![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
112 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the soft tissue analogue of a dentigerous cyst? |
Eruption cyst |
|
|
How big must a dentigerous cyst be before it is considered a dentigerous cyst?
|
>3.0mm from crown to edge of radiolucency
|
|
|
What is the histology of an OKC? |
Uniformally thin Devoid of rete pegs Prominent basal cell layer |
|
|
Will a dentigerous cyst recur? |
Not likely |
|
|
Will an OKC recur? |
Recurrence rate high 5-62% |
|
|
Which syndrome has multiple OKC? |
Basal Cell Carcinoma syndrome |
|
|
What are the features of gorlin (nevoid basal cell carcinoma) syndrome? |
Multiple basal cell carcinomas Multiple OKC Bifid ribs Calcified Falx Cerbri Frontal and temporoparietal bossing, hypertelorism, and mandibular prognathism Palmar Plantar pits |
|
|
Gorlin syndrome is caused by a mutation on what gene? and what chromosome? |
PTCH gene on chromosome 9q |
|
|
What is a calcifying odontogenic cyst also called? |
Gorlin cyst |
|
|
What is a gorlin cyst also called? |
Calcifying odontogenic cyst |
|
|
What cyst is associated with odontomas in younger age (17) |
Calcifying odontogenic cyst |
|
|
Where are calcifying odontogenic cyst most commonly found? |
65% found in incisor canine region Maxilla = mandible |
|
|
What is a ghost cell and what cyst is it associated with? |
Ghost cell = altered epithelial cells characterized by loss of nuclei with preservation of cell outline
Ghost cell is a characteristic feature of calcifying odontogenic cyst |
|
|
Will calcifying odontogenic cyst recur? |
few recurrences |
|
|
What age group do ameloblastomas usually occur? |
30-70s |
|
|
Average age for unicystic ameloblastoma |
23 |
|
|
Most common location for unicystic ameloblastoma |
Mandibular posterior |
|
|
Mean age for ameloblastoma |
35 |
|
|
3 patterns of ameloblastoma |
86% - Conventional solid or multicystic, plexiform, follicular 13% - Unicystic - within wall of cyst 1% - Peripheral - in soft tissue |
|
|
Which lesion is associated with snowflake calcifications? |
Adenomatoid odontgenic tumor |
|
|
Most common presentation for adenomatoid odontogenic tumor? |
Circumscribed unilocular radiolucency that involves crown of unerupted tooth, most often canine. |
|
|
What population are adenomatoid odontogenic tumors usually found? |
Age 10-19 Females 2x as much as males |
|
|
What is calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor also called? |
Pindborg tumor |
|
|
What is a pindborg tumor also called? |
Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor |
|
|
Most common location for calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor? |
Posterior mandible |
|
|
Liesegang ring calcifications is associated with what? |
Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor |
|
|
What is the recurrence rate of calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor? |
15% |
|
|
True mixed tumor of epithelial and mesenchymal elements |
Ameloblastic fibroma |
|
|
Most common site for ameloblastic fibroma? |
Posterior mandible |
|
|
Combination of Ameloblastic fibroma and odontoma |
Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma |
|
|
This tumor of the jaw is composed of ground substances such as glycosaminoglycans, which are made of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate |
Odontogenic Myxoma |
|
|
What are the three variants to ameloblastoma- plexiform and follicular presentations? |
Acanthomatous variant - forms keratin Granular cell variant - forms granular cells (ultrastructurally lysosomal elements) Basal cell variant |
|
|
Rare inflammatory condition of minor salivary glands |
Chelitis Glandularis |
|
|
Most common intraoral location for pleomorphic adenoma |
Palate (60%) Upper lip 20% Buccal Mucosa 10% |
|
|
2 10's of Warthin Tumor |
10% bilateral 10x males |
|
|
This salivary gland tumor characteristically has perineural invasion |
Adenoid cystic carcinoma |
|
|
Describe the four types of osteogenesis imperfecta |
Type 1 - most common, mildest, blue sclerae Type 2 - most severe 90% stillborn or die within 1 month Type 3 - most severe beyond perinatal period. Children usually die during childhood from cardiopulmonary complications due to kyphoscoliosis Type 4 - moderate sever bone fragility throughout life as opposed to type I which is preschool year |
|
|
This bone pathology is associated with cranial nerve compression |
Osteopetrosis |
|
|
Tx for osteopetrosis |
Interferon gamma 1-b with calcitriol |
|
|
dental findings for cleidocranial dysplasia |
Narrow-high arched palate numerous retained primary and unerupted supernumeray permanent teeth |
|
|
RL of several mm to several cm diameter in posterior mandible in post-menopausal females |
Focal osteoporotic marrow defect |
|
|
Generalized hypercementosis is pathognomonic for what disease? |
Paget's disease of bone |
|
|
Generalized widening of PDL is pathognomonic for what disease? |
Scleroderma |
|
|
Generalized loss of PDL is pathognomonic for what? |
Hyperparathryoidism |
|
|
What disease have histology similar to giant cell granulomas? |
Central giant cell granulomas Brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism Cherubism - multiple central giant cell granulomas |
|
|
What are the components of McCune-albright syndrome? |
-Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia -Cafe au lait macule with uniform pigmentation - large irregular edged "coast of Maine" macule -Endocrinopathoy |
|
|
Two types of edges of Cafe au lait macules and what is the difference? |
Coast of maine - irregular edge (McCune-Albright syndrome) Coast of california - smooth edge |
|
|
Superior displacement of mandibular canal is highly suggestive of what pathology? |
Fibrous dysplasia |
|
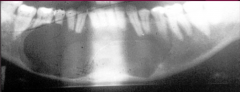
Well circumscribed, sharply defined border. Equidirectional expansion is characteristic.
|
Cemento-Ossifying fibroma |
|
|
It is important to differentiate fibrous dysplasia from what pathology? |
Cemento-Ossifying fibroma |
|
|
Why is it important to distinguish fibrous dysplasia from cemento-ossifying fibroma? |
The treatment modalities are different. Cemento-ossifying fibroma can be completely enucleated.
Cemento-ossifying fibroma does not usually recur |
|
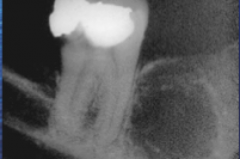
|
Focal osteoporotic marrow defect |
|
|
Phases of Paget's disease |
Stage 1 - Osteolytic Stage 2 - osteoblastic Stage 3 - combined |
|
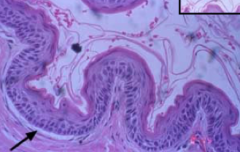
What disease has this histology? |
OKC |
|
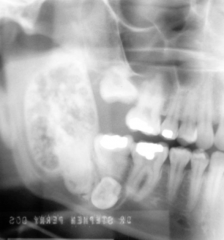
What is the ddx? |
Calcifying odontogenic tumor ameloblastic fibroodontoma |
|
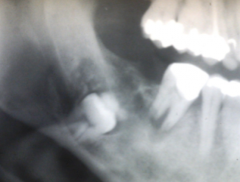
|
Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor |
|
|
CEOT is frequently associated with what? |
Impacted 3rd molars |
|
|
What syndrome has multiple osteomas? |
Gardner's |
|
|
What chromosome is affected in Gardner's syndrome? |
Chrosome 5 |
|
|
5 W's of post-op fever and what days |
POD1-2 - wind - pneumonia, aspiration, and pulmonary embolism POD3-5 - water - UTI, related to indwelling catheter POD4-6 - walking - DVT or pulmonary embolism POD5-7 - wound - surgical site infection POD7+ - wonder drug - drug fever, infection due to IV line, or reaction to blood products |
|
|
What is the prescription for penicillin? |
Pen VK (500mg/tab) Disp: 28 (twenty eight) Sig: One tab orally 4 times a day |
|
|
What is the prescription for amoxicillin? |
Amoxicillin (500mg/tab) Disp: 21 (twenty one) Sig: One tab orally 3 times a day |
|
|
What is the prescription for augmentin? |
Augmentin (500mg/tab) Disp: 21 (twenty one) Sig: One tab orally 3 times a day |
|
|
What is the prescription for cephalexin? |
Cephalexin (500mg/tab) Disp: 28 (twenty eight) Sig: One orally 4 times a day |
|
|
What is the prescription for clindamycin? |
Clindamycin (300mg/tab) Disp: 21 (twenty one) Sig: One orally 3 times a day |
|
|
What is the prescription for Zofran? |
Zofran (8mg/tab) Disp: 6 (six) Sig: One tab every 6 hours as needed for nausea |
|
|
What are the sources for the blood and nerve supply to the sternocleidomastoid muscle? |
Blood: Superior thyroid artery supplies middle third Occiptal artery - supplies remainder Nerve: spinal accessory nerve [CN] XI C2 and C3 |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN I |
Olfactory nerve - cribiform plate |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN II |
Optic nerve - optic foramen |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CNIII |
Occulomotor - superior orbital fissure |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN IV |
Trochlear - superior orbital fissure |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN V1 |
Trigeminal (Opthalmic) - Superior orbital fissure |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN V2 |
Trigeminal (Maxillary) - Foramen rotundum |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN V3 |
Trigeminal (Mandibular) - Foramen ovale |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN VI |
Abducens - Superior orbital fissure |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN VII |
Facial nerve - Internal acoustic meatus, facial canal, stylomastoid foramen |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: VIII |
Vestibulocochlear - internal acoustic meatus |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN IX |
Glossopharyngeal - Jugular foramen |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN X |
Vagus - Jugular foramen |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN XI |
Spinal accessory - Jugular Foramen |
|
|
What nerve and where does it exit: CN XII |
Hypoglossal - Hypoglossal canal |
|
|
What nerve exits through the superior orbital fissure? |
3-Occulomotor 4-Trochlear 5-Trigeminal V1 6-Abducens |
|
|
What nerves exit through the jugular foramen? |
9 - glossopharyngeal 10 - vagus 11- spinal accessory |
|
|
What are the attachments for the lateral pterygoid muscle? |
Superior head - origin: infratemporal surface of the greater wing of sphenoid insertion: articular capsule and disc Inferior head - origin: lateral surface of the lateral pterygoid plate insertion - pterygoid fovea of the condyle |
|
|
What are the intracranial branches of the facial nerve? |
Greater petrosal nerve Nerve to stapedius Chorda tympani |
|
|
Cutaneous nerves from V1 |
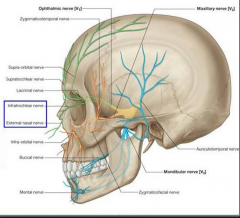
Supra-orbital Supratrochlear Lacrimal Infratrochlear External nasal |
|
|
Cutaneous nerves from V2 |
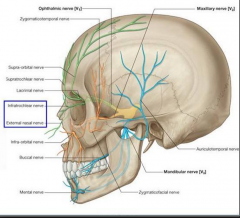
Infra-orbital Zygomaticofacial Zygomaticotemporal |
|
|
Cutaneous nerves from V3 |
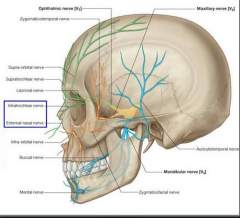
Auriculotemporal Buccal Mental |
|
|
Which bones form the orbital cavity? |
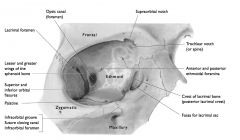
Maxillary Frontal Zygomatic Ethmoid Lacrimal Sphenoid Palatine Many Friendly Zebras Enjoy Lazy Summer Picnics
|
|
|
What does SMAS stand for? and what muscles does it consist of? |
Superficial musculoaponeurotic system -platysma -risorius -triangularis -articularis
|
|
|
Components of MEN Type 1, 2a, 2b |
I - pitiuitary tumors, parathyroid tumors, pancreatic tumors IIa - Medulary thyroid carcinoma, pheochromocytoma, parathyroid hyperplasia IIb - Medullary thyroid carcinoma, mucosal neuromas, pheochromocytoma |
|
|
8 Branches of the External Carotid Artery starting from inferior moving superior |
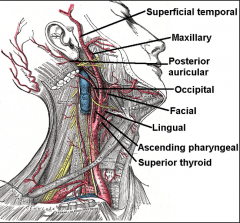
Some Angry Ladies Fight Off PMS Superior thyroid Ascending pharyngeal Facial Occipital Posterior auricular Maxillary Superficial temporal |
|
|
What are the most common vessels involved with anterior epistaxis? |
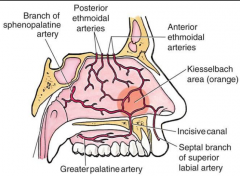
Kiesselbach's plexus of septum. Four arteries that make it up are: Sphenopalatine Anterior ethmoidal Greater palatine Superior labial
|
|
|
What is the space between open eyelids called? |
The palpebral fissure (rima) |
|
|
What is the autonomic innervation to the lacrimal gland? |
Superior salivatory nucleus --> facial nerve --> greater petrosal --> pterygopalatine ganglion --> zygomatic nerve --> lacrimal nerve --> lacrimal gland |
|
|
What occurs during the autonomic nerve supply to the pupil? |
Sympathetic: Postganglionic fibers from superior cervical chain reach the dilator pupil muscles via short and long ciliary nerves Parasympathetic: Edinger-Westphal nucleus in brain travel to ciliary ganglion to the orbit via the oculomotor nerve |
|
|
What are the sebaceous and sweat glands of the eyelids called? |
Sebaceous = glands of Zeis Sweat = gland of Moll |
|
|
What are crocodile tears? |
Injury to facial nerves carrying parasympathetic fibers that normally innervate the salivary gland heal with the lacrimal gland nerve fibers leading to crying when patient eats. |
|
|
What are the contents of the carotid sheath? |
Carotid artery, Jugular vein, and vagus nerve |
|
|
What are the layers of the scalp? |
Skin Connective Tissue Aponeuoriss Loose areolar tissue Periosteum or pericranium |
|
|
What nerves innervate the TMJ? |
Auriculotemporal V3, masseteric of V3 |
|
|
How do you tests the five branches of the facial nerve clinically? |
Temporal - raise eyebrows Zygomatic - squeeze eyes closed Buccal - Smile Marginal Mandibular - Whistle or pucker lips Cervical - constrict platysma |
|
|
What are each of the portions of the joint capsule responsible for in terms of movement? |
Upper joint - gliding Lower joint - rotation |
|
|
What is bright on T1 vs T2 weighted MRIs? |
T1 = Fat T2 = Water |
|
|
What are the components of Horner's syndrome? What is damaged? |
Miosis (constrictd pupil) Ptosis (weak, droopy eyelid) Anhidrosis (decreased sweating) Sympathetic trunk damage |
|
|
Which jaw movement is most stable? |
Maxilla Up Mandible Forward Chin any direction |
|
|
Which jaw movement is stable but not highly stable? |
Maxilla Forward Maxilla Asymmetry |
|
|
Which jaw movement is stable with rigid fixation only? |
Mx Up + Mn Forward Mx Forward + Mn Back Mandible, Assymetry |
|
|
Which jaw movement is unstable? |
Mandible back Maxilla down Maxilla wider |
|
|
How big must a dentigerous cyst be before it is considered a dentigerous cyst? |
>3.0mm from crown to edge of radiolucency |
|
|
What is the distance between the external auditory canal and the temporal branch of the facial nerve? |
8-35mm Average is 20mm |
|
|
Describe the House-Brackmann scoring system?
|
-Superior movement of the mid portion of the eye brow-lateral movement of the angle of the mouth-each 0.25cm with max of 1cm is given 1 point-max points = 8
|

