![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Continental Waters: waters found on the continent
|
|

|
River/Stream: a large stream of water flowing through land
|
|

|
Upstream: the direction from which a river flows
|
|

|
Downstream: the direction toward which a river flows
|
|

|
Source: the place where a river begins, usually in highlands
|
|
|
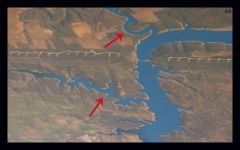
Tributary: a river or stream that flows into a larger river
|
|

|
Mouth: the place where a river flows into a larger body of water
|
|

|
Delta: land deposited at the mouth of a river
|
|

|
Lake: an inland body of water smaller than a sea
|
|

|
Fresh Water Lake: a lake which has water entering in and out of it
|
|

|
Salt Water Lake: a lake which has water entering, but it has no outlet
|
|

|
Channel: a deep, narrow body of water connecting two larger bodies of water; the deeper part of a waterway
|
|

|
Canal: a man-made ditch for transportation or irrigation
|
|

|
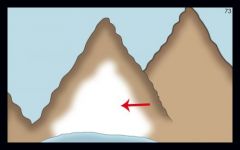
Reservoir: a lake where water is stored for future use; sometimes formed by a dam
|
|
|
Glacier: a large body of slowly moving ice
|
|

|
Ice Sheet: a glacier forming on an extensive area of relatively level land and flowing outward from it center
|
|

|
Groundwater: the water found beneath the surface of the ground; the source of water in springs and wells
|
|

|
Lithosphere: the portion of the earth that is land
|
|
|
Landforms: land distinguished by its shape or form
|
|
|
Continents: seven large bodies of land on the earth
|
|
|
Peninsula: a body of land almost surrounded by water
|
|

|
Isthmus: a narrow strip of land that connects two larger bodies of land
|
|

|
Cape: a point of land sticking out into a body of water
|
|

|
Island: land entirely surrounded by water; smaller than a continent
|
|

|
Archipelago: a group of islands
|
|
|
Fjord: a narrow inlet of the sea with steep banks made by a glacier
|
|

|
Sea Coast: land next to the sea
|
|

|
Topography: land distinguished by its elevation
|
|

|
Mountain: high, rocky land, usually with steep sides and a pointed or rounded top, higher than a hill
|
|

|
Divide: a height of land that separates river basins
|
|

|
Mountain Range: a group of mountains bordered by lowlands
|
|

|
Volcano: a mountain formed of rock or ash thrown up from inside the earth
|
|

|
Plateau: a region that is mostly high and flat
|
|

|
Hill: a raised part of the earth's surface, with sloping slides; smaller than a mountain
|
|

|
Plain: broad, level land
|
|
|
Valley: lowland between hills or mountains
|
|

|
Basin: a region drained by a river; land largely enclosed by higher land
|
|

|
Canyon: a deep, narrow valley with steep walls
|
|

|
Cliff: a high, steep wall of rock
|
|
|
Rift: a separation of the earth formed by an earthquake
|

