![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is geography |
geography is the science that tries to understand how the Earth works and how humans change it
•it examins the Earth's surface and the processes that shape it •it looks at the relationship between people and Earth's environment |
|
|
what are the two main focuses of geography?
|
1. the Earth's physical geography (natural things, such as; energy, air, water, weather, climate, landforms, soils, animals, plants, etc.)
2. the Earth's human geography (people and things related to people, such as cities) |
|
|
what are the five themes if geography?
|
location
place human-environment interaction movement region |
|
|
features of a map
|
title
legend scale direction border date of publication |
|
|
bearings
|
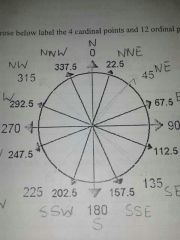
|
|
|
types of map scales
|
direct statement
representative fraction linear scale |
|
|
direct statement
|
this type of scale is written in words
you measure the distance between the two points on the map in centimeters then calculate the actual distance in kilometers |
|
|
representative fraction
|
this scale is expressed in fraction or ratio form
in representative fraction scale form, the units expressing the map and the earth distance are always the same |
|
|
linear scale
|
this scale is shown using a divided line
a special type of ruler to go with the map |
|
|
12 oriental directions and their bearings
|
N 0
NNE 22.5 NE 45 ENE 67.5 E 90 ESE 112.5 SE 135 SSE 157.5 S 180 SSW 202.5 SW 225 WSW 247.5 W 270 WNW 292.5 NW 315 NNW 337.5 |
|
|
what is a map?
|
a map is a representation of the Earth's features drawn on a flat surface
maps use symbols and colours to represent features of an area, simplifying the real world |
|
|
title
|
identifies the area shown, topic, focus, or purpose of the map
|
|
|
legend
|
explains the meaning of symbols and colours used on the map
|
|
|
scale
|
represents the relationship between distance on the map and distance in the real world
|
|
|
direction
|
often represented with a compass rose
|
|
|
border
|
sets the maps apart from other information
|
|
|
date of publication
|
indicates how recent the map is
|
|
|
latitude
|
•are imaginary lines, divide the world into sections, measured in degree
•the equator is a line of latitude - 0° latitude •lines are used as political boundaries •latitude values increase as you travel North or South of the equator - up to 90°N or 90°S •also called parallels |
|
|
longitude
|
•are imaginary lines, divide Earth into sections, run up and down - measure °East and West
•the Prime Meridian is an imaginary line that cuts the Earth in half - 0°longitude •lines are used for time zones •longitude increases as you travel East or West of the Prime Meridian •the westernmost longitude and easternmost longitude meet halfway around the globe at 180°, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean at the International Date Line •lines of longitude are also called meridians |
|
|
10 provinces in order West to East
|
British Columbia
Alberta Saskatchewan Manitoba Ontario Quebec Newfoundland and Labrador New Brunswick Prince Edward Island Nova Scotia |
|
|
3 territories West to East
|
Yukon
Northwest Territories Nunavut |
|
|
3 oceans that surround Canada
|
West - Pacific Ocean
North - Arctic Ocean East - Atlantic Ocean |
|
|
capital of Yukon
|
Whitehorse
|
|
|
capital of Northwest Territories
|
Yellowknife
|
|
|
capital of Nunavut
|
Iqaluit
|
|
|
capital of British Columbia
|
Victoria
|
|
|
capital of Alberta
|
Edmonton
|
|
|
capital of Saskatchewan
|
Regina
|
|
|
capital of Manitoba
|
Winnipeg
|
|
|
capital of Ontario
|
Toronto
|
|
|
capital of Quebec
|
Quebec
|
|
|
capital of Newfoundland and Labrador
|
St. John's
|
|
|
capital of New Brunswick
|
Fredericton
|
|
|
capital of Prince Edward Island
|
Charlottetown
|
|
|
capital of Nova Scotia
|
Halifax
|
|
|
3 major lakes and locations
|
Great Bear Lake - top lake in Northwest Territories
Great Slave Lake - bottom lake in Northwest Territories Lake Winnipeg - Manitoba |
|
|
great lakes in order from West to East
|
Lake Superior
Lake Michigan Lake Huron Lake Erie Lake Ontario |
|
|
4 major rivers and main provinces
|
MacKenzie River - Northwest Territories
Peace River - Alberta Fraser River - British Columbia St. Lawrence River - Quebec |
|
|
capital of Canada
|
Ottawa
|
|
|
where is Victoria Island
|
the island shared by the Northwest Territories and Nunavut
|
|
|
where is Baffin Island
|
the big island Iqaluit is on
|
|
|
where is Vancouver Island
|
the Island Victoria is on
|
|
|
where is Vancouver
|
bottom left corner of British Columbia
|
|
|
where is Calgary
|
below Edmonton in Alberta
|
|
|
where is Saskatoon
|
above Regina in Saskatchewan
|
|
|
where is Churchill
|
top rightish part of Manitoba, on Hudson's Bay
|
|
|
where is James Bay
|
the bottom dip in Hudson's Bay
|
|
|
where is Thunder Bay
|
bottom left part of Ontario, on Lake Superior
|
|
|
where is Sudbury
|
middleish right part of Ontario, on Quebec's border
|
|
|
where in Montreal
|
bottom right part of Quebec
|
|
|
where is the gulf of St. Lawrence
|
mouth of the St. Lawrence River, in the Maritimes
|
|
|
where is Cape Breton Island
|
top island of Nova Scotia
|
|
|
5 types of maps
|
political map (map of Canada)
physical map (elevation through colour) road map topographical map (contour lines) thematic map |
|
|
how many timezones are there
|
24
|
|
|
how often are timezomes
|
•1 timezone every 15° of longitude
•we measure from the Prime Meridian -every 15° to the east = +1hr -every 15° to the east = -1hr |
|
|
How many time zones are in Canada
|
six primary time zones
|
|
|
names of Canadian time zones east to west
|
Newfoundland Time Zone
Atlantic Time Zone Eastern Time Zone Central Time Zone Mountain Time Zone Pacific Time Zone |
|
|
north pole
|
90°N
|
|
|
Arctic Circle
|
60°N
|
|
|
tropic of cancer
|
23.5°N
|
|
|
equator
|
0
|
|
|
tropic of Capricorn
|
23.5°S
|
|
|
Antarctic circle
|
66.5°S
|
|
|
south Pole
|
90°S
|

