![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Loci |
A specific location/position on a chromosome. |
|
|
Recessive |
An allele only shown if the dominant is not present. |
|
|
Homozygous |
An individual with 2 identical alleles for a particular gene. |
|
|
Genotype |
An individual's combination of alleles. |
|
|
Heterozygous |
An individual with two different alleles for the same gene. |
|
|
Gene |
A section of DNA coding for a specific protein. |
|
|
Dominant |
Always shown in the phenotype. |
|
|
Carrier |
An individual with a recessive gene for a genetic disorder- does not affect them but may affect offspring. |
|
|
Phenotype |
The physical expression of an individual's genotype. |
|
|
Allele |
Variation of a particular gene. |
|
|
Homologous pair |
A pair of chromosomes which have the same genes but possibly different alleles. One inherited from each parent. |
|
|
Requirements of respiration |
Moisture, high to low concentration gradient, large surface area, thin walls, access to oxygen. |
|
|
Protein |
A polymer of amino acids. |
|
|
Amino acid |
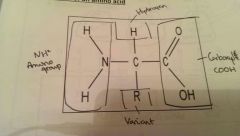
Monomer of a protein. |
|
|
Dipeptide |
Two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond. |
|
|
Condensation reaction |
Joins bonds producing water. |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
Splits bonds using water. |
|
|
Primary structure of DNA |
A chain of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. |
|
|
Secondary structure of DNA |
Folds are formed by hydrogen bonds. Alpha helix or beta sheet. |
|
|
Tertiary structure |
Further folds due to R-groups forming a globular shape. |
|
|
Globular proteins |
Soluble, enzymes usually, globular structure. |
|
|
Fibrous proteins |
Chains, insoluble, used for structure. |
|
|
Cell membrane structure |
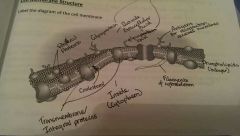
|
|
|
Phospholipid molecule |
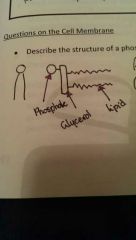
|
|
|
Diffusion |
Net mo cement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration until they reach an equilibrium. |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
Along concentration gradient assisted by channel or carrier proteins. |
|
|
Channel protein |
Assists transport of substances. |
|
|
Carrier protein |
Assists transport of molecules. |
|
|
Osmosis |
Net movement of water from a high concentration of free water molecules to an area of low concentration of free water molecules . |
|
|
Active transport |
Uses protein pump to move substances against the concentration gradient. |
|
|
ATP |
Source of all energy. |

