![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
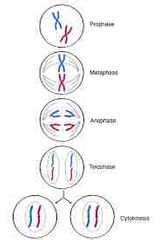
Mitosis |
Produced diploid cells (full copy of DNA, all chromosomes). how most cells in the body reproduce The cell makes copies of chromosomes and then the cell splits and makes two new cells Other definition: process of cell replication in which the chromosomes duplicate themselves and the cell into Two cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the original cell. |
|
|
|
Meiosis |
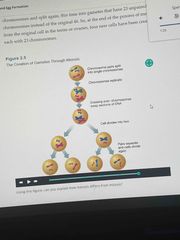
Produced haploid cells (half of each chromosome). How gamers (sperm and egg cells) made. 4 cells total, each with half of the original cells DNA Sex differences include males is completed before sperm are released, but females final stage of meiosis only takes place when and if the country is fertilized by sperm. Also in males the outcome is four viable sperm, whereas in females produces only one viable ovum along with three Lilian bodies that are not functional (ovum has cytoplasm) |
|
|
|
Fertilization |
Haploid gametes (sperm + egg) combine to produce diploid offspring with unique DNA. Sperm cell + egg cell = fertilized egg cell that will develop into child: |
|
|
|
Codominance |
Phenotypes of both parents are expressed separately in the offspring Black guy + white girl = black and white kid |

|
|
|
Incomplete dominance |
Phenotypes of parents blend together to crear new phenotype in the offspring Black woman+ white guy = brown kid |

|
|
|
Polygenetic inheritance |
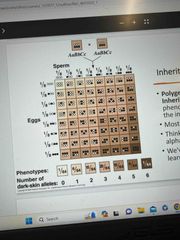
Expression of phenotypic characteristics due to the interaction of multiple genes Most common form of inheritance. Think of genes like letters in the alphabet; combination is important. We’ve learned words they make |
|
|
|
Autosomes |
The first 22 pairs of Chromosomes; non sex chromosomes (Keep in mind the bigger the chromosome. The more knowledge it has) |
|
|
|
Sex chromosomes |
Chromosomes that determine whether an organism is male or female Woman XX man XY Y is small. (Father sperm is what the child will be.) |
|
|
|
Conjoined twins |
They |
|
|
|
Reaction range |
Range of possible developmental paths established by genes. The environment then determines where development takes place within that range (eg height, athleticism Genes determine the minimum and maximum environment shape actual score |
|
|
|
X linked inheritance |
Pattern of inheritance in which a recessive characteristic is expressed because it is carried on the males chromosome. Mom D(good) r (bad) Boy kid r r genetic disorder are likey to be recessive because they are more sneaky and likely to get past to reproduce. |
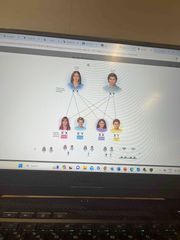
|
|
|
Theory of genotype —> environment effects |
theory that genes influence the kind of environments we experience |
|
|
|
Genotype -> environment effects: Passive |
environmental effects stemming from the fact that in a biological family the parents provide both the child’s genes and their environment |

|
|
|
Genotype -> environment effects: Evocative |
responses from others in the environment evoked by a persons inherited characteristics |
|
|
|
Genotype -> environment effects: Active |
Genotype -> environment effects: environmental effects caused by people seeking our environments based on their genotype |
|
|
|
Behaviour genetics |
Field In the study of human development that aims to identify the extent to which genes influence behaviour, primarily by comparing persons who share different amounts of their genes |
|
|
|
Concordance rate |
Degree of similarity in phenotype among pairs of family members expressed as a percentage This is saying how simialr in genes they are so MZ twins will most likely have schizophrenia ID kne has it |

|
|
|
Ovum |
Mature egg that develops in ovaries, about every 28 days in human females. This is before the sperm meets the egg |

|
|
|
Gametes |
Cells, distinctive to each sex, that are involved in reproduction (egg cell in the ovaries of the female and sperm in the testes of the male) |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
In an ovum, fluid that provides nutrients for the first 2 weeks of growth if the ovum is fertilized until it fezzes the uterus and begins drawing nutrients from the mother |

|
|
|
Tetrogens |
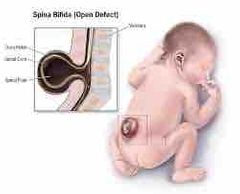
The critical period you don’t want this is in the embryonic period which is where the baby is forming major organ systems at a rapid rate. The fetal stage can have bad things like alchool. Malnutrition’s women must gain 25-35 pounds. They can gain too much which can cause obesity. Also think about the issues of the season. And think about the specific food like folic acid When they don’t get this then the baby can have a spins bífida which can make a extreme shape of the spinal cord. And the anencephaly makes the baby’s brain underdeveloped. So earring it before is good. Eating iron can add weight to the baby and eating iodine can prevent miscarriage, still birth and abnormalities in the fetal brain. Salt is idoloized. Infectious diseases. The most common is rubella which can effect things like blindness, deafness, interllectusl disability, and abnormalities of heart, genitals or intestinal system. Weight problems too. Although a vaccine was made. AIDS damage the immune system. Birth and breast milk can infect the child. Which they can prevent by using medicines before birth, cesarean sections and using a breast milk formula. Most of these happen in Africa. Second hand smoking can be inhaled by those near them. (Possible cancer) Other things like pollution can effect birth weight by 9%. Nicotine but accutane cause problems even tho it’s for achne. Also non prescription drugs. Dress can effect the baby and work with hazards |
|
|
|
Essentials of prenatal care |
Medical care. Have a medical examination to make sure no diseases or vaccinations for rubella and to make sure you taking folic acids. Avoid drugs and all that. During pregnancy Exercise, engage in mild to moderate exercise regularly, including aerobic exercise, to stimulate circulatory system and muscles as well amas kegel exercises to strengthen vaginal muscles. Aerobic exercise like walking and jogging can help. Although avoid stenuous exercise like sports and long distant running or horse ridding. |

|
|
|
Chromosomal disorders |
This can happen because of a underdeveloped penis or testicals can cause it. For females their is no ovulation in girls but it can be fixed with hormonal supplements Downsydrome: a genetic disorder due to carding and extra chromosome in the 21st pair. Most people will have too much or too little but the zygote never develops or it’s aborted early. They have speech problems. Hearing and heart problems. Some smile less and less eye contact. But they chill. They she faster and their alimentes catch up with them in their 30-40’s which can cause them to have cancer. Parents don’t have a fertility problem but it’s the age for mothers which is 1/30 at age 30 but goes higher after that age slightly. Fathers sperm Is the cause 5-10% of the time |
|
|
|
Multifactorial disorder |
Parental age is linked to multifactorial disorders which involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Like the autism spectrum. They say genetic mutation in the Sperm which cause issues as men get old |

|
|
|
Techniques of prenatal monitoring : ultra sounds, maternal blood screening, amniocentesis and chronic villus sampling |
Ultra sounds are high frequencies that are safe, cheap and they can show things like movements, facial expression, genitals, and some fancy ones give you a 3D model. It’s used with twins and it helps parents the parent feel involved. Maternal blood screaming used in the first and second trimester to screen rises to fetus by looking at substances in maternal blood including proteins hormones and fragments of fetal DNA. This is only used when it’s necessary if the baby may have an issue like spine bífida and Down syndrome. Amniocentesis is when’s needle is used in the abs to withdrawal some amniotic fluid containing fetal cells from the placenta, allowing possible prenatal problems to be detected. They do this 15-20 weeks in the pregnancy. It is 100% accurate and it can detect 40 defects but it can cause a miscarriage. They also use a ultrasound to help. Chronic villus sampling tried to detect genetic problems. This is 5-10 weeks In. They put a tube in a vagina and in the uterus to get a cell sample which could cause a miscarriage. So it’s only used when they have a family history of abnormalities or the woman is over 35. Also it’s 99% accurate |
|
|
|
Crossing over |
At the outset of melosis, the exchange of genetic material between paired chromosomes. Bassicly the genetic and chromosomes rearrange so much that only twins will be simialr to you This is how we are so different from each other. The chromosomes can be made in a infinite amount of ways. |

|
|
|
Ova |
Women make these ova while in the womb. So crossing over begins when oca are created so unique genotypes are made before the mom is born. Women make 2 mil ova and they stop making it when they reach their 40’s. But when they reach puberty it goes to 300 thousand. And 400 will mature in child bearing years |

|
|
|
Folicle |
During the female reproductive cycle, the ovum plus other cells that sprung the ovum and provide nutrients The ovum matured into a follicle. Which the ovum is 2k times bigger then sperm because of cytoplasm |
|
|
|
How are baby’s made |
Basically when the sperms are going in the ovum they penetrate the membrane which makes the head separate from the tail of the Sperm. Then it cock blocks other sperm. Then it goes for the nuclear and the final phase of meiosis happens in the ovum. Ferterlization takes place |
|
|
|
Milestones of prenatal development: week 1-8 |
Germinal 1-2 weeks: zygote divides and forms blastocyst (ball of about 100 cells formed), which implants in uterus during the second week and begins forming the amnion, placenta, and umbilical cord. Embryonic 3-4 weeks: three layers form; the ectoderm (the outer layer of cells which will become the skin, hair, nails, sensory organs, and nervous system [brain and spinal cord]), mesoderm (middle layer which becomes the muscles, bones, reproductive system and circulatory system.), and endoderm (the inner layer of cells which will become the digestive system and the respiratory system), neural tube develops (will be spinal cord and brain and is apart of the ectoderm) ; heart begins beating; ribs, muscles and digestive tract form. ALSO neurogensis begins at 7 weeks by the neural tubes 5-8 weeks: arms and legs develop, then fingers, toes; placenta and umbilical cord function; digestive system develops; liver produces blood cells; embryo responds to touch; neural tube begins producing neurons. |
|
|
|
Trophoblast and embryonic disk |
The blastocyst has two layers of cells, which the trophoblast will go on to form structures that provide protection and nourishment to the embryo. Also keep in mind that if the blastocyst successfully implants during the germinal stage then it could cause infertility And the second layer, the embryonic disk is the in we layer of cells who can will go on to form the embryo. Skin, hair, nails, sensory organs and nervous system |

|
|
|
Amnion and umbilical cord |
The trophoblast forms a membrane called the amnion which is a fluid filled membrane that surrounds and protects the developing organism in the womb like from movements. The umbilical cord if s structure connecting the placenta to the northwest uterus. Which can produce hormones and nutrition |

|
|
|
Trimester, vernix |
Three month period of prenatal development. They get 3 ounces and three inches. Second trimester the fetus begins to respond to the environment. They can hear the moms voice and music. (Has preferences) It kicks, hiccups, breathes amniotic fluid in and out and it turns. They also get filled with VERNIX which is this oily cheesy substance that protects their skin from chapping in the womb. I’d 2 pounds and 14 inches. The viability is low as it is rare they survive under 22 weeks and 24 weeks is a 50/50. 26 is 80%. Before get cerebral palsy and usually only high SES survive. Their lungs are too weak Third trimester will have a sleep cycle of a new born. They will have a internal environment reaction like mothers stress. They can also remember books |

|
|
|
Midwife |
Person who assists in pregnant women’s prenatal care and the birth process. Like a prenatal massage like is the position of the baby properly. Baby needs to face properly so they will make it face the buttocks |
|
|
|
Infertility psychological and social implications |
It is said that in infertile people are sadder and feel like they lost something in the west. So do the Swedes except they also loose sexual relations and they have fail living up to social and personal expectations. So infertility usuals makes people strong Remember Marie Antoinette. Women get blamed for infertile baby. Also Asian and African cultures expect your ancestors to be worshiped so if no baby comes then it sucks and lower status. Some also pefer dad. Some go for herbal remedies given by midwife. Some that try to fix the issue just leave the wife or go look for a shaman |
|
|
|
Causes for infertility |
Men and women are equally likely to cause it. For men can be too little sperm, quality May be poor because of diesease, or it may have bad motility which means it’s slow do it doesn’t make it to the fallopian tubes. Or age like over 40 it takes three times longer to impregnate. Women issues are in the ovulation which can happen with dieases, alchool abuse, over/under weight, and age because they can’t ovulate. 40 |
|
|
|
treatments for infertility |
Assisted reproductive methods technologies are for the infertile or single women. Which are listed below Intrauterine insemination is a procedure of injecting Sperm directly into the uterus. Usdualy dor men problems also gays. This is where the Sperm comes from. This is the simplest and cheapest way which has a 10-20% success rate per trial. For women in ovulation problems then drugs help with mimics the activity of the hormones which help the quality and quantity of follicles. It’s a 22-35% success rate when in 4 trials. But they carry risks for blood clots, kidney damage, and damage to the ovaries. But it makes 10-25% of double birth. Although this is bad. After you take the fertile drugs which will stimulate growth of numerous follicles in the woman’s ovaries, the ripe ova are then extracted from her body and combined with the man’s sperm. The most promising two or three zygotes will be placed in the uterus. But the baby turn out fine. It’s close to 50% but 38-40 it’s 24% but 42 is 4 % and it’s pricey. |

|
|
|
Milestones of prenatal development: week 9-38 |
Fetal 9-12 weeks: genitals form and releases sex hormones; fingernails, toenails, and taste buds develop; heartbeat audible with stethoscope. You know it’s a boy when their is more activity 13-24 week mother feels movements; fetus kicks, turns, hiccups, sucks thumb, breathes amniotic fluid; responds to sounds, especially music and familiar voices; Vernon and lanugo develop on skin 25-38 weeks: lungs develop fully: ovar Two thirds of birth weight is gained; brain developments accelerates; sleep-wake cycles resemble newborns |

|

