![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Transformation? |
Transformation is the horizontal transfer of genetic material from one bacteria to another. The genetic material can come from a living or deceased host. |
|
|
How did Avery and his colleagues (MacLeod and and McCarty) demonstrate the transforming principle of DNA. |
They tested the elusive "genetic substance" with three digestive enzymes. One targeted DNA, RNA, and Proteins. The two that targeted RNA and Protein still transformed their genes to living bacteria. The one that targeted DNA didn't pass on its genes. Leading them to believe that DNA is the genetic substance. |
|
|
Identify the three main components of a DNA Nucleotide. |
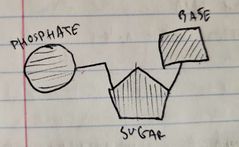
Phosphate Sugar Base |
|
|
RNA Nucleotide vs DNA Nucleotide |
RNA - contains Uracil (instead if Thymine) - has -OH group at the 2' spot. DNA - contains Thymine (instead of Uracil) - Contains just H's at the 2' position. |
|
|
3 DNA Nucleotide segment |
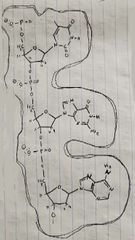
|
|
|
Composition and Structure of Nucleosome |
The repeating core of proteins. And DNA produced by difestionvw/ nuclear enzymes is the simplest level of chromatin structure. It consists of DNA wrapped two times around an octane of eight histone proteins. |
|
|
What are the four different kinds of histone proteins in a octamer. |
H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. |
|
|
What are Telomeres? |
Natural ends of a chromosome. They serve as a cap to stabilize the chromosome much like the plastic cap on the end of a shoelace that prevents it from unraveling. They also provide a means of replicating the ends of the chromosome. |
|
|
What is the structure of a Telomere? |
At the end of each Telomere are many short telomeric sequences. They consist of Cytosine and Adenine nucleotides, they consist of repeated sequences.
One strand protrudes beyond the other, creating some single-stranded DNA at the end. |
|
|
Kossel |
Determined that DNA contains nitrogenous bases. |
|
|
Watson and Crick |
Worked out the helical structure of DNA by building models. |
|
|
Levene |
Discovered that DNA consists of repeating nucleotides. |
|
|
Miescher |
Determined that DNA is acidic and high in phosphorus. |
|
|
Hershey and Chase |
Identified DNA as the genetic material in bacteriophage. |
|
|
Avery, McCarty, and MacLeod |
Determined that DNA is responsible for transformation in bacteria. |
|
|
Griffith |
Demonstrated that heat killed material from bacteria could genetically transform live bacteria. |
|
|
Franklin and Wilkins |
Took X-Ray diffraction pictures used in determining the structure of DNA. |
|
|
Chargaff |
Discover regularity in the ratios of different bases in DNA. |
|

|
No, he needs to perform more experiments to rule out the possibility of other variables that could account for his results. |
|
|
What causes DNA to migrate towards the positive poles during electrophoresis? |
The negatively charged backbone of the DNA structure interacts with the electronegative gradient established during electrophoresis. Causing its negatively charged backbone to be attracted to the positive pole. |
|
|
Prokaryotic Chromosome vs Eukaryotic Chromosome. |

|
|
|
What is semiconservative replication? |
Each strand acts as a template for a new double helix. The established model of DNA replication in which each double-stranded molecule is composed of one parental strand and one newly polymerized strand. |
|
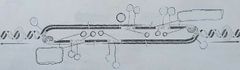
Identify: (1) origin, (2) polarity [5' and 3' ends] of all templates and newly synthesized strands, (3) leading and lagging strands, (4) Okazaki Fragments, and (5) location of primers. |
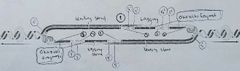
|
|
|
3 Major Requirements of Replication |
1) Template 2) Substrates 3) Enzymes |
|
|
Requirement of Replication: Template |
A template consisting of single stranded DNA. |
|
|
Requirements of Replication: Substrate |
Raw materials (substrates) to be assembled into a new nucleotide strand. |
|
|
Requirements of Replication: Enzymes |
Enzymes and other proteins that "read" the template and assemble the substrates into a DNA molecule. |
|
|
What substrates are used in DNA synthesis? |
dNTPs: dATP, dGTP, dCTP, and dTTP. |
|
|
Why is primase required for replication? |
It produces short stretches of nucleotides, or primers, that initiates replication. |
|
|
What is the end-of-chromsome problem? |
The DNA at the very end of the chromosome cannot be fully copied in each round of replication, resulting in a slow, gradual shortening of the chromosome. |
|
|
What must genetic material be able to do? |
The genetic material must be capable of carrying large amounts of information, replicating faithfully, and translating its coding instructions into phenotypes. |
|
|
Griffiths Experiment |
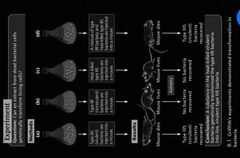
|
|

|
Protein is the genetic material. |
|
|
Hershey and Chase Experiment |

|
|

|
No, because carbon is found in both protein and nucleic acid. |
|

|
The sugar of RNA has a hydroxyl group thst is not found in ths sugar of DNA. |
|

|
Ther opposite direction of the two stands of nucleotides. |
|

|
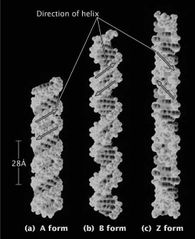
Z-DNA has a left-handed helix; B-DNA has a right-handed helix. The sugar–phosphate backbone of Z-DNA zigzags back and forth, whereas the sugar–phosphate backbone of B-DNA forms a smooth continuous ribbon. |
|

|
Negatively supercoiled. |
|

|
Bacterial DNA is not complexed to histone proteins and is circular. |
|

|
They would separate from the DNA. |
|

|
All of the above... |
|
|
Unique-sequence DNA. |
|

|
Without knowledge of the structure of DNA, an understanding of how genetic information was encoded or expressed was impossible to achieve. |

