in continental crust |
rhyolite and granite |
|
|
Melting occurs when (3) |
temperature rises, pressure decreases, the solidus moves due to volatile content |
|
|
baseline (average) of normal planet, average change in temperature with depth |
geotherm |
|
|
condition at which rock completely melts |
liquidus |
|
|
conditions at which rock starts to melt |
solidus |
|
|
when do we move the solidus line? |
when there is a change in pressure or temperature |
|
|
Decompression melting takes place when the _______ acting on a hot rock ___________. When the pressure decreases a lot due to the rock rising, but the rock only cools a little, the rock begins to ____. |
pressure; decreases; melt |
|
|
Heat-transfer melting occurs when ________ _________ brings heat up with it and melts _______ or _______ rock. |
rising magma; overlying; surrounding |
|
|
Heat rising from magma _______ ___ ______ |
melts the crust |
|
|
________ magma pools at the base of the crust |
basaltic |
|
|
To melt it means that something is moving _____ enough that it is not on the geotherm |
fast |
|
|
Decompression melting can occur (3) |
in a mantle plume, beneath a rift, and beneath a mid-ocean ridge |
|
|
In Flux melting, common volatiles include ___ and ___. These substances are brought into _________ ________ in sediment and fractures in the subducting crust. |
H2O and CO2; subduction zones |
|
|
Flux melting occurs where __________ enter ___ ____; this happens at ____ zones. |
volatiles, hot mantle; subduction |
|
|
At a mantle plume or hot spot, there will be ____ ________ or ________ melting because we are _____ __ what's already there. |
heat transfer; decompression; heating up |
|
|
At a subduction zone there will be ____ and ____ _______ melting. Examples of what will be found there are _____ ______ and ________ stuff. |
Obsidian glass; extrusive |
|
|
At a mid-ocean ridge, there will be ________ and _____ melting because ________ circulates and can change physical properties. Examples of what can be found there are ___________ and _____. |
decompression; flux; seawater; basalt; gabbro |
|
|
At a continental rift there will be ______ and ____ ________ melting. |
decompression; heat transfer |
|
|
Coarse-grained rocks are _______. |
intrusive |
|
|
Granite is (3) |
more felsic, has more silicate, can be under subduction zones |
|
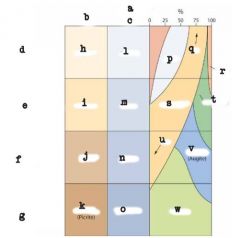
|
Crystalline; Fine; Coarse; felsic; intermediate; mafic; ultramafic; rhyolite; andesite; basalt; komatilite; granite; diorite; gabbro; peridotite; quartz; Na; Biotite; Plagioclase; Amphibole; Ca; Pyroxene; Olivine |
|
|
*Bowen's reaction series -A ____ melt starts to cool. -_________ and __-rich ______ starts to sink -If the residual melt escapes and freezes, it produces ___ _____. -_______ starts to form, and _______ contains more __. -With decreasing temperature, _______ __________ begins and the composition of the remaining magma becomes more _______. -The rocks change as the ______ and the _____ change. _____ minerals _________ first, at highest temperature. The last minerals to crystallize are _____, __________ and ___________. |
mafic; olivine; Ca; plagioclase; felsic rock; Pyroxene; plagioclase; Na; fractional crystallization; felsic; mafic; crystallize; quartz; muscovite; and k-feldspar |
|
|
In intrusive settings, magma invades preexisting ____ ____ by percolating upward _______ ______, wedging ____ ______, melting and breaking off bloacks of wall rock. |
wall rock; between grains; open cracks |
|
|
Xenoliths and plutons |
chunks of wall rock incorporated into the magma |
|
|
Plutons may intrude by _______. When blocks of wall rock fall into the magma, some ________ but others may remain as ________. |
stoping; dissolve; xenoliths |
|
|
fill space formed when crust undergoes horizontal stretching |
dikes |
|
|
intrude between layers and may cause the uplift of the land surface |
sills |
|
|
typify extrusive behavior of high viscosity felsic magmas |
explosive ash eruptions |
|
|
deadly avalanches of superheated volcanic ash and debris |
pyroclastic flows |
|
|
Pyroclastic flows race down volcanic slopes as a ________ _________ moving on a carpet of ___ ____. Thick layers of volcanic tuff ________ from explosive eruption. |
density current; hot air; accumulate |
|
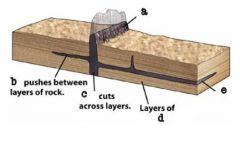
|
dike; sill; dike; sandstone; sill |
|
|
The conditions leading up to decompression melting occur in several geologic environments. In each case, a volume of ___ _____________ rises to a _________ _______ and ______ forms. |
hot asthenosphere; shallower depth; magma |

