![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The nervous system is composed of ? |
nervous tissue, blood vessels, and connective tissue |
|
|
What two cell types are found in nervous tissue? |
neurons and neuroglial cells |
|
|
Function of neurons? |
react to physical and chemical reactions in their surroundings -send and receive signals |
|
|
Function of Neuroglial? |
cells that support and protect neurons |
|
|
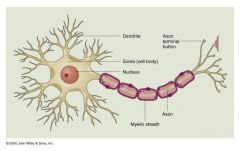
What are dendrites ? |
small cellular processes that receive input |
|
|
What are axons? |
long cellular processes that carry information away from neurons |
|
|
What are nerve impulses? |
bioelectric signals produced by neurons |
|
|
What are nerves? |
bundles of axons |
|
|
What is a synapse ? |
the small space between a neuron and the cells with which it communicates |
|
|
What are Neurotransmitters? |
biological messengers produced by neurons |
|
|
What is the central nervous system composed of? |
it contains the brain and the spinal cord |
|
|
What is the peripheral nervous system composed of ? |
it contains the cranial and spinal nerves |
|
|
What are three general functions of the nervous system ? |
sensory, motor, and integrative |
|
|
Sensory receptors are located ___________________ of peripheral neurons and provide the ____________ function of the nervous system. |
at the ends, sensory |
|
|
What is the function of receptors? |
To gather information |
|
|
What do receptors do with the information they receive? |
they convert their information into nerve impulses, which are transmitted over peripheral nerves to the central nervous system. |
|
|
What do the motor functions of the nervous system do? |
use neurons to carry impulses from the central nervous system to the effectors |
|
|
Examples of effectors? |
muscles and glands |
|
|
Two divisions of the motor division of the nervous system? (Peripheral Nervous System) |
Somatic and Autonomic |
|
|
Function of the Somatic Nervous System? |
-involved in conscious activities -controls skeletal muscle contractions |
|
|
Function of the Autonomic Nervous System? |
-involved in unconscious activities -controls smooth and cardiac muscle |
|
|
Three parts of all neurons? |
cell body, axon, and dendrites |
|
|
What does a neuron's cell body contain? |
granular cytoplasm, mitochondria, lysosomes, a Golgi appartus, and many microtubules. It also contains are large nucleus, chromatophillic substance, and cytoplasmic inclusions. |
|
|
What are neurofibrils? |
fine threads that extend into axons |
|
|
What is Chromatophillic substance? |
a membranous sac that contains rough endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Mature neurons generally do/do not divide but neural stems cells do/do not |
do not, do |
|
|
Why are dendrites usually high branced? |
to provide receptive surfaces to which processes from other neurons communicate |
|
|
Dendritic spines are? |
tiny, thornlike spines on the surface of dendrites |
|
|
What is an axonal hillock? |
the initial portion of an axon closest to the cell body |
|
|
What is an axon specialized to do? |
Carry nerve impulses away from the cell body |
|
|
What does the cytoplasm of an axon include? |
mitochondria, microtubules,and neruofibrils |
|
|
What are collaterals? |
branches of axon |
|
|
What is a synaptic knob? |
a specialized ending of an axon |
|
|
What is a synaptic cleft? |
the space between a synaptic knob and the receptive surface of another cell |
|
|
What is axonal transport? |
the process an axon uses to convey biochemicals that are produced in the neuron cell body |
|
|
What is the function of Schwann cells ? |
produce myelin |
|
|
What is myelin? |
a lipid rich substance |
|
|
What is a myelin sheath ? |
a coating produced by Schwann cells that is wrapped around an axon |
|
|
What is a neurileema ? |
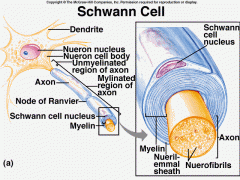
a portion of a Schwann cell outside of the myelin sheath |
|
|
What is a node of Ranvier? |
a narrow gap between myelin sheaths |
|
|
Myelinated axons have? |
Myelin sheaths |
|
|
Unmyelinated axons have? |
no Myelin sheaths |
|
|
White matter is composed of? |
myelinated axons |
|
|
Gray matter is composed of? |
unmyelinated axons, dendrites, and cell bodies of neurons |

