![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is aerial view? |
-From directly above. -Gives a general view of a certain area to show large buildings, main road patterns and landscapes. -Its in 2D and taken from earth |
|
|
What is satellite view? |
-Its used to give the general shape/size of an area including landscape -Its a 2D photo taken from space |
|
|
What's an oblique view? |
-Its a detailed view of a specific area -Its taken from an angle on earth to show a 3D image of buildings and the landscape -Its taken from earth |
|
|
What are the 6 points to include in a field sketch? |
1) date 2) location 3) title of place 4) direction of view 5) features-human and physical 6) clear labels |
|
|
What are the 6 key points of drawing a sketch map? |
1) frame 2) title 3) key 4) north arrow 5) labels where appropriate 6) scale if drawn from an OS map |
|
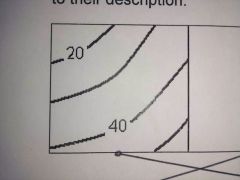
What do these contour lines show? |
A moderate slope |
|
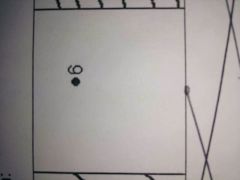
What do these contour lines show? |
Flat land |
|
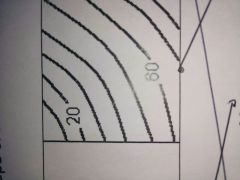
What do these contour lined show? |
Steep slope |
|
|
What is altitude? |
The distance something is above sea level |
|
|
What is relief? |
The shape and height of the land |
|
|
What is aspect? |
The direction in which a slope faces |
|
|
What 7 factors affect site and why? |
1) nearby forests - useful for wood which can be used as a fuel and building materials 2) fertile soil - makes it easier to grow crops 3) shelter - protects site from the elements 4) flat surfaces - makes building homes easier 5) nearby water source - lakes/rivers are good for drinking, transport and a source of food 6) suitable temperature - this can affect lots of factors such as the crops growing and general wellbeing 7) defensive - its suitable to be on a hill to see the enemy (however you are exposed to harsh weather) |
|
|
What is situation? |
Where a settlement is located in comparison to other surrounding features such as other settlements , rivers and communications. |
|
|
What is site? |
Describes the land upon which a settlement is built. |
|
|
What are the 5 main types of sites? |
1) Dry point - built on higher , drier ground to avoid flooding 2) wet point - built by a water source to improve access to water 3) Defence - built on a protective area and surrounded by water. 4) Bridging point - an area with a shallow river that a bridge could be built over 5) nodal point - when natural routes in the landscape meet such as valleys |
|
|
What are the 6 main settlement shapes? |
1) Linear - when the buildings follow the line of a river or road 2) Planned - when buildings and roads are in an organised pattern with evenly spread roads (type of nucleated) 3) Ring - when buildings are based around one object in the centre of the town e.g. a well or green (type of nucleated) 4) Cross - when the buildings surround cross roads in the centre ( type of nucleated) 5) Dispersed - when the buildings are uneavenly spread apart, away from the road / lake and each other 6) Nucleated - centered around a feature |
|

What type of graph is this? |
Pie chart |
|

What type of graph is this? |
Bar chart |
|
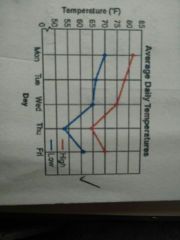
What type of graph is this? |
Line graph |
|
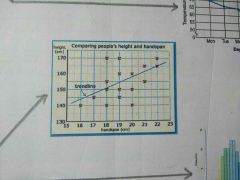
What type of graph is this? |
Scatter graph |
|
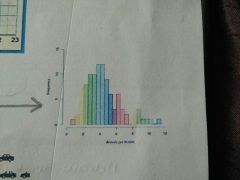
What type of graph is this? |
Histogram |
|
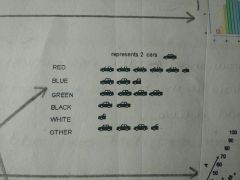
What type of graph is this? |
Pictogram |
|

What type of graph is this? |
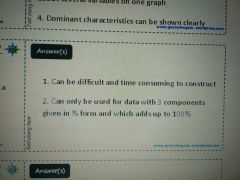
Triangular graph |
|

What type of graph is this? |
Compound bar graph |
|
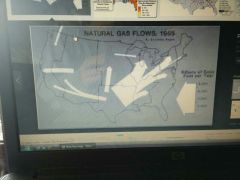
What type of graph is this and how do you interpret it? |
Flow line graph Shows movement between places as the direction of the arrow showd the direction of movement and the thickness shows the amount. |
|
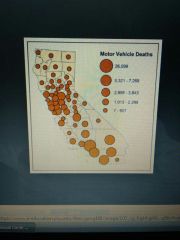
What type of graph is this and how do you interpret it? |
Proportional circle diagram The circles represent the values so the larger the circle the higher the value. |
|
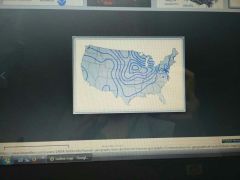
What type of graph is this and how do you interpret it? |
Isoline map It joins places of equal value using contour lines |
|
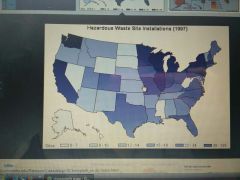
What type of graph is this and how do you interpret it? |
Choropleth map Shaded to show different data with each colour representing a specific range of values. |
|
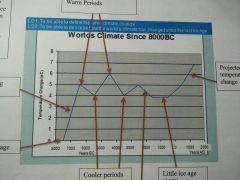
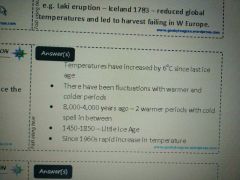
How has the worlds climate changed since the last ice age? |
The climate is constantly changing as there are warmer and cooler periods, however it is predicted to continue rising increasingly with less cooler periods. |
|
|
How has methane contributed to climate change? |
- 2nd largest contributor to global warming - occurs naturally and has a short lifetime - can be produced from burning fossil fuels , landfills and cows stomachs - stored in clathrates so if the sea heats up more will be released - contributes to climate change by retaining heat in the atmosphere |
|
|
How does CO2 contribute to climate change? |
- largest cause of global warming - created by burning fossil fuels - amount of CO2 is constantly steadily increasing - it raises earth's temperature and it can stay in the atmosphere for up to 200 years - creates a 'blanket' around earth so less energy from the sun can reach earth |
|
|
How does CFCs contribute to climate change? |
- manmade compound containing chlorine, fluorine and carbon - used in fridges, first produced in 1930s - nowadays used in aerosols, AC and as blowing agents in foam - they have a long lifetime and trap heat, enhancing the greenhouse effect - destroy the ozone layer do earth is no longer protected from the suns rays |
|
|
How does nitrous oxide contribute to climate change? |
- large scale burning of fossil fuels releases high levels of nitrous oxide ad fumes - it helps to destroy the ozone layer - ammonia in fertilisers leakes into rivers increasing growth of algae which then blocks sunlight killing the aquatic life.
|
|
|
How do volcanoes contribute to climate change? |
- release large amounts of CO2 and ash when they erupt - high level winds spread ash across the globe - ash forms a 'cloak' stopping solar radiation reaching earth - |
|
|
How do plate tectonics contribute to climate change? |
- cause continents to move further/closet to equator making them warmer/cooler - ocean currents carry heat around the world due to more land at higher latitudes - small stores of heat only neat small changed to create a large impact on earth |
|
|
How does atmospheric gas contribute to climate change? |
- greenhouse based trap infrared radiation to help keep earth warm - without greenhouse gased earth would be -18 degrees - some solar radiation is reflected back to space by atmospheric gases |
|
|
What 6 countries show an example of the negative effects of clknste change? |
Montana, USA The glacier national park was created in 1910 with 150 glaciers, now there's only 30. Its predicted they will all be gone in another 30 years. Colca region, PERU Villages have been abandoned because water supplies have dried up due to the lack of snow falling. KENYA Droughts now occur every 3 years instead of 10. UK More storms and floods will occur meaning the cost of flood damage will increase for buildings on flood plains. BANGLADESH Suffers from coastal flooding meaning if the sea level rises by 1m 17.5% of the land will be lost Wrangle island, RUSSIA Loss of sea ice meaning the polar bears in this nature reserve can't travel overland to catch their pray
|
|
|
What is an environmental refugee? |
Someone who's been forced to leave their home due to climate change |
|
|
What are some global agreements in response to climate change? |
- in June 1992 the UN held a meeting which resulted in the first environment treaty aiming to stabilise greenhouse gases - lead to Kyoto protocol in December 1997 signed by 181 countries - Came into force in February 2005 where each country agreed on a national emissions limit |
|
|
What are some actions of NGOs in response to climate change? |
- Greenpeace - campaigns focused on trying to make government produce sustainable energy - transport produced 22% of UK CO2 emissions so by adding taxes to flights or refusing to build airports, this amount would be reduced - from 2005 industry has been required to reduce its emissions or buy carbon credits from other countries |
|
|
How have local organisations responded to climate change? |
- 'live simply' is a group initiated by the Catholic church providing schools with the resources to teach children to think about their impact - many schools introduced energy efficient water and heating systems. - Woking CHP has cut carbon emissions and is helping those who havent - 15% UKs carbon emissions are from houses |
|
|
How are local interest groups responding to climate change? |
- 'Manchester is my planet' encourages individuals to reduce their carbon footprint - started in 2005, there's now over 20,000 people who have made a pledge to work towards a lower carbon future - the green badge parking permit allows people with low emission cars to park within Manchester in NCP car parks for 12 months using a GBPP with a 25% discount |
|
|
How is traffic in London being managed? |
What: the congestion charge fee means motorists who travel in the congestion charge zone (area with a high amount of traffic) have to pay. When: it was introduced to London on 17th February 2003 extending into west London on 19th February 2007. Where: currently operates in central and west London. Who: ken Livingston introduced the charge though TFL administers the charge, costing motorists £8 per day or a fine of £60-180. Why: it was needed to reduce congestion and raise money to improve things like public transport
|
|
|
What are the benefits and problems with London congestion charge? |
Benefits: - 12% reduction in pollution - money can be invested in public transport - 12% increase with bicycle journeys within the zone - increased number of people using public transport Problems : - bad for small businesses who use large cars to transport goods as they have a high fee to pay - increases amount of traffic in areas outside of the zone |
|
|
Causes of traffic congestion: |
1) Work zones (road works) If certain roads are closed it makes others busier or if part of a road is closed down to a single lane (bottle neck) the same amount of cars are in a smaller place making it busier. 2) Traffic accidents This could cause lanes to close making traffic busier 3) Special events in an area Lots of crowds in one place makes traffic 4) Bad weather In harsh conditions people are less likely to walk/cycle creating more traffic and in some instances trees can block roads |
|
|
What are problems with traffic congestion? |
1) Economic -Petrol is constantly being used whilst cars are sat in traffic -it costs to park in certain areas -its expensive to fund cycle lanes 2) Social/health - more cars means more crashes leading to an increased number of injuries -pollution is bad for health and too much cab contribute to problems such as asthma 3) Environmental - lots of pollution - habitats damaged ad new roads need to be built |
|
|
What are some solutions to traffic congestion ? |
-use more electric cars as they don't produce fumes -improve public transport e.g. build more cycle lanes or have buses run more frequently -have parking meters to stop people from parking -reduce speed limits to limit crashes to a minimum |
|
|
What countries demonstrate resource extraction of tropical rainforests and its management? |
CAMERON, Logging Large areas of rainforest are being cut down for wood . The roads built by logging companies for easy access to the forests are being used by illegal companies and for commercial hunting, leading to the deaths of gorillas and elephants to be sold at high prices. INDONESIA, Mining The Freeport mining company had been going since 1960, mining an area of 3.6 million hectares. 285,000 tonnes of waste is left in the river Aghawagon each day meaning the turtles and crocodiles are on the brink of extinction. BRAZIL, Mining A large variety of materials can be extracted from the Amazonian rainforest . The Carajus iron ore mining project uses wood to power its plant creating a loss of 6100km2 of deforestation annually . Also the mercury used for mining is highly toxic as 90% of the fish in the region around the river Tapajos are contaminated. |
|
|
What are the effects of resource extraction in the Amazon rainforest? |
South America, Ecuador Why: below the surface is crude oil and natural gas as well as the forest containing 201 bird species and 101 different animal species. Which: The oil is being extracted by maxus energy and Texaco have been extracting it since 1960 Who: Ecuador's economy is booming from this process, however inhabitants of tjr forest are at a high risk of developing cancer What: to manage it sustainably underground pipes are being built and the government forced Texaco to pay £40 million to 'clean up' their mess SEE Impacts: Social - conflict between companies and indigenous tribes Economic - 50% of Ecuador's revenue comes from oil Environmental - create air pollution, deforestation and created pollution from oil leakes |
|
|
What is the London congestion charge? |
A fee motorists in London pay in travelling in the 'congestion zone, running on automatic number plate recognition. Where: central London since 2003 and west London since 2007 Social impacts: there are 4000 less people entering the zone each day. Economic impacts: government gain money to improve public transport. Environmental impacts: reduces pollution making the air much healthier and safer for people living in that area. |
|
|
What is oxford street car? |
A company allowing people to hire cars for a certain period of time (30mins-6months) Where: oxford, but benefitting summertown, Jericho, city center and Cowley road as well. Social impacts: 250 people signed up to the scheme as people who drive less than 6,000 miles a year can save up to £3,500. Economic: Drivers pay a joining fee of £60 and £5+ per hour to hire the car Environmental: There's less cars on the road reducing traffic |
|
|
What is Cambridge park and ride? |
Its an organisation that provides direct travel in Cambridge town center by customers parking in one of the 5 sites and getting a bus. Social: one bus can accommodate 70 people which is more than a car Environmental: it only costs £2 per day Economic: there's less pollution from cars |
|
|
How are Marriott hotels sustainable? |
-use environmental action plans to help their properties achieve energy and water reduction goals -use low energy lightbulbs and recycled key cards -they are aiming to further reduce energy consumption by 20% in 2020 |
|
|
How are Nokia sustainable? |
-they were abkr to utilize 96% of their waste in 2013 -38% of the energy they use I'd renewable -they collect 388 tonnes of used mobile phones, batteries and accessories to be recycled. |
|
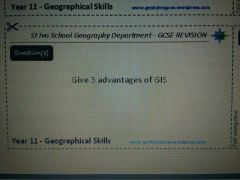
|

|
|
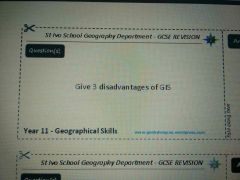
|

|
|
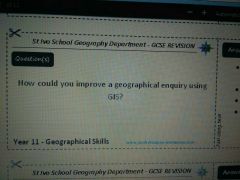
|
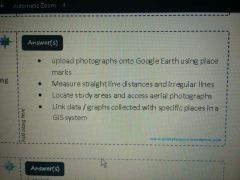
|
|
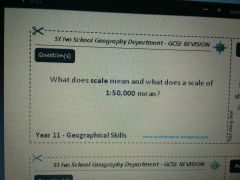
|
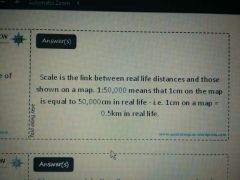
|
|
|

|
|
|
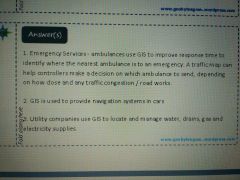
|
|
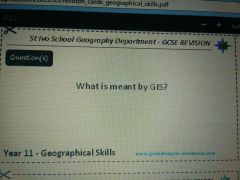
|
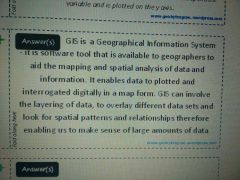
|
|
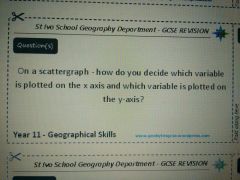
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

