![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The Uterus and the overies are |
The two main parts of the Female reproductive system |
|
|
|
The microbiota of the female genital tract varies with |
The pH and estrogen concentration of the mucosa which depends on age of the host. |
|
|
|
Lactobacilli |
The predominant organisms in the secretion of normal, healthy vaginas |
|
|
|
An infection of the uterus and its contents during pregnancy is known as |
Chorioamnionitis |
|
|
|
Nongoncocal uretthritis |
Is most commonly associated with C. trachomatis infection . Also, U urealyticum and M genitalia may also be isolated in the spacimen. |
|
|
|
A common sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium N.gonorrhoeae |
Gonorrhea |
Can be diagnosed directly by gram staining a simple from ureter discharge. Definitive diagnosis in females most include confirmation by cultures |
|
|
The two Female genital tract infections are |
Lower genital tract (vulva, vagina, and cervix) Upper genital tract ( Uterus, fallopian tube, overies and abdominal cavity). |
|
|
|
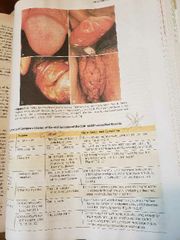
Clinical manifestation of lower genital tract infections is diverse and varied and may include |
Asymptomatic Dysuria Urethral discharge Lesion of the skin and mucus membranes |
|
|
|
Infections in male reproductive organ organs includes |
Epididymitis( inflammation of the epididymis) seen in sexually active men Prostatitis( caused both infectious and nonifectious means) |
|
|
|
Genital tract infections maybe classified as; |
Endogenous ( infections resulting from normal genital microbiota) Exogenous ( acquired as people engage in sexually activities. E.g. STDs) |
|
|
|
Laboratory diagnosis of genital tract infections |
Direct microscopic Examination Culture Nanculture method |
|

