![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Abrasion |
Pebbles rubbing against rock (sandpaper effect) |
|
|
Hydraulic action |
Sheer force of the river impacting on the sides of the river bank |
|
|
Corrosion / Solution (Erosion) |
Minerals dissolved in acidic water. |
|
|
Attrition |
Pebbles and rocks collide into each other frequently. Knock pieces off (Tap Tap) |
|
|
Traction |
Boulders roll along the bottom of the riverbed (Tractor) |
|
|
Saltation |
Lighter rocks bounce/roll along riverbed |
|
|
Suspension |
Small grains of sand and silt are carried along in the water |
|
|
Solution (Transportation) |
Minerals dissolve into the water, then carried along |
|
|
Deposition |
Loss of energy in shallow water Rocks are deposited |
|
|
Mouth |
Where the river flows into the sea or lake |
|
|
Tributary |
A small river that joins onto the main river |
|
|
Source |
The start of a river |
|
|
Confluence |
Where 2 rivers join |
|
|
Watershed |
The boundary dividing 2 drainage basins A hill that collects and stores water |
|
|
Catchment |
Where the water drains into a particular drainage basin |
|
|
Floodplain |
The wide flat area of land either side of a river It's in the middle and lower courses of a river |
|
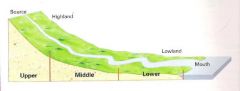
Long profile of a river (features) |
Upper: Gorges, Waterfalls Middle: Meanders, Ox bow lakes Lower: Delta, Estuary |
|
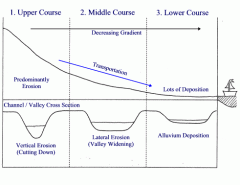
Cross section of a river |
Upper course: Steep, fast flowing river, with little water. Lots of erosion Middle course: River starts to slow down. Much more water, still eroding (laterally) Lower course: River very slow, much more water. No erosion, depositing |
|
|
Erosion in the upper course |
As water flows over the harder rock, it erodes downwards against the softer rock |
|
|
Waterfalls |
1. Water flows over the hard rock and plunges over. It hits the soft rock at the bottom it erodes 2. This creates a plunge pool 3. It erodes the soft rock at the side of the WF as it falls 4. The plunge pool slowly expands 5. The soft rock underneath erodes away, causing a overhang of hard rock. It breaks away and falls into PP. 6. It's repeated. A steep sided gorge is formed |
|
|
Middle course |
Flowing over flatter land Main direction of erosion is lateral Carries more water (greater discharge) More energy to transport material Velocity decreases |
|
|
Meanders and Ox bow lakes |
Erosion occurs on the outside of a river Deposition occurs on the inside of a bend This eventually creates a meander The erosion cuts through the meander, causing it to join the other bend This creates an ox bow lake It eventually dries up due to deposition |
|
|
Levee |
Natural embankments of silt along the banks of a river Often several meters higher than floodplain |
|
|
Levee formation |
1. Formed by deposition after flooding 2. The river's load is composed of different sized sediments 3. When flooding, the water overflows the banks and slows down due to friction 4. It drops larger sediments first at the channel's edge, building up a raised riverbank 5. Thin sediments are deposited on the outer parts of the floodplain |
|
|
Drainage basin |
The area of land from which precipitation flows into a stream |
|
|
Discharge |
The amount of water in a river at a given time |
|
|
Factors affecting discharge |
>Amount of rainfall (May create saturated ground) >Temperature (Eg: Hot = more evaporation) >Previous weather conditions >Rock type (Determines how much water infiltrates) >Soil >Land use (Buildings, forest ETC) >Slope |
|
|
Flooding in an LEDC - Bangladesh (2007) CASE STUDY |
>>Why? Low lying land Deforestation Monsoon season Increasing urban areas >>Primary effects: Deaths Contamination of clean water Food destroyed >>Secondary effects: Disease Destroyed roads Homelessness problems No food or clean water >>Short term responses: Flood aid from other countries Water purification tablets distributed Repaired embankments Free seeds to farmers >>Long term responses: New embankments Raised flood shelters Flood warning systems Emergency planning Reduced deforestation |
|
|
Hydro graphs |
Records of river discharge over a period of time, they show how certain rivers respond to a rainstorm |
|
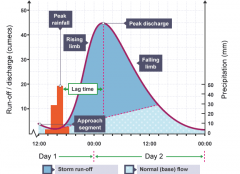
<<Hydro graphs example>> |
<<STUDY BOOK>> |
|
|
Flooding in a MEDC - Cockermouth (2009) CASE STUDY |
>>Why? Heavy downpour Saturated ground Steep slopes >>Primary effects: Roads destroyed Debris in water People trapped Food and water contaminated >>Secondary effects: Rebuilding homes and businesses Cleaning debris No clean water and food Repairing railways >>Short term responses: Helicopters sent to rescue people £1 million given by Govt. £1 million raised by charities Temporary shelter >>Long term responses: Britain's first self closing flood barrier Raised embankments New floodgates |
|
|
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hard engineering |
>Ad: Effective control of water Save lives and homes A chance to prepare >Dis: Expensive An eyesore |
|
|
Advantages and Disadvantages of Soft engineering |
>Ad: Lives saved A chance to prepare Natural sources Doesn't look bad >Dis: Land can't be used for anything else Not as effective as Hard engineering |
|
|
Porous |
Rock with spaces between particles |
|
|
Permeable |
Rock that allows water to pass through the pore spaces |
|
|
Pervious |
Rock that allows water to pass through cracks |
|
|
Impermeable |
Rock that doesn't allow water to pass through |
|
|
Ground water |
Water stored underground in areas of permeable rock |
|
|
How to be more efficient with water |
Have showers rather than baths Wash up by hand rather than dishwashers Hosepipe bans Have plants that don't need much water |

