![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nucleic acids are linked togther by |
Phosphodiester bonds |
|
|
Nucleotide bases are |
Base sugar and phosphate A-T (adenine and thymine) C-G (cytosine and guanine) |
|
|
Purines |
A and G (2 rings) |
|
|
Pyrimidines |
C and T (1 ring) |
|
|
Nucleoside |
Base and sugar (ribose) |
|
|
dNTP |
3 phosphates deoxy nucleoside tri phosphate |
|
|
Watson-crick model of DNA |
Right handed double helix with H-bonds between bases |
|
|
Double stranded DNA is |
Antiparallel (one side is 5' to 3', the other is 3' to 5') |
|
|
A is bonded to T with how many H bonds |
2 |
|
|
C is bonded to G with how many H bonds |
3 |
|
|
H bonds in nucleotides always pair a _____ with a _____ |
Purine with a pyrimidine |
|
|
DNA is always written in the direction of |
5' to 3' |
|
|
Is DNA acidic or basic? |
Acidic because of phosphates |
|
|
Genome |
The total genetic information of an organism |
|
|
Chromosome |
Each piece of double stranded DNA |
|
|
How many chromosomes does each human have? How many is inherited from each parent? |
46. 23. |
|
|
Supercoils |
DNA Gyrase twists the DNA even more into a circular molecule |
|
|
What is DNA wrapped around proteins to make it even more compact? |
Histones-basic |
|
|
What are the beads on a string called for DNA wrapped around an octomer of histones? |
Nucleosomes |
|
|
What is fully packed DNA called? |
Chromatin is closely stacked nucleosomes |
|
|
During meiosis/mitosis the DNA is condensed even more into |
Chromosomes |
|
|
Heterochromatin |
Densily packed More repeats Darker colored |
|
|
Euchromatin |
Looser packaging Higher rates of transcription and gene activiity Looser makes DNA more accesible to enzymes and proteins Lighter colored |
|
|
Centromere |
Region of chromosome where the spindle fibers attach during cell division |
|
|
Kinetochore |
Where the spindle fibers actually grab onto |
|
|
What is the p and q arms of chromosomes? |
Short and long arms |
|
|
Metacentric |
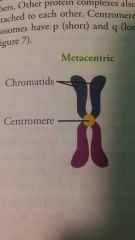
|
|
|
Submetacentric |
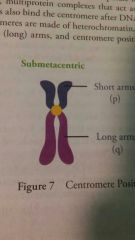
|
|
|
Acrocentric |
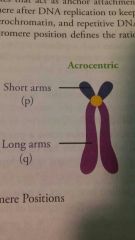
|
|
|
Telocentric |
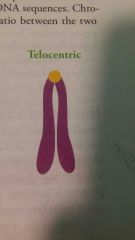
|
|
|
Telomeres |
The ends of linear chromosomes Repetitions of sequences-guanine rich |
|
|
What is the function of telomeres? |
To prevent chromosome deterioration Prevent fusion with other chromosome Stabilize the ends of chromosomes At the very end it is single stranded DNA |
|
|
Codon |
3 letter word for mRNA |
|
|
DNA replication is conservative, disrutpive or semiconservative? Each new daughter strand is _____ to the parent strand. |
Semiconservative Complimentary |
|
|
Helicase |
Unwinds the DNA double strand for replication |
|
|
ORI |
Place where helicase begins to unwind the DNA for replication |
|
|
Topoisomerase |
Cut strands of DNA to unwind them and uwrap the helix releasing the tension created |
|
|
Single stranded binding proteins SSBPs |
Protect single strands of DNA and help keeps the strands separate |
|
|
Primase |
RNA primer for the template strand |
|
|
DNA polymerase |
Requires a template: must copy from parent chain DNA sequence Requires a primer: cannot begin a nee chain without RNA |
|
|
Polymerization occurs in the ___ to ___ direction. Read the parent strand from ___ to ___ direction. |
5' to 3' 3' to 5' |
|
|
Leading strand |
5' to 3' continuous |
|
|
Lagging strand |
5' to 3' discontinous okazaki fragments |
|
|
DNA ligase |
Joins okazaki fragments |
|
|
DNA polymerase III |
Leading strand 5' -> 3' polymerase activity 3' -> 5' exonuclease activity |
|
|
DNA polymerase I |
Removes RNA primer via 5' -> 3' exonuclease activity while adding DNA in a 5' -> 3' direction |
|
|
Point mutations |
Single base pair substitution |
|
|
3 types of point mutations: |
1. Missense mutation: 1 a.a. replaced by another 2. Nonsense mutation: a stop codon replaces a regular codon 3. Silent mutation: a codon is changed into a new codon for the same a.a. |
|
|
What types of mutations shift the reading frame? |
Insertion and deletion |
|
|
Inversion mutation |
When a chromosome part break offs and flips |
|
|
Chromosome amplification |
A mutation where a segment is replicated |
|
|
Trabslocation |
Recombination between nonhomologous chromosomes |
|
|
DNA methylation |
Parent strand methylated to know which strand is correct and which is mismatched/mutated |
|
|
RNA |
Single stranded Uracil instead of thymine Ribose instead of deoxyribose |
|
|
mRNA |
Carries genetic info to the ribosome where it can be translated into protein Has open reading frame |
|
|
hnRNA |
Unmature mRNA that goes thru adding caps and tails and splicing |
|
|
tRNA |
Carries a.a. from cytoplasm to ribosome to be added to growing proteins |
|
|
rRNA |
Major component of the ribosome |
|
|
Ribozymes |
RNA enzyme |
|
|
miRNA/siRNA |
Postranscriptional gene regulation of gene expression Can bind specific mRNA molecules to increase or decrease translation |
|
|
Splicing |
Introns are removed and exons are put together in mRNA |
|
|
Splicosome |
The complex that facilitates splicing |
|
|
5' cap and 3' poly-A tail |
Methylated guanine cap and adenine tail prevents digestion of the mRNA |
|
|
RNA polymerase I |
Transcribes rRNA |
|
|
RNA polymerase II |
Trabscribes hnRNA |
|
|
RNA polymerase III |
Transcribes tRNA |
|
|
Anticodon |
Part of the tRNA that links up with the mRNA |
|
|
Amino acid acceptor site |
3' end of tRNA that links with a.a. |
|
|
Wobble hypothesis |
Inosine 3rd position of anticodon can bond to different codon bases |
|
|
Ribosome binding site order |
A to P to E |
|
|
What is the first a.a. in all prokaryotic proteins? |
Fmet formylmethionine |
|
|
Differences in eukaryotic vs prokaryotic replication, transcription and translation |

|
|
|
Lac Operon parts |
P-promoter- where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription of Y, Z, A gene O-operator-where the lac repressor binds Z- enzyme beta-galactosidase cleaves lactose into glucose Y- permease transports lactose into cell A- transacetylase cleaves acetyl |
|
|
Lac operon presence of glucose and absence of lactose |
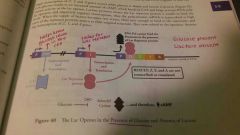
Repressor activated |
|
|
Lac operon in the presence of glucose and lactose |
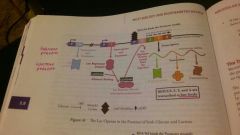
Low levels if transcription |
|
|
Lac operon in the absence of glucose and presence of lactose |
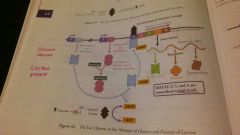
High levels of transcription |
|
|
Trp operon |
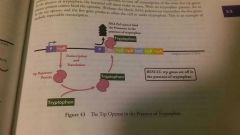
In presence of tryptophan decrease gene expression |
|
|
Eukaryotic regulation of transcription |
Tata box binded with tata box binding protein which initiates transcription at the promoter |
|
|
RNA translocation |
A way that the eukaryotic cell regulates trabscription by moving mRNA to different parts of the cell and arent translated until they are in the right area of the cell |
|
|
mRNA surveillance |
A way that the eukaryotic cell regulates transcription by making sure the mRNAs are high quality and are not defective |
|
|
RNAi |
A way that the eukaryotic cell regulates transcription by silencing gene expression after a transcript has been made. Can decrease protein expression |

