![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
290 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Down syndrome symptoms
|
IQ < 70, microcephaly, generalized hypotonia, brachydactyly (short fingers and toes), single transverse palmar crease, sandal gap, increased risk of Alzheimer dz if get old enough
|
|
|
|
Epicanthal folds, Brushfield spots in iris, upsloping palpebral fissues, small round ear, midface hypoplasia, tongue protrusion
|

Facies in Down Syndrome
|
|
|
|
Genetic c/o Down Syndrome
|
Trisomy 21 or disomy 21 c translocation of 21 onto another chromosome leading to 3 copies of 21 (5%)
|
|
|
|
Risk factors for Down Syndrome
|
Maternal age > 35
|
|
|
|
Indications for chromosomal analysis
|
3 or more miscarriages in 1st trimester
Clinical phenotype consistent c known anomaly Multiple congenital anomalies Unexplained mental retardation Growth retardation/short stature in females Primary amenorrhea and infertility Ambiguous genetalia, cryptorchidism, hypogonadism Prenatal (advanced maternal age, abnl triple screen, ultrasound) Malignancies, chromosome breakage syndromes |
|
|
|
Most common type of nondisjunction in chromosomal anomalies
|
Meiosis I
Associated with advanced maternal age |
|
|
|
Heart defects in Down syndrome
|
AV canal defects
|
|
|
|
Recurrence risk of Down syndrome in 21;21 translocation
|
100%
|
|
|
|
Manifestations of Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18)
|
*overlapped fingers
*rocker bottom feet |
|
|
|
Coloboma
cat eye, or keyhole shape, in iris Assoc with Patau and others |
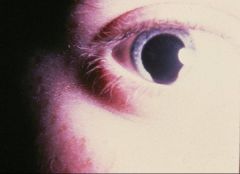
coloboma
|
|
|
|
What is nondisjunction
|
abberant segregation of homologous chromosomes into the same daughter cell
occurs in Meiosis I of oogenesis most often assoc c advanced maternal age |
|
|
|
Most common chromosomal abnormality in liveborns
|
Down syndrome
|
|
|
|
GI problems in Down syndrome
|
duodenal atresia (double bubble), Hirschprung disease, Celiac disease
|
|
|
|
Hematologic problems in Down syndrome
|
AML--> megakaryoblastic leukemia
|
|
|
|
Endocrine problems in Down syndrome
|
Hypothyroidism
|
|
|
|
M:F ratio in trisomy 18 (Edwards)
|
Females > males
|
|
|
|
What is recurrence risk for trisomy 18?
|
1%
|
|
|
|
GU problems in trisomy 18
|
cryptorchidism, renal anomalies
|
|
|
|
Heart problems in trisomy 18
|
VSD, valvular disease
|
|
|
|
What do trisomy 18 babies look like?
|
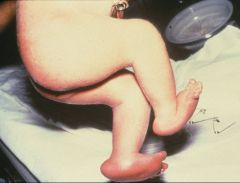
wasted, short sternum, overlapped fingers, rocker bottom feet, microcephaly, micropthalmia, low set malformed ears, micrognathia, small mouth, triangular face
|
|
|
|
CNS problems in trisomy 18
|
hypertonia, seizures, other CNS anomalies; severe mental retardation
|
|
|
|
trisomy 18, 13, and 21-cause?
|
advanced maternal age--> nondisjunction event in meiosis I of mother's egg
|
|
|
|
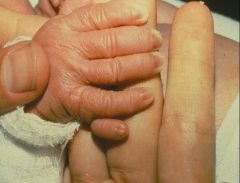
These are the overlapping fingers of trisomy 18.
You will also see rocker bottom feet and fetal wastage. |
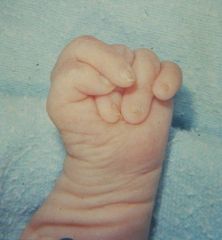
What does this picture represent? What other abnormalities will you see in such a child?
|
|
|
|
Stand-out features of trisomy 13
|
cleft lip/palate, hypertonia, small low set ears
holoprosencephaly c cleft lip scalp defects polydactyly iris coloboma malformed and low set ears |
|
|
|
Diagnosis of duplications: which is better, CMA (hybridization chromosomal micro array; aka aCGH) or FISH?
|
CMA is wayy better at detecting duplications...and deletions too!
|
|
|
|
CNS problems in trisomy 13
|
holoprosencephaly, MR
|
|
|
|
Heart problems in trisomy 13
|
VSD, ASD
|
|
|
|
Limb problems in trisomy 13
|
postaxial polydactyly
|
|
|
|
GU problems in trisomy 13
|
cryptorchidism, horse-shoe kidneys, double ureters
|
|
|
|
Sex chromosome disorder that is caused by paternal origin in 70% of cases
|
Turner syndrome: 45,X
Due to loss of either the paternal X or Y Not associated with advanced maternal age |
|
|
|
only chromosomal aneuploidy NOT associated with advanced maternal age
|
Turner syndrome
|
|
|
|
Manifestations of Turner syndrome
|
web neck/cystic hygroma
edema of hands and feet in infancy cubitus valgus wide set nipples and shield-like chest short metacarpals short stature protruding ears pigmented nevi after "puberty" |
|
|
|
GU problems in Turner syndrome
|
horseshoe kidneys, streak gonads (must be removed if contain Y chromosome)
|
|
|
|
Heart defects in Turner syndrome
|
Coarctation of the aorta
|
|
|
|
Endocrine problems in Turner syndrome
|
hypothyroidism; Hashimoto thyroiditis
|
|
|
|
Mosaic Turner syndrome genotype
|
45,X/46,XX (15%)
|
|
|
|
Mandelung deformity
|
associated with Turner syndrome
|
|
|
|
Parental origin of Klinefelter syndrome
|
50% maternal origin (assoc c advanced maternal age), 50% paternal
|
|
|
|
Appearance of pts c Klinefelter syndrome
|
eunuchoid
gynecomastia after puberty very tall IQ 10-15 points lower infertility, small penis, small testes |
|
|
|
Genotype of Klinefelter
|
47, XXY
|
|
|
|
Deletion in Cri du chat
|
5p deletion (terminal portion)
|
|
|
|
Recurrence risk of Cri-du-chat
|
very unlikely unless due to an inherited translocation
|
|
|
|
Features of cri-du-chat
|
growth deficiency, microcephaly, hypertelorism (wide-set eyes), large low-set ears, short metacarpals and clinodactyly (bent 4th finger), cat cry at birth
|
|
|
|
Frequent cause of microdeletion/duplication syndrome
|
recombination btwn non-allelic low copy repeat (LCR) sequences
|
|
|
|
Frequency of duplications versus deletions
|
about equal
|
|
|
|
FISH vs array CGH
|
array CGH is much better at detecting duplications/deletions than FISH
|
|
|
|
Picture of kid with triangular facies, periorbital fullness, full lips, long philtrum
|
Williams syndrome
|
|
|
|
Cardio problems in Williams syndrome
|
Elastin arteriopathy-->
supravalvular aortic stenosis diffuse aortic hypoplasia SIDS renal artery stenosis |
|
|
|
What is a contiguous gene syndrome
|
Syndrome caused by microdeletion that spans two or more genes tandemly positioned along a chromosome. Microdeletion is often too small to be visualized using conventional cytogenetic techniques; detection often requires FISH.
Result from subtle or submicroscopic deletions and duplications that alter nl gene dosage |
|
|
|
GU problems in Williams syndrome
|
hypercalcemia/hypercalciuria
sx: irritability, vomiting, constipation, muscle cramps renal anomalies nephrocalcinosis due to hypercalciuria |
|
|
|
Genotype of Williams syndrome
|
microdeletion in 7q11.23
|
|
|
|
Behavior in Williams syndrome
|
Overfriendliness, generalized anxiety, attention deficit syndrome
|
|
|
|
Language vs drawing in Williams syndrome
|
Language is MUCH better developed than visuo-spatial skills
Can't draw elephants Can describe an elephant very well Can name more animals than nl kids of matched age, IQ, sex |
|
|
|
How can deletion be passed on?
|
Microdeletion can be passed on in autosomal dominant fashion (mother with Williams--> child with Williams)
|
|
|
|
Detection of Williams syndrome
|
FISH for elastin gene
|
|
|
|
Manifestations of duplication 7q11.23
|
developmental delay (esp speech)
some dysmorphic features (mild and variable) autistic spectrum behaviors aggression self-injury |
|
|
|
Definition of genomic imprinting
|
Epigenetic phenomenon in which the activity of a gene is reversibly modified depending on sex of parent that transmits the gene.
Leads to unequal fxn of inherited copies from parents. |
|
|
|
Examples of diseases dependent on genomic imprinting.
|
Prader-Willi and Angelman are both problems with the same chromosome but from different sex parent.
|
|
|
|
Deletions of 15q11-q13
|
Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome
|
|
|
|
Mnemonic for chromosome deletion in Prader-Willi and Angelman syndrome
|
deletion 15q11-13
Prader...Willi...Angelman 5 10 15 Count in fives...until you get to 15. Then you are probably ok. Alternatively, Prader-Willi is too much mom's 15q11-13 and not enough dad. Sarah says sometimes that her mom is evil like Dolores Umbridge. The kids with this disease look like Dolores Umbridge (hyperphagia and obesity at 2 yrs, MR, obsessive-compulsive,short stature, small hands and feet). Dolores Umbridge appears in the 5th Harry Potter book, in which the main characters are all 15. Sorry, where was I? |
|
|
|
Which is due to a loss of paternal 15q11-q13
|
Prader-Willi
P = Prader = loss of Paternal |
|
|
|
Which is due to a loss of maternal 15q11-q13
|
Angelman
|
|
|
|
Other ways to get Prader-Willi syndrome
|
Uniparental disomy of the mother (due to a maternal nondisjunction due to advanced maternal age) (2-5%)
Imprinting center paternal mutations (2-5%) |
|
|
|
Other ways to get Angelman syndrome
|
Uniparental disomy of the father due to paternal nondisjunction (2-5%)
UBE3A gene mutations--> loss of function of ubiquitin protein ligase A (5%) [must be from MOTHER to get dz] Imprinting center maternal mutations (2-5%) |
|
|
|
Hypotonia and feeding difficulties in infancy
Deletion 15q11-q13 |
Prader-Willi syndrome
|
|
|
|
GU problems in Prader Willi
|
Cryptorchidism
|
|
|
|
Generalized obesity c hyperphagia
small hands and feet mental retardation obsessive-compulsive behavior dysmorphic features: almond-shaped eyes |
Adult Prader-Willi patients
|
|
|
|
Detection of PWS
|
can use FISH...or aCGH I suppose
|
|
|
|
MR in PWS vs in Angelman
|
worse MR in Angelman
|
|
|
|
Angelman syndrome features
|
Weird head (microcephaly, brachycephaly) but nl head circumference at birth
Severe MR (IQ<40) Seizures, abnl EEG's Midface retrusion (back too far) Prognathism (jaw in or out) Wide spaced teeth Drooling Macrostomia (huge mouth) No speech |
|
|
|
Gait in Angelman syndrome
|
Ataxia, wide based gait with upheld arms, poor coordination, tremors
|
|
|
|
Another hallmark symptom of Angelman syndrome
|
unprovoked bursts of laughter
|
|
|
|
Picture of Angelman syndrome
|
Girl with bowling ball and bent knee, Girl with protruding jaw
|
|
|
|
Picture of obese lady
|
Prader-Willi syndrome (obesity)
|
|
|
|
Kid on bed having his leg moved
|
Prader-Willi syndrome (hypotonia)
|
|
|
|
Another picture of Angelman syndrome
|
Kid with open mouth (macrostomia) and hands up against chest like a tyrannosaurus rex (flexion of arms)
|
|
|
|
Which is more common, PWS or Angelman
|
PWS is more common. In fact there was a CSI episode a while back with a PWS guy in a hot dog eating contest...so I hear...
|
|
|
|
So whose fault is Angelman with the UBE3A gene deletion?
|
I guess it's the mom's fault--her UBE3A gene is deleted/mutated on that chromosome, so the kid only gets the paternal version, which is inactivated or something. Inheritance is complex.
|
|
|
|
Detection of PWS and Angelman
|
CMA detects the deletion in 70% of cases (aCGH)
|
|
|
|
Father has the deletion in UBE3A gene; he passes it on to his kids. What happens to them?
|
The paternal copy of UBE3A is switched off, anyway, so it doesn't matter in his kids. However, his female children will be carriers of a deletion of UBE3A, which they will pass on to 50% of their kids. Whenever one of their kids gets the mutated and (in the gametes) reactivated version of chromosome 15, they will manifest with Angelman.
|
|
|
|
Mnemonic for Angelman
|
UBE an Angel (UBE3A). Prader-Willi is Paternal loss, so Angelman is maternal loss.
|
|
|
|
Del 5p
|
Cri-duchat.
|
|
|
|
How big is the Cri-du-chat syndrome deletion
|
10-12 megabases of DNA
|
|
|
|
del 7q11.23
|
Williams syndrome
|
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance of Williams syndrome
|
Autosomal dominant
|
|
|
|
Loss of function mutation in 22q11.2
|
DiGeorge/Velocardiofacial syndrome
Detect with FISH/CMA |
|
|
|
Common simple causes of autism
|
7q11.23 duplication (vs deletion in Williams)
Fragile X syndrome |
|
|
|
Disorders with complex inheritance
|
Autism, schizophrenia, other psychiatric conditions
DM 1 and 2 Cardiovascular dz Hyperlipidemia Cancer Neural Tube defects Cleft lip/cleft palate Rxns to or metabolism of pharmacological agents (warfarin, for example) Response to infectious disease |
|
|
|
Are there any monogenic forms of diseases that are usually associated with complex inheritance?
|
Yes, all of the disorders mentioned on the previous card have monogenic forms as well (MODY--> type II DM; fragile X/dup 7q --> autism; trisomy 13--> cleft lip/palate)
|
|
|
|
Disorders affected by copy number variation (CNV)
|
Complex traits; hae more copies, more likely to get the disease.
Alzheimer Dz: APP gene Parkinson Dz: SNCA gene HIV susceptibility: CCL3L1 gene Lupus glomerulonephritis: FCGR3B gene Crohn dz: HBD-2 gene Pancreatitis: PRSS1 gene |
|
|
|
Define:
Polygenic Oligogenic Multifactorial |
Disorders that are not due to single genes.
These disorders are not inherited in the simple Mendelian fashion. |
|
|
|
Familial aggregation:
Definition? How is it measured? |
Relatives are more likely to be affected/have similar trait due to shared alleles.
Affected individuals tend to cluster in families. This may be due to shared alleles and/or shared environment. Measured by comparing prevalence in relatives vs. population. |
|
|
|
Concordant phenotypes
|
Shared alleles --> shared phenotype
|
|
|
|
Define:
Non-genetic factors |
Shared alleles does NOT always equate with a shared condition.
|
|
|
|
Discordant phenotypes
|
Shared alleles but NOT shared phenotype
|
|
|
|
Qualitative traits
|
The trait is either PRESENT or ABSENT. (Yes or No)
EX: Schizophrenia vs. not schizophrenia, achondroplasia vs. not achondroplasia, type I diabetes, multiple sclerosis |
|
|
|
Quantitative traits
|
The features of the trait fall along a CONTINUUM and are usually PHYSIOLOGICAL. (Degrees)
EX: Blood pressure, height (including among ppl with achondroplasia), BMI, cholesterol levels |
|
|
|
Alleles 1st degree relatives have in common
|
1/2
|
|
|
|
Alleles monozygotic twins have in common
|
100%
|
|
|
|
Alleles 2nd degree relatives have in common
|
1/4
|
|
|
|
Alleles 3rd degree relatives have in common
|
1/8
|
|
|
|
Trisomy 18
|
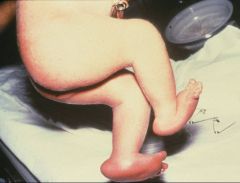
What is this syndrome
|
wasted, short sternum, overlapped fingers, rocker bottom feet, microcephaly, micropthalmia, low set malformed ears, micrognathia, small mouth, triangular face
|
|
|
wasted, short sternum, overlapped fingers, rocker bottom feet, microcephaly, micropthalmia, low set malformed ears, micrognathia, small mouth, triangular face
|
Trisomy 18
|
|
|
|
Trisomy 13
|
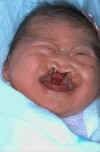
What is this syndrome?
|
Holoprosencephaly
|
|
|
Trisomy 13
|
What syndrome is this?
|
More holoprosencephaly and cleft lip
|
|
|
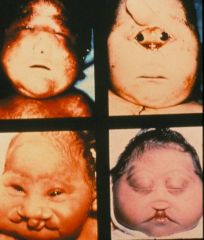
Trisomy 13; scalp deformities are common
|
What syndrome is this?
|
|
|
|
Trisomy 13; this is polydactyly
|
What syndrome is this?
|
|
|
|
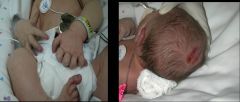
Turner syndrome: 45,X. Note the webbed neck, horseshoe kidneys, and edema of hands and feet.
The heart malformation associated with this disease is coarctation of the aorta. |
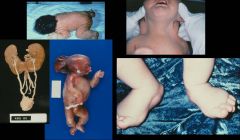
What disorder is this? What is the heart malformation associated with this disease?
|
|
|
|
Trisomy 18, Edward's syndrome.
Heart defects: VSD and polyvalvular heart disease. The baby is most likely female because the ratio of liveborns is 1:4 M:F Recurrrence risk is 1%, as with the other trisomies (as long as it's not a translocation) |

What does this baby have?
What heart defects are associated with this disorder? What sex is this baby, most likely? What is the recurrence risk of this disorder? |
|
|
|
duplication of 7q11.23
|
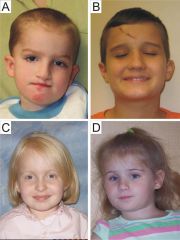
What genetic abnormality do these autistic kids share?
|
it's the opposite of Williams syndrome
|
|
|
Williams syndrome.
Deletion of 7q11.23 He's very outgoing and has a huge vocabulary vs his peers. He has terrible visuo-spatial ability, however. The elastin gene is lost. |

What does this youngster have?
What's the chromosomal abnormality? What are the developmental features? What gene is lost? |
|
|
|
Angelman syndrome.
MATERNAL deficiency of 15q11-q13 OR MATERNAL deletion of UBE3A gene (mom could have inherited it from her dad) |

What does this girl have?
What is the genotype? |
|
|
|
Prader-Willi syndrome
PATERNAL deficiency 15q11-q13 If you could see his eyes, they would be almond shaped. If you could see his testes, they would be undescended. |
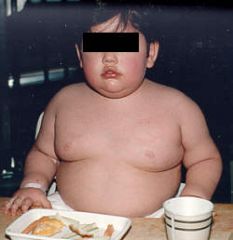
What does this strapping young fellow have?
What's the genotype? If you could see his eyes, what would they look like? If you could see his testes, what would they look like? |
|
|
|
Copy number variant
|
the number of copies of a particular gene
|
|
|
|
Period of time with low teratogenicity
|
1-2 weeks, because not in contact with maternal circulation and because of limitied differentiation of cells
|
|
|
|
Mechanical/Physical agents that can cause birth defects
|
uterine compression (from bicornate uterus or uterine fibroids) Heat (from sauna, hot tub, infection) radiation
|
|
|
|
Palpebral fissure
|
serpation between lower and upper eyelid
|
|
|
|
Philtrum
|
groove between nose and upper lip
|
|
|
|
Use of Diethylstillbestrol
|
synthetic estrogen used to help women with recurrent abortions, caused vaginal adenosis -> birth defects
|
|
|
|
Current uses of thalidomide
|
HIV, multiple myeloma, crohn's, leprosy
|
|
|
|
Rubella
|
during primary infection during first trimester, often asymptomatic infection
|
|
|
|
Down syndrome
|
IQ <70, generalized hypotonia, brachydactyly (short fingers and otes, single transverse palmar crease, sandal gap deformity of feet
|
|
|
|
DiGeorge
|
wide spectrum of presentation: partial or complete thymus absence, parathyroid hypoplasia, mild mental deficiency
|
|
|
|
Velocardiofacial syndrome
|
feeding difficulties, mild mental retardation, psychiatric illness
|
|
|
|
Williams
|
mild mental retardation, histology: disorganized elastin in arterial wall, hypercalcemia (irritability, constipation, muscle cramps, nephrocalcinosis and stones), overlyfreindly, generalized anxiety,
|
|
|
|
Duplication of 7q11.23 Syndrome
|
developmental delay, especially speech delay, mild and variable dysmorphic features, autistic spectrum behaviors
|
|
|
|
Smith Magenis
|
|
|
|
|
Potocki-Shaffer
|
|
|
|
|
Prader Willi
|
birth: severe hypotonia, poor feeding, cryptorchordism, by age 3: voracious appetitie and increased weight gain, short stature, small hands and feet, obsessive compulsive behavior
|
|
|
|
Angelman
|
severe mental retardation, seizures, abnromal EEG's, lack of speech, unprovoked burst of laughter, ataxia with wide based gate, flexed arms
|
|
|
|
Fragile X Tremor and Ataxia Syndrome
|
intention tremor and ataxia, hypotonia, developmental delay, mental retardation, peripheral neuropathy, proximal weakness, autistic features, hyperactivity, macrochordism (large testicles develop in adults), usually males but can be females (will have more significant family history), pathology: abnormal dendritic spine morphology
|
|
|
|
Premutation
|
not associated with mental retardation, females have premature ovarian failure
|
|
|
|
Huntington Disease
|
most present in midlife but age of onset depends on number of triplet repeats, early: subtle changes in coordination, minor involuntary movements, difficulty in planning, depressed or irritable, able to continue to function, mid stage: chorea more prominent, worsening dysarthria and dysphagia, some degree of personal independence, outburst of aggressive behaviors and social disinhibition ; late stages: behavior problems are lessened, motor disability become severe, extreme cognitive impairment, mute and incontinent
|
|
|
|
Juvenile Huntington Disease
|
onset of symptoms before age 21: frequent falls, clumsiness, hyperreflexia, oral motor dysfunction, rigidity, motor and cerebellar symptoms but no chorea, seizures,
|
|
|
|
Trisomy 18
|
more affected females, growth deficiency, short sternum, overlapped fingers, rocker bottom feet, cryptorchordism, renal anomalies, <10% last more than 1 yr, small and wasted, scissoring of lwer extremities, hypertonia, microcephaly, heart defects, clenched hand, abdominal wall defects
|
|
|
|
Trisomy 13
|
up flexion of arms (hypertonia), mental retardation, scalp defects, only 15% survive first year, postaxial polydactyly, cryptorchidism, horse-shoe kidneys, double ureters, cystic kidneys, heart defects, holoprosencephaly
|
|
|
|
Turner Syndrome
|
99% result in first trimester miscarriages, short stature, short metacarpals, scoliosis, short wide webbed neck, low posterior hairline, dysfunctional lymphatic development: edema of the hands and feet and cystic fibromas, nail dysplasia, pigmented nevi as they get older, horseshoe kidney, increased carrying angle of arms, streak gonads, infertility, hypogenitalism, hypoplastic uterus, hypothyroidism
|
|
|
|
Klinefelter Syndrome
|
tall, slim, eunochoid appearance, tendency to obesity, testicular atrophy after puberty wth hyalinization and fibrosis of seminerferous tubules from excess of gonadotropins, gynecomastia, small penis, inadequate testosterone production, dull mentation
|
|
|
|
Cri du Chat
|
high pitch cry first 2 weeks from abnormal pharyngeal structure (cat cry), severe mental retardation, hypotonia -> hypertonia, short metacarpals
|
|
|
|
Neural tube defects
|
involves any region of the neural tube, lower limb deformities and incontinence
|
|
|
|
Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)
|
clinical picture that of DM2 but occurs at any age, may not be overweight, non-ketotic onset <50 yo, no diabetes antibodies
|
|
|
|
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
|
high LDL's, deposition of LDL in tendons and skin (xanthomas) and in arteries (atheromas), LDL: heterozygote: 250, homozygote: 700, arcus corneae
|
|
|
|
Alkaptonuria
|
accumulation of pigment in the sclera from , ear wax turns red or black, urine exposed to air becomes dark, progressive arthritis
|
|
|
|
Phenylketonuria
|
untreated: developmental delay ; irritability, vomiting, rash, musty odor (from accumulation of phenylketones), lighter pigmentation (melanin is biproduct of tyrosine metabolism) ; microcephaly, severe to profound mental retardation
|
|
|
|
In utero maternal PKU
|
mother with PKU, microcephaly, dysmorphic features, mental retardation
|
|
|
|
Urea cycle disorders
|
present in neonatal period with elevated ammonia and catastrophic illness (except arginase I deficiency which is milder), diagnostic serum amino acids:
|
|
|
|
Ornithine Transcarbamoylase deficiency
|
homozygote: low citrulline, high glutamine, elevated urine orotic acid, heterozygote: protein avoidance, vomiting, cognitive delay, presentation depends on diet and pattern of X inactivation
|
|
|
|
Arginase I deficiency
|
milder presentation, look like cerebral palsy (hard time walking)
|
|
|
|
Tay Sachs Disease
|
progressive neurological deterioration: loss of motor skills, decreased attention, increased startle, muscular hypotonia, decreased deep tendon reflexes -> seizures, blindness, spacticity ; cherry red spot surrounded by pale clearing in fovea ; lipid laden ganglion cells
|
|
|
|
Gaucher disease
|
different sub-types change course and presentation of disease, hepatosplenomegaly, pancytopenia, perinatal and cardiovascular forms also exist, foamy histiocytes, enlarged cells in the spleen
|
|
|
|
type I
|
affects young adults, no nervous system problems, varies from mild to severe, bone marrow problems, anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, infiltrates in lungs
|
|
|
|
type II
|
affects infants; early nervous sytem problems, die in infancy
|
|
|
|
type III
|
affects children-young adults, late onset nervous system problems, becomes severe
|
|
|
|
Alzheimer's disease
|
progressive cognitive and functinal decline, memory impairment, disorientation, language disorders, loss of executive function, agitation, apathy, hallucinations, gross: widened sulci from atrophy (especially pre-frontal lobes)(hydrocephalus ex vacuo), Microscopic: neurofibrillary tangle, neuritic plaque
onset in 40s or early 50s, associated with seizures, myoclonus and language deficits, wider range of age of onset early onset alzheimer's diseaes with cerebral amyloid angiopathy |
|
|
|
Spinal bulbar muscular atrophy--what's the genetic problem?
|
nucleotide repeat in androgen receptor
|
|
|
|
Myotonic Dystrophy
|
multisystem disorder: skeletal and smooth muscle, eye, heart, endocrine (testicular failure) and CNS , percussion myotonia (percuss thenar eminence)
|
|
|
|
mild myotonic dystrophy
|
cataract and mild myotonia, normal life span, insulin resistance
|
|
|
|
classic myotonic dystrophy
|
onset in teen to adult, muscle weakness and wasting, myotonia (can't release when tonic), cataract, cardiac conduction abnormalities, gynecomastia
|
|
|
|
congenital myotonic dystrophy
|
present in prenatal period and at birth: polyhydramnios from no swallowing, severe generalized weakness at birth, respiratory insufficiency,
|
|
|
|
Osteogenesis Imperfecta: what's the genetic problem?
|
commonly affects the Gly-XY region of COL1A1 (critical for collagen shape)
|
|
|
|
Manifestations of OI type I
|
little deformity at birth (maybe a couple of fractures) mild form, normal stature, lots of fractures, little or no bone deformity, blue sclera, fractures common during labor, fish shaped vertebrae (biconcave) , steady rate of fractures throughout childhood and then decreases after puberty then increase again after menopause or >60 yo men
|
|
|
|
Manifestations of OI type II
|
lethal in neonatal period, very little calvarial mineralization, beaded ribs, compressed and bowed legs, platyspondyly (flattened vertebrae), tons of fractures in utero, accordian bones from many fractures, very small thoracic cavity, usualy die within hours of birth
|
|
|
|
type III
|
moderate deformity at brith, dentinogenesis imperfecta, hearing loss, very short stature in adulthood, can survive with proper care
|
|
|
|
type IV
|
normal sclerae, mild to moderate bone deformity, variable short stature, dentinogenesis imperfecta, hearing loss
|
|
|
|
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
|
skin fragility, skin hyperextensibility, joint hypermobility, easy bruising, cigarette paper scars
|
|
|
|
type I
|
classical presentation of ehlers-danlos, velvety skin
|
|
|
|
type II
|
similar to but less severe than type I
|
|
|
|
type IV
|
vascular or ecchymotic type, thin translucent skin with prominent venous pattern, abnormal scarring, minimal joint hypermotility
|
|
|
|
Marfan Syndrome
|
tall stature, arm span longer than height, arachnodactyly (long wiry fingers), scoliosis, pes planus (flat feet), genu recurvatum (hyperextension of the knee), ligament and tendon dysfunction, pectus excavatum, ectopia lentis (upward subluxation of the lens)
|
|
|
|
Achondroplasia
|
Macrocephaly, frontal bossing, lordosis, trident hands, rhizomelic shortening (proximal section short), may have extra space around the brain from normal brain with large skull
|
|
|
|
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
|
similar to homozygous achondroplasia, severe agenesis of the thorax
|
|
|
|
type I
|
|
|
|
|
type II
|
|
|
|
|
Costello Syndrome
|
mental retardation,
|
|
|
|
Retinoblastoma
|
abnormal light reflection in pupils, bilateral tumors in family history, unilateral when sporadic
|
|
|
|
Li Fraumeni Syndrome
|
|
|
|
|
Cowden's disease
|
macrocephaly
|
|
|
|
Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndromes
|
early onset (risk begins at 25) and often bilateral
|
|
|
|
BRCA 1
|
|
|
|
|
BRCA 2
|
|
|
|
|
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
|
>100 colorectal adenomatous polyps, polyps appear around 16 yo, avg age at diagnosis is 39 yo, extracolonic manifestations: epidermoid cysts odontogenic cysts(especially on the jaw and skull), hyperpigmented retina from hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium, desmoid cysts,
|
|
|
|
Heridatry Non-polyposis colon cancer (Lynch Syndrome)
|
risk of colon cancer without polyposis
|
|
|
|
Xeroderma Pigmentosum
|
1 yo: easy sunburn, photophobia, freckling -> wrinkling, solar keratoses, telangectasias ; some have neurologic phenotype: sensorineural deafness, ataxia, demyelination
|
|
|
|
Von Hippel Lindau
|
brain retinal and renal tumors
|
|
|
|
Neurofibromatosis I
|
Derm: 6 Café au lait spots >5 mm (macules color of coffee and milk, visible by 12 mo's), cutaneous neurofibromas (small, button holed onto skin, increase in pregnancy, not associated with malignancy) , axillary or inguinal freckling, , 2 or more Lisch nodules (pigmented nodules on the iris, 90% have by 16),
|
|
|
|
|
Tumors: plexiform neurofibroma (tumors that invade and extend through muscle bone and nerve causing distortion and involvment and lymphedema of entire limb distal to lesion, major cause of deformity and morbidity, present at birth but may not be symptomatic until later, Cafe au lait spots often overlay, risk of transformation to peripheral nerve sheath tumor), 2 or more peripheral neurofibromas, optic pathway tumors (1/3 have visual compromise, typically present in first 3 yrs of life) at risk for other CNS tumors
|
|
|
|
|
Bone: pseudoarthrosis (false joint in the mid tibia that won't heal) , scoliosis
|
|
|
|
|
Neuro: 50% have severe learning disabilities, 50% have normal intelligence, don't have severe mental retardation
|
|
|
|
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
|
Hypomelanotic macules (ash leaf spots), angiofibromas of the face (looks like acne, in children), forehead plaque, cardiac rhabdomyomas in utero that can cause obstruction and regress after birth, retinal hamartomas, angiofibromas of the eyelids, ungal fibromas (teens or adulthood), renal angiomyolipomas (only rarely impede renal function)
|
|
|
|
|
CNS: cortical tubers, early calcification of the falx, subependymal nodules progressing to subependymal giant cell astrocytomas, frank mental retardation is common, seizures (usually present when infant), autism
|
|
|
|
Charcot-Marie-Tooth
|
heterogenous disorders leading to chronic motor and sensory polyneuropathy: motor: distal muscle weakness and atrophy ; sensory: mild to moderate loss, depressed deep tendon reflexes, high arched feet, carpal tunnel syndrome
|
|
|
|
type 1A
|
70-80% of all CMT
|
|
|
|
HNPP (Hereditary Neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies)
|
more mild phenotype than CMT1A, presents after trauma or stress
|
|
|
|
Duchenne Muscular dystrophy
|
mild mental retardation, progressive symmetric muscle weakness with proximal greater than distal, gower sign, hypotonia, hyporeflexia, pseudohypertrophy (especially of the calves), elevated CPK, wingd scapula, sway back, symptoms present before age 5, may be associated with intellectual impairment if nearby brain dystrophin isoform is also mutated
|
|
|
|
Becker Muscular Dystrophy
|
progressive symmetrical muscle weakness and atrophy with proximal greater than distal and calf hypertrophy, weakness in quads may be the only sign, activity induced cramping, flexion contractures of the elbows, later onset than DMD, preservation of neck flexor strenght (different from DMD)
|
|
|
|
Duchenne Muscular dystrophy- related dilated cardiomyopathy
|
rapidly progressive heart failure in teenage years, death from heart failure 1-2 yrs after diagnosis, heterozygote females present later in life and with slower progression, subclinical skeletal muscle disease
|
|
|
|
Rett Syndrome
|
progressive neurological disorder only in girls (lethal to males), normal birth and early development then begin to miss milestones, loss of purposeful hand movement, characteristic hand posture and movements, acquired microcephaly, dystonia, spacticity, seizures, panic like attacks, GI dysmotility and gallbladder dysfunction, EKG abnormalities,
|
|
|
|
Spinal Muscular Atrophy
|
symmetric and proximal muscle weakness and atrophy
|
|
|
|
type I werdnig hoffman
|
progressive, onset in first 6 mo's, hypotonia and muscle weakness, never sits without support, facial weakness, fasciculations of the tongue, involvement of the diaphragm late, normal cerebral function
|
|
|
|
Galactosemia
|
inability to metabolize galactose
|
|
|
|
Homocysteinuria
|
marfanoid habitus, mental retardation and CV diseases: stroke
|
|
|
|
Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency
|
immunodeficiency
|
|
|
|
Hurler Syndrome
|
reduced size of liver, spleen, heart, corneal clouding, full lips, progressive joint rigidity
|
|
|
|
Krabbe Disease
|
infants with spacticity and diffuse sclerosis of brain, decreased white matter, globoid cells (phagocytes storing glactocerebroside)
|
|
|
|
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
|
46XX: ambiguous genitalia, ovaries and mullerian structures present, or may have without ambiguous genitalia but have life threatening aldosterone/cortisol deficiency
|
|
|
|
21-Hydroxylase Deficiency
|
most common form, deficient in cortisol and aldosterone, 17-hydroxyprogesterone accumulates in the blood, 46XX: amiguous genitalia -> hirsutism and clitoromegaly ; may have normal female genitalia but still have life threatening aldosterone/cortisol deficiency ; 46XY: appear as males but with precocious puberty and hyperpigmentation of genital skin ; both can have acute adrenal crisis ; may manifest as vomiting and failure to thrive
|
|
|
|
17-alpha hydroxlase deficiency
|
no sex steroid production, feminization of XY
|
|
|
|
Complete Androgen Insensitivity
|
XY female presents with primary amenorrhea or inguinal mass (testis), no mullerian structures, no pubic hair, breast development, blind ending vagina, estrogen higher than normal, elevated LH
|
|
|
|
Partial Androgen Insentivity
|
range from infertile male to incomplete testicular feminization, higher estrogen, normal male testosterone, elevated LH, may have hypospadius or cryptorchordism
|
|
|
|
Reifstein Syndrome
|
perineoscrotal hyposadias, normal axillary and pubic hair, scant beard and body hair, breast enlargement at puberty, testes often cryptorchoid
|
|
|
|
5-alpha reductase deficiency
|
ambiguous genitalia, testes present, female appearing XY before puberty -> virilization of female at puberty (very similar to androgen insensitivity except virilize at puberty) ; XX are normal
|
|
|
|
Gonadal Dysgenesis
|
ambiguous genitalia (incomplete differentiation fo the gonad), dysmorphic body/facies, organ involvement, 46XX or XY
|
|
|
|
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
|
genital anomalies in males, defect in cholesterol biosynthesis, multiple congential anomalies: Y shaped 2,3 syndactyly, cleft palate, congenital heart defects, accumulation of 7 dehydroxycholesterol
|
|
|
|
Camptomelic Dysplasia
|
skeletal dysplasia: bent looking bons, short limgs bowing of the femurs and tibias, extraskeletal: cleft palate, congenital heart defects, CNS anomalies, usually lethal
|
|
|
|
Leptin receptor mutations
|
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism -> delayed puberty, irregular menses in 3rd or 4th decades, increased respiratory infections, normal leptin levels
|
|
|
|
Leptin deficiency
|
more severe form of obesity and excess eating than leptin receptor mutations
|
|
|
|
Primary Dopamine responsive dystonia (DYT5a)
|
dystonia and psychiatric disorders, diurnal variation in symptoms
|
|
|
|
Alport Syndrome
|
kidney dysfunction and hearing loss, no proteinuria
|
|
|
|
Pierson's
|
die quickly around birth, severe proteinuria
|
|
|
|
Steroid resistant congenital nephrotic syndrome
|
|
|
|
|
Congenital nephrotic syndrome of the finnish type
|
severe proteinuria, low birth weight, prematurity, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, abdominal distention, edema
|
|
|
|
Limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2a
|
proximal symmetric muscular dystrophy, present in teens to middle age, males progress faster, elevated creatine kinase
|
|
|
|
Malignant Hypethermia Susceptibility
|
acidosis , hypercapnia, tachycardia, hypoxemia, rhabdomyolysis, hyperkalemia (cardiac arrythmias), myoglobinuria (risk of renal failure)
|
|
|
|
Aminoglycoside Ototoxicity
|
hearing loss, vestibular damage leading to oscillopsia (when head is moving object blur, like when driving)
|
|
|
|
Thiopurine methyl transferase deficiency
|
severe myelosuppression with azathioprine or 6-Mercaptopurine administration for leukemia, inflammatory bowel disease or severe eczema
|
|
|
|
Non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss
|
|
|
|
|
DFNA
|
|
|
|
|
DFNB
|
|
|
|
|
DFNB1
|
mild to profound sensorineural hearing impairment
|
|
|
|
DFN3
|
|
|
|
|
Syndromic sensorineural hearing loss
|
|
|
|
|
Usher syndrome
|
retinitis pigmentosa: progressive loss of rods from the periphery to the center of vision
|
|
|
|
Pendred syndrome
|
thyroid problems and malformations of the turns of the cochlea
|
|
|
|
Jervell and Lange-Neilsen syndrome
|
prolonged QT with risk of sudden cardiac death with hearing loss, may only have history of cardiac disease, heterozygotes may have long QT but won't have the hearing loss
|
|
|
|
Waardenburg
|
pigmentary abnormalities, variable degrees of sensorineural hearing loss
|
|
|
|
type I and II
|
pigmentary abnormalities of the iris, complete or partial heterochromia of the eys with brilliant blue irides, frontal tuft of hair hypopigmented, dystopia canthorum (wide spaces between the canthi of the eyes), may also have medial eyebrow flare, synophyrs (unibrow) and congenital leucoderma (white patches)
|
|
|
|
Brachio-Oto-Renal syndrome
|
branchilal cleft abnormalities (preauricular pits, cervical sinuses, bifid uvula, malformed pinnae, cochlear malformation) and renal disease
|
|
|
|
Treacher collins
|
hypoplasia of the zygomatic arch
|
|
|
|
Stickler
|
myopia and arthritis with hearing loss, micrognathia (small mandible and cleft palate
|
|
|
|
X-linked ocular albiniism
|
wil have the typical features of ocular albinism and may have Kallman's syndrome in addition to X-linked albinism if contiguous genes involved
|
|
|
|
Oculocutaneous albinism
|
ocular albinism also with loss of melanin in the skin and hair
|
|
|
|
How to study a disease in which there is familial aggregation?
|
Calculate relative risk ratio:
λr = (prevalence of trait in a relative of affected person)/(population prevalence of trait or condition) |
|
|
|
What is the significance of a much larger λr in monozygotic twins vs siblings?
|
The disease must have a very large genetic component.
|
|
|
|
Use of twin studies
|
To tell if something is more genetic than environmental (you still have the environment problem in most cases, though)
|
|
|
|
Use of adoption studies
|
To tell if something is more influenced by genes or environment.
|
|
|
|
Use of allele association
|
Ex: there is a higher incidence of HLA in diabetes mellitus
|
|
|
|
Meaning of dz concordance < 100% in MZ twins
|
STRONG evidence that nongenetic factors play a role in the dz (infxn, diet, stress, somatic mutations, aging, epigenetic factors (X-inactivation))
|
|
|
|
Concordance of sickle cell anemia in MZ twins
|
100%
|
|
|
|
Concordance of type I diabetes in MZ twins?
DZ twins? |
MZ: 40%
DZ: ~5% |
|
|
|
What is the significance of greater concordance in MZ vs DZ twins?
|
STRONG evidence of a genetic component to the condition.
|
|
|
|
Limitations to twin studies
|
MZ twins do not have precisely identical gene expression despite identical genotypes.
Environmental exposure may not be the same in utero. Blood supply, placentation may play a role. Disease in question may not be genetic/may be a non-genetic phenocopy (same phenotype despite different gene, as in autism) Ascertainment bias: recruitment for studies |
|
|
|
How to map and identify the genes involved in complex traits?
|
Affected sibpair method
aCGH of a single trait as one component of a single disorder (a rare patient can tell you about more common patients) Disease association studies |
|
|
|
What is the affected sibpair method?
|
Affected sibpair method = a model free linkage analysis.
Assumes 2 affected sibs have dz-predisposing alleles in common. Genome-wide scan of polymorphic markers. Locus "suspicious" when there is increased allele sharing Imprecise method Requires many sibpairs for significance |
|
|
|
What are disease association studies?
|
Frequency of an allele is compared among affected and unaffected individuals.
Strength of association is measured as Odds ratio. Must be interpreted with caution as an increased Odds ratio does not prove that the allele is INVOLVED in the dz pathogenesis. Look at heritable and accurately measured phenotypes with carefully matched large samples, well-chosen genetic markers, and adequate standards in genotyping, analysis, and interpretation. |
|
|
|
Neural tube defects
|
Inability of neural tube to close.
Can involve any region of neural tube--anencephaly, sacral meningomyelocele, etc. |
|
|
|
Familial hypercholesterolemia: inheritance
|
Autosomal dominant with a gene dosage effect
Homozygotes affected more severely than heterozygotes |
|
|
|
Familial hypercholesterolemia: features
|
Elevated [LDL] (cholesterol transporter)
Xanthomas and atheromas form from deposition of cholesterol on tendons and bld vsls Arcus corneae |
|
|
|
What do xanthomas look like?
|
Warts
|
|
|
|
What does the LDL receptor do?
|
It is a cell surface receptor primarily in the liver.
Facilitates LDL uptake by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Facilitates LDL delivery to lysosomes. |
|
|
|
Effects of deficiency of LDL receptors
|
Decreased rate of removal of LDL from plasma.
Increase in plasma LDL which is deposited in scavenger cells and other cell types-->xanthomas and atheromas |
|
|
|
LDL receptor gene and protein
|
Gene encodes a single-chain 893aa glycoprotein.
|
|
|
|
Mutations in the LDL receptor
|
Mutations can happen all along the gene.
There are five classes of mutations. |
|
|
|
Obesity genetic syndromes
|
Prader-Willi syndrome, Bardet-Beidel syndrome
|
|
|
|
Obesity monogenic disorders
|
Leptin deficiency; leptin receptor deficiency
|
|
|
|
Pharmacogenetic testing for Warfarin metabolism
|
CYP2C9: warfarin metabolic enzyme
VKORC1: warfarin target enzyme, vitamin K epoxide reductase complex 1 Variations in these greatly influence effective warfarin dose |
|
|
|
What is malignant hyperthermia?
|
Release Ca stores from SR, causing contracture of sk mm, glycogenolysis, increased cellular metabolism, heat production, xs lacate
Sx: acidosis, hypercapnia, tachycardia, hypoxemia, rhabdomyolysis, hyperkalemia, arrhythmia, cardiac arrest, myoglobinura, renal failure. Death s TX |
|
|
|
Genes implicated in malignant hyperthermia susceptibility
|
AD inheritance
RYR1 CACNA2D1 CACNA1S |
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance of malignant hyperthermia susceptibility
|
Autosomal dominant
|
|
|
|
Transmission of aminoglycoside ototoxicity
|
Maternally-transmitted
Mitochondrial DNA mutation Autosomal dominant 12S rRNA gene (1555A-->G) |
|
|
|
A kid with nl intelligence and a huge tongue comes into your office. He's way to tall for his age, and he has pits in front of his ears. He tells you when he was young he had an omphalocele. What is his cancer risk?
|
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (11p15 paternal UPD)
He has risk of neoplasms, adrenocortical tumors, nephroblastomas, and heptatoblastomas. Whew. |
|
|
|
Kid with beckwith wiedemann syndrome. What's up with his organs?
|
He has huge organs--his liver and kidneys are just enormous (visceromegaly)
His tongue is huge too. |
|
|
|
Mutation in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
|
Loss of methylation at DMR2, gain of methylation at DMR1.
Cytogenetic testing for mutaions in CDKN1C--positive in 40% of familial cases |
|
|
|
Kid with Rett syndrome or Angelman-like syndrome. Presented with infantile hypotonia, now has square head and midface hypoplasia, language delay, seizures, autistic features, and is wheelchair-bound. What's the mutation?
|
MeCP2 region duplication
Seen in Rett syndrome Isolated mental retardation Autistic spectrum speech disorders Angelman-like syndrome |
|
|
|
Name the contiguous gene syndromes
|
Prader Willi/Angelman del 15q11-13
DiGeorge del 22q11 Williams del 7q11 Smith Magenis syndrome del 17p11 Miller-Dieker syndrome del 17p13 |
|
|
|
Pharyngeal problems in embryonic development?
|
DiGeorge syndrome--probs c 3rd and 4th pharyngeal pouches and the 4th branchial arch. No thymus! Hypocalcemia! Immune problems! Bifid uvula! TOF, TA, VSD!
|
|
|
|
The Stork comes to you with an offer: I have this kid for you. He has a prominent nose, long fingers, and a bifid uvula already. Oh, and a cleft palate. I'm also going to make him not want to eat. I'm planning on giving him a heart defect. Which one do you think I should give him?
|
You tell The Stork he has a lot of options, which he can remember with the mnemonic TIVA (not TIVO):
TOF Interrupted aortic arch type B Truncus arteriosus VSD ASD |
|
|
|
Ulta location?
|
610, exit westpark, left on richmond.
|
|
|
|
What organ problems should you check for in a kid with VCFS?
|
Renal abnormalities
Hypocalcemia, too (DiGeorge has absent parathyroids) |
|
|
|
Is there a monogenic form of
-Autism, schizophrenia, other psych conditions -DM 1 and 2 -Cardiovascular dz -Hyperlipidemia -Cancer -Neural tube dfx -Cleft lip/cleft palate -Rxns to or metabolism of pharmacological agens -Response to infectious disease |
yes, yes, yes...yes.
|
|
|
|
What is it called to have too many APP repeats, leading to Alzheimer disease?
|
Copy number variation in a complex trait. Other complex traits are Parkinson dz, HIV susceptibility, lupus glomerulonephritis, Crohn disease, pancreatitis
|
|
|
|
What can cause twin study discordance?
|
Infection, diet, stress
Somatic mutations Aging Epigenetic factors (X-inactivation) |
|
|
|
MZ concordance greater than DZ concordance
|
STRONG evidence of a genetic component to the condition
|
|
|
|
Disease concordance less than 100% in monozygotic twins
|
Discordance (strong evidence that nongenetic factors play a role in the disease) due to environmental factors, epigenetic factors, somatic mutations
|
|
|
|
Limitations of twin studies
|
MZ twins don't have identical gene expression despite identical genotype
Environmental exposure in utero: bld supply, placentation Dz in question may not be genetic (non-genetic phenocopy is possible) Ascertainment bias (recruitment for studies is biased) |
|
|
|
What is the affected sibpair method of model free-linkage analysis?
|
Used in genetic mapping of complex traits.
Assumes 2 affected sibs have dz-predisposing alleles in common. A genome-wide scan of polymorphic markers is done. A locus is considered "suspicious" when there is increased allele sharing. This is an imprecise method that requires many sibpairs for significance. |
|
|
|
What is the utility of identifying the chromosomal abnormality of a trait? What bout learning that the trait in question is one component of a multisystemic disorder?
|
Used in genetic mapping of complex traits.
It is much easier to map the gene when the chromosomal abnormality is identified or if the trait is one component of a multisystemic disorder. |
|
|
|
What is a disease-association study?
|
Used in genetic mapping of complex traits.
Frequency of an allele is compared among affected and unaffected individuals. Strength of association is measured as an Odds ratio. You have to interpret this with caution because an increased Odd ratio doesn't prove that the allele is actually involved in the pathogenesis. You need heritable and accurately measured phenotypes, carefully matched large samples, well-chosen genetic markers, adequate standards in genotyping, analysis, and interpretation. |
|
|
|
Trisomy 13: how does the extra chromosome get there?
|
75% of cases are due to de novo non-disjunction advanced maternal age
20% are due to Robertsonian translocations (13q14q) |
|
|
|
Trisomy 18: how does the extra chromosome get there?
|
Advanced maternal age is the usual etiology--> meiotic nondisjunction.
Also: translocations, mosaicism |
|
|
|
Problem with subcutaneous fat + short sternum + VSD
|
Trisomy 18
|
|

