![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Weathering |
Is the wearing away of the rocks & soil by actions of the weather. |
|
|
|
What does weathering affects? |
Affects the shape & composition of the rocks and soil . |
|
|
|
What are the most important agents of weathering? |
》》Temperature 》》Water
|
|
|
|
Agents |
Are natural forces the cause an effect/results . |
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of weathering? |
》》 Physical weathering 》》 Chemical weathering 》》 Biological weathering |
|
|
|
Physical weathering |
Is the weathering that involves forces like ice , water & temperature change to break rocks. |
|
|
|
What are the Examples of Physical weathering? |
》》 Freeze thaw action 》》 exfoliation |
|
|
|
Freeze thaw action |
Is the physical weathering when water collects in the cracks of the rocks. |
|
|
|
During the freeze thaw process, the .... expands when it turns into .... & increase .... & put .... on the .... of the rocks. |
During the freeze thaw process, the water expands when it turns into ice & increase volume & put pressure on the sides of the rocks. |
|
|
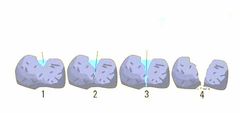
Explain the process from 1-4 in detail. |
1. Water fill in a crack in a rock. 2. Water freeze from the top of the crack. 3. The ice can't expand upwards because the top layer is already frozen. 4. The ice expands sideways putting pressure on the rock. |
|
|
|
.... is the removal of the outer layer of the rocks after repeated contractions & expansions. |
Exfoliation is the removal of the outer layer of the rocks after repeated contractions & expansions . |
|
|
|
What are the causes of exfoliation in the dry climate? |
Due to the extreme temperature changes between the day & night cause the other layers of the rocks to expand in the heat of the day & contract in the cool nights. |
|
|
|
Chemical weathering |
Is the weathering that changes the chemical composition of rocks and weakening them to break up due to the different kinds of the chemical reactions that is contributed. |
》》Carbonation 》》Hydrolysis 》》Oxidation |
|
|
Carbonation |
Is a chemical weathering process that attacks the rocks that contain calcium carbonate. |
|
|
|
Explain this process 1-3 in detail. |
1. Carbon dioxide mixes with water in the rain clouds to form a weak carbonic acid. -------------------------- CO2 + H2O ---> H2CO3 2. Carbonic acid changes calcium carbonate into calcium bicarbonate when acidic water comes in contact with limestone. -------------------------- H2CO3 + CaCO3 ---> Ca(HCO2 )3 3. Soluble Calcium bicarbonate dissolved in the water and is washed away. |
|
|
|
Dissolved |
Has become part of the liquid solution. |
|
|
|
Insoluble |
Does not dissolve in water. |
|
|
|
Soluble |
does dissolves in water |
|
|
|
Carbonation is greater and strong in .... because cold water absorbs more .... than warm water. |
Carbonation is greater and strong in Cold Climates because cold water absorbs more Carbon dioxide than warm water. |
|
|
|
Oxidation |
Is a chemical weathering when water comes in contact with rocks and objects that contain iron to make the chemical structure more weaker and to easily being broken down. |
It causes rocks to have reddish iron oxide |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
Is a sequence of chemical reactions that involves water & minerals called silicates. |
|
|
|
Silicates are minerals that present in .... & .... |
Silicates are minerals that present in Granite & sandstone. |
|
|
|
When does hydrolysis take place? |
When Silicates absorb water to make clay that is soluble & result washed out of the rocks to make them unstable and crumble grain by grain. |
|
|
|
Biological weathering |
Weathering that is caused by animals, plants & Human. |
|
|
|
What animals causes bio. Weathering? |
》》 Worms 》》 moles 》》 porcupines |
They burrow & dig the soil thus it becomes weaker and rocks are exposed to other kinds of Weathering. |
|
|
Lichens |
Very small plant organisms that are made up of algae & fungi which live together. |
|
|
|
What are the Lichens' functions? |
Their roots penetrate between grains of the rocks to slowly loosen them so that they can eventually fall away. |
|
|
|
What so lichens produce? |
They produce acid that breaks down the minerals in rocks. |
|
|
|
What are the activities Humans cause weathering? |
》》 Roads expose new rocks to weathering. 》》 Machines remove vegetation and soil. 》》 Chemicals added from the human made objects are exposed to the air, soil and water. 》》 Dams take up land which could be used for farming. 》》 Fire changes the rocks and soils' composition chemically and physically. 》》 Animals expose soil to weathering when they burrow, dig and spread their wastes. 》》 Underground Tunnels weaken the soil and rocks. 》》 Roads and railways provides pollution to the rural areas. 》》 home settlements pollute that air, soil & water |
|

