![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cloning
|
Making a genetically identical organism.
|
|
|
DNA cloning
|
Making multiple copies of a gene - usually by cloning a bacterial cell containing the recombinant gene.
|
|
|
Transgenic animal.
|
Transgenic animals carry foreign genes that have been inserted into the genome by genetic recombination.
|
|
|
Name four steps of gene cloning.
|
1. Cutting - to obtain the DNA fragment containing the gene.
2. Joining - to recombine the DNA fragment into a cloning vector. 3. Cloning - to incorporate the recombinant DNA into the genome of a cell, so that it replicates along with the genome when the cell divides. 4. Screening - to identify the clonal cell line containing the gene of interest. |
|
|
Restriction enzymes.
|
Enzymes used in DNA cloning, cutting stage. Enzymes that recognise specific short sequences of DNA and cleave the DNA at or near the site. Restriction enzymes are produced by bacterial cells to destroy non-self DNA as defence against invasion by viral DNA.
|
|
|
Palindromic
|
Recognition sites on DNA are palindromic - same on both strands:
5' GAATTC 3' 3' CTTAAG 5' reads the same from 5' to 3' |
|
|
Ligase
|
Enzyme that joins two DNA fragments. Used in DNA cloning in the joining stage.
|
|
|
Recombinant DNA
|
A DNA molecule made in vitro with segments from different sources.
|
|
|
Plasmid
|
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of a bacterial chromosome; also found in some eukaryotes, such as yeast.
|
|
|
Cloning vector.
|
Independently replicating piece of DNA e.g. plasmid or viral genome, into which foreign gene can be inserted.
|
|
|
What is shown on the picture?
|
|
|
|
What is shown on the picture?
|
|
|
|
What confers selectable phenotype on a host cell or organism (e.g. antibiotic resistance), so that the host containing it can be identified?
|
Clone vector.
|
|
|
What confers selectable phenotype on a host cell or organism (e.g. antibiotic resistance), so that the host containing it can be identified?
|
Clone vector.
|
|
|
Transduction
|
Transduction is the process by which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus. It also refers to the process whereby foreign DNA is introduced into another cell via a viral vector. This is a common tool used by molecular biologists to stably introduce a foreign gene into a host cell's genome.
|
|
|
How is antibiotic resistance used in screening process during cloning?
|
Incorporation of an antibiotic resistance gene into the cloning vector - only cells containing the vector can grow in medium containing the antibiotic.
|
|
|
Describe selection by colour (blue/white) in screening process during cloning.
|
Insertion of a DNA fragment into the vector disrupts a gene that normally leads to a production of a coloured product (blue) - desired cell colonies are colourless (white).
|
|
|
What does lacZ gene do?
|
This gene is required for cell to be able to metabolize X-gal - blue coloured substance.
|
|
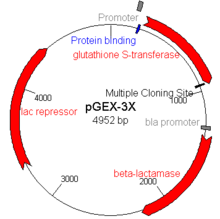
What is shown on the picture?
|
Clone vector.
|

