![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
West- United States |
Washington, Oregon, California, Idaho, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, Montana, Wyomming, Colorado, New Mexico |
|
|
Mid West- United States |
North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, Minnesota, Iowa, Missouri, Wisconsin, Illinois, Michigan, Indiana, Ohio |
|
|
South- United States |
Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Louisana, Kentucky, Tennessee, Mississippi, Alabama, Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia, Maryland, Delaware, Ohio |
|
|
North East- United States |
Pennsylvania, Delaware, New Jersey, New York, Connecticut, Rhode Island, Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts |
|
|
5 Themes Of Geography- Location |
Absolute: exact location Relative: in the area -lines of latitude- |lines of longitude| hemispheres |
|
|
5 Themes Of Geography- Place |
Features, physical characteristics, culture |
|
|
5 Themes Of Geography- Region |
North America, Latin America, Oceania |
|
|
5 Themes Of Geography- HEI |
How we interact with the world/planet |
|
|
5 Themes of Geography- Movement |
Traveling, moving, transfer of ideas ex. Music, fashion |
|
|
Planets- Closest to Farthest From the Sun |
1. Mercury. 2. Venus. 3. Earth. 4. Mars. 5. Jupiter. 6. Saturn. 7. Uranus. 8. Neptune. |
|
|
Mercury |
1st closest |
|
|
Venus |
2nd closest |
|
|
Earth |
3rd closest |
|
|
Mars |
4th closest |
|
|
Jupiter |
5th closest |
|
|
Saturn |
6th closest |
|
|
Uranus |
7th closest |
|
|
Neptune |
Farthest away |
|
|
Pangea |
Super-continent |
|
|
Water Cycle |
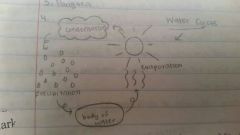
evaporation, condensation, precipation |
|
|
Landforms |
1. Volcano 9. Harbor 2. Strait 10. Bay/ Gulf 3. Island 11. Sea Level 4. Swamp 12.Cape/Peninsula 5. Flood Plain 13. Butte 6. Delta 14. Oasis 7. Marsh 15. 8. River Mouth 16. Steppe 17. Mountain 18. Valley 19. Glacier 20. Mesa 21. Cataract 22. Plateau 23. Canyon 24. Cliff |
|
|
Ring of Fire |
A zone around the rim of the Pacific Ocean. The location of the vast majority of active volcanoes |
|
|
Plate Boundaries |
1) Divergent 2) Convergent Subduction 3) Convergent Collision 4) Transform |
|
|
Weathering |
Mechinal: processes that break rock into smaller pieces Chemical: occurs when rock is changed into new substance as a result of interaction between elements in the or water and the minerals in rock |
|
|
Erosion |
Water: pulls sediment along water Wind: basically same as water but with wind Glacial: as the glaciers move it pulls rock and dirt with it |
|
|
Fault |
Sometimes the rock isn't flexible and will crack under the pressures exerted by the plate movement. It I'd at the fault line that the plates move past each other. |
|
|
Epicenter |
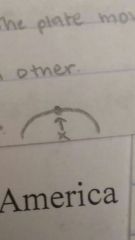
Middle center |
|
|
Richter Scale |
Measures the power of the earthquake |
|
|
What Starts a Season? |
Because of Earth's revolution and it's tilt, different parts of the earth receive the direct rays of the sun for more hours of the day at same times in the year. |
|
|
What Causes Weather? |
The sun provides the energy that drives earth's weather. The sun haters the air in various parts of earth's atmosphere by different amounts. Masses of warm and cold air then move from place to place, creating winds. |
|
|
Weather Extremes- Hurricanes |
Storms that firm over warm, tropical ocean waters are called hurricanes. Air flowing over an ocean with water temperature of 80°F or higher picks up huge amounts of moisture and heat energy. ( days to develop ) |
|
|
Weather Extremes- Tornadoes |
Form quickly and sometimes without warning. A powerful funnel-shaped column of spiraling air. |
|
|
Weather Extremes- Blizzards |
A heavy snow storm with winds of more than 35 miles per hour and reduced visibility |
|
|
Weather Extremes- Droughts |
A long period of time without rain or with very minimal rainfall |
|
|
Weather Extremes- Floods |
When water spreads over land not normal covered with water. Melting snow or rainwater fills streams or rivers until they reach flood stage, the point at which banks can no longer contain water. |
|
|
Different Types of Climate |
1) Tropical Wet 2) Tropical Wet + Dry 3) Semiarid 4) Desert 5) Mediterranean 6) Marine West Coast 7) Humid Subtropical 8) Humid Continental 9) Subarctic 10) Tundra 11) Ice Cap 12) Highlands |
|
|
Innovation |
Taking existing technology and resources and creating something new to meet a need. |
|
|
Diffusion |
When people from different societies, or their ideas and inventions, come into contact with one another. |
|
|
Acculturation |
Occurs when a society changed because it accepts or adapts an innovation |
|
|
Language Tree |
Proto-Indo-European to Balto-Salvo-Germanic to Western Germanic to English |
|
|
Religion |
Consists of a belief in a supernatural power or powers that are regarded as the creators and maintainers of the universe |
|
|
Belief Systems- Monotheism |
Belief in one God |
|
|
Belief Systems- Polytheism |
Belief in more than one God |
|
|
Belief Systems- Ahimistic |
Belief in divine forces in nature |
|
|
5 Major Religions |
1) Judaism 2) Christianity 3) Islam 4) Hinduism 5) Buddhism |
|
|
Government- Democracy |
Ex. United States |
|
|
Government- Monarchy |
Ex. The United Kingdom and Saudi Arabia |
|
|
Government- Dictatorship |
Ex. North Korea |
|
|
Government- Communism |
Ex.? |
|
|
Natural Boundaries |
Are based on physical features of the land, such as rivers lakes or chains of mountains. |
|
|
Artificial Boundaries |
Are fixed lines generally following lines of latitude and longitude lines |
|
|
Columbian Exchange |
-Citrus Fruits -Grapes -Bananas -Sugar Cane -Honey Bees -Coffee Beans -Peaches, Pears -Onions -Olives -Turnips
Grains: wheat, rice, barley and oats Dieases: small pox, influenza, typhus, measles, malaria, diphtheria, whooping cough Lice Stock: cattle, sheep, pigs, horses |
|
|
3 Branches of US Government |
1) Executive: President 2) Legislative: Congress 3) Judicial: Supreme Court |

