![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Allele |
Variations of the same gene |
|
|
Define Gene |
Sections of DNA in Chromosomes |
|
|
Define Genotypes and Phenotypes |
Genetic description of the gene combination The physical manifestation of the gene combination |
|
|
Define Chromosome |
Long thin strands of DNA. Humans have 23 pairs |
|
|
Define Dominant and Recessive |
The stronger gene that will always overpower the recessive gene The weaker gene that will only show when both pairs are recessive |
|
|
Compare Mitosis and Meiosis (What type of reproduction, process and number of chromosomes) |
Asexual reproduction for growth & repair. Process is IPMATC. Both cells have diploid number of chromosomes Sexual reproduction of two gametes coming together. Process is IPMAT with an extra MATC. The gametes each have haploid number of chromosomes and is combined. |
|
|
Describe Monohybrid Punnet Squares |
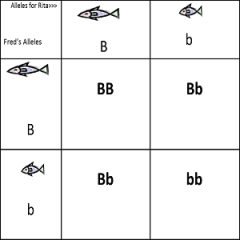
Used to study only one trait in the potential offspring of two mated individuals |
|
|
Describe Dihybrid Punnet Squares |
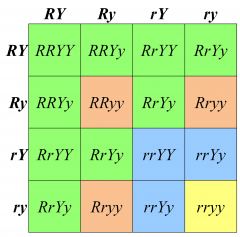
Used to study two traits in the potential offspring of two mated individuals |
|
|
Compare Co-dominance and Incomplete Dominance (Description of the genes and their physical manifestation) |
Both alleles are so strong they need to share space. This creates patterns. Both alleles are not completely dominant and therefore blends together, creating different shades. |
|
|
Describe Pedigree Tree and their purpose |
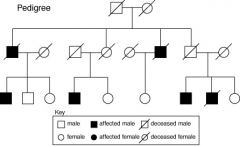
They can identify various traits or diseases and assume they have a sex linkage or are autosomal, and whether they are dominant or recessive. |
|
|
Define Mutation |
Changes in the genetic code. They can be harmful, beneficial or neutral |
|
|
List 2 evidence of evolution (Historical records and anatomy) |
Fossil records in rock and homologous structures in different species |
|
|
Define Variation |
Differences within the same species due to mutation or meiosis |
|
|
Define Isolation and list the three types discussed (Outside influence and inner influence) |
The process of which species become separate. The three types of isolation is geographical, behavioral (reproductive), temporal/ecological |
|
|
Define Genetic Drift and Gene Flow |
Changes in allele frequency of a certain population The frequency of genes in a population |
|
|
Define Natural Selection and Sexual Selection |
Traits/mutations that are beneficial for survival Traits/mutations that are favoured by potential mates |
|
|
Define Speciation |
The process of which a certain population becomes a whole new species due to variation, isolation and selection. Also known as Evolution |
|
|
List and define the 4 types of evolution |
Divergent: The same species evolving different traits Convergent: Different species develop similar traits Co Evolution: Two species evolving together Parallel: The same species evolving similar traits |

