![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the Four general principles of teratology?
|
1. Exposure to the teratogen must occur during the critical period, usually, but not always, the first 12 weeks of gestation.
2. Each teratogenic agent produces a specific pattern of anomalies. 3. Teratogens are species specific. 4. Some element of genetic predisposition is likely, since almost no teratogen affects all exposed fetuses. |
|
|
when does Alcohol and ACE inhibitors act.
|
after the first 12 weeks of gestation
|
|
|
Does Bendectin cause the same tetratogenic effect on children?
|
NO, wide variey to defects
|
|
|
Do twins respond the same to the a common tetrogenic exposure?
|
DZ twins can respond differently to same teratogenic exposure
|
|
|
what are the challenges to a tetrogenic studies?
|
1. Background risk exists for congenital anomalies in unexposed controls
2. Ascertainment bias if cases are collected after outcome is known 3. Randomized prospective trials may be unethical if a teratogenic effect is suspected 4. Many confounding variables cannot be controlled: time of exposure, other drugs 5. Genetic susceptibility may vary with racial or ethnic background. 6. Mothers of affected children may have a recall bias compared to control mothers |
|
|
Maternal insulin dependent diabetes leads to what defects
|
Cardiac defects, spina bifida, sacral agenesis, holoprosencephaly, heterotaxy, large birth weight
|
|
|
Maternal Phenylketonuria (PKU) leads to what defects
|
Mental retardation, microcephaly and cardiac lesions common in untreated maternal PKU. Low phenylalanine diet should be initiated prior to conception to maintain maternal blood phenylalanine between 2-6 mg/dl.
|
|
|
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome leads to what defects
|
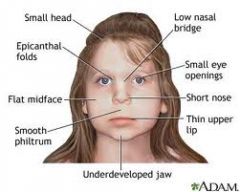
Twenty percent of those with IQs in the 50-80 range and 1/6th of those with cerebral palsy are victims of fetal alcohol exposure. However, less than 50% of the offspring of chronically alcoholic women are affected. Children have low birth weight, microcephaly, short palpebral fissures, smooth philtrum, thin upper lip, small nails, behavior and intellectual problems.
|
|
|
Folic Acid Responsive Defects leads to what defects
|
Spontaneous abortions (SAb), spina bifida, cleft lip and possibly heart and limb defects are more frequent when folic acid is low in the first trimester.
|
|
|
is Folic Acid Responsive Defects a tetrogen
|
no, its a morphogen
|
|
|
what does the CDC recommend for the intake of folic acid
|
all women of childbearing age take 400 micrograms/day of folic acid. Mothers of children with spina bifida should take 4mg/day to prevent a recurrence. Folic acid supplementation should begin at least one month before conception to reduce neural tube defects by the maximum 60-70%.
|
|
|
Anticonvulsants: Hydantoin and Valproate cause what defect?
|
About 40% of exposed infants have some effects: developmental delay, nail hypoplasia, cleft lip, and dysmorphism. Valproate and carbamazapine increase the chance of spina bifida to 1-2% (background risk 1/1000). Valproic acid is associated with radial ray (thumb or radius) defects
|
|
|
What effect does Rubella have?
|
Eighty percent of first trimester infections produce fetal effects: cataracts, intrauterine growth retardation, microcephaly, retinitis, deafness, cardiac defects, mental retardation. More common now in immigrant, unimmunized populations.
|
|
|
What effects does Accutane (Isotretinoin) have on fetal development?
|
Risk of SAb is 40%, anomalies 25%. Critical period is 2-5 weeks after conception. CNS, facial palsy, major ear anomalies, conotruncal heart defects, thymic aplasia.
|
|
|
Lithium criticle period?
|
Critical period is approximately 4-6 weeks
|
|
|
what effect does lithuim have on fetal development?
|
Increased chance of tricuspid atresia (Epstein’s anomaly). Later prospective studies showed weaker effect.
|
|
|
what is the critical period of warafin
|
Critical period is first 100 days.
|
|
|
what is the effect of warafin?
|
Anomalies in 17-30%: Mental retardation, microcephaly, stippled epiphyses, and optic atrophy. Severe nasal hypoplasia. Phenocopy of chondrodysplasia punctata, a single gene disorder.
|
|
|
what is the critical period of Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors?
|
Critical period is after the first trimester
|
|
|
what is the effect of Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors on fetal development?
|
Interferes with renal blood flow causing anuria, oligohydramnios, death in utero due to renal failure
|
|
|
what is Thalidomide used for ?
|
Effective therapy for oral ulcers in AIDS, leprosy, chronic graft v. host disease, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis
|
|
|
what is the mechanism of Thalidomide
|
Mechanism of action is angiogenesis inhibition
|
|
|
what are the defects associated with thalidomide?
|
Phocomelia (“seal limb”), polydactyly, cleft lip and palate and other defects in majority of fetuses when given in first trimester.
|
|
|
what are the safety precautions for Thalidomide
|
. Two forms of contraception and a negative pregnancy test each month are required before a 28-day refill is given.
|

