![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Define Structural Adaptations |
Physical characteristics of the body that gel it to survive e.g hair, spikes |
|
|
|
Define Physiological Adaptations |
Body functions that help it to survive e.g sweating, vomitting |
|
|
|
Behavioural Adaptations |
Physiological decisions that help it to survive e.g hiding from predators |
|
|
|
Define Homeostasis |
The maintainence of a stable interval environment kept within narrow limits. |
|
|
|
Define Thermoregulation |
Regulation of body temperature |
|
|
|
Define Pokilothermic |
Body temperature varies with environmental temp (not birds or mammals) |
|
|
|
Define Homeorhermic |
Body temperature is constant. Birds and Mammals |
|
|
|
Sources of Body Heat |
Ectotherm - Environment Endotgerms - Metabolism e.g food gets converted to heat |
|
|
|
What is Giberllin? |

It is a plant hormone., which increases the length of the Stems, allowing more fruit and leaves to grow |
|
|
|
What are 2 great adaptations that organisms? |
Animal - Concentrated urine Plant - Desert plants have less stomata |
1 plant and 1 animal |
|
|
Define a Diurinal Animal |
Animals such have fluctuating body temperatures. |
|
|
|
Define Monogomy |
One male mates with one female. |
|
|
|
Define Polygamy |
Males and females have multiple partners for a season. |
|
|
|
Define R selection |
Quick and many - little parenting care of offspring -fast sexual maturity -higher chance of species survival |
|
|
|
Define K Selection |
Slower and Fewer -More advanced species develop from long pregnancies -Longer Lives -trained offspring |
|
|
|
Define Oviparity |
Eggs are released by the mother and develop outside her body. There are enough nutrients in the yolk to enable growth. |
|
|
|
Vivaparity |
Embryos develop inside a mothers body and are born as copies of the adult e.g Humans |
|
|
|
What does an ecosystem consist of? |
-The living community -The non living surroundings -The interaction between the living and the non living |
3 |
|
|
What is the major source of energy? |
SUN |
|
|
|
What are the 4 types of consumers? |
Herbivores - Plant eaters e.g cows Carnivores - Animal Eaters e.g tigers Omnivores - Eat both plant and animals e.g Humans Detritivores - Decomposing matter Eaters e.g Dung Beetles |
|
|
|
Define Competition |
Animals competing for something e.g food |
|
|
|
Whay is a Predator-Pray relationship? |

One species eats another e.g Lion eats zebra |
|
|
|
What is Parasitidm? |
One species suffers, other species benefits e.g worms in humans |
|
|
|
What is Mutualism? |
Both species benefits e.g clown fish and anonme |
|
|
|
What is commensalism? |
One species benefit the other nor gains or harms. |
|
|
|
Where do we lose energy from? 6 |
-Body temperature maintainence -Muscle Contraction -Synthesis of biomolecules -Producing new cells -Nerve Impulses RESPIRATION |
|
|
|
How much % of Energy do we get from the sun? |
1% |
|
|
|
How much energy is lost from the first trophic level to the last? |

90% is loose and 10% carries on to the next trophic level |
|
|
|
What are the ecological pyramids? 3 |
Pyramid of numbers Pyramid of energy Pyramid of biomass |
|
|
|
What is the pyramid of numbers? |

Shows number of organisms at each level. |
|
|
|
What is the pyramid of biomass? |

Shows total mass of organisms at each level. |
|
|
|
What is the pyramid of energy? |

Shows total energy of organisms at each level. |
|
|
|
What does species richness depend on? |
Size of an area Latitude |
|
|
|
Define Abundance of Population |
The number of individuals per unit area. Basically another term for density. |
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of distribution? |

Uniform Random Clumped |
|
|
|
Which is the most common type of Population distribution? |
Clumped |
|
|
|
Define Succesion |
Means one after the another. It's the nature's formation of a community over time. |
|
|
|
Define Primary Succesion |
New species grown in an area not previously colonised. |
|
|
|
Define Secondary Succession |
A major event removes original community (e.g FIRE) and a new community forms. |
|
|
|
Why are introduced species so bad? |
They are successful predators of native species. They bring DISEASES. INTERSPECIFIC COMPETITIONKILLS NATIVE SPECIES KILLS NATIVE SPECIES |
|
|
|
What type of growth is a J shape curve? |

It is exponential growth. Exponential growth is the unlimited growth of a population. |
|
|
|
What is Lofistic growth? |

Also known as Density dependant growth as it depends on factors such as carry Capacity (K). It is S shaped! |
|
|
|
Define Density Dependant |
Factors whose impact is related to population size are said to fee density dependant. E.g disease, lack of food |
|
|
|
Define Density Independent |
Population are also affected by droughta, bushfire and floods that are density dependant. It is not influenced by the population size. |
|
|
|
First Trophic Level are and examples |

PRODUCERS Grasses Trees and Shrubs Ferns Phytoplankton Algae |
|
|
|
2nd Trophic Level are and examplea |

PRIMARY CONSUMERS HERBIVORES Plant eating insects Small Birda Possums ZooPlankton Whelks |
|
|
|
3rd Trophic Level |

SECONDARY CONSUMERS Carnivores Antechinus Owls Starfish Smallfish |
|
|
|
4th Trophic Level |

TERTIARY CONSUMERS Snakea Eagles Large Fish Sharks |
|
|
|
FOOD CHAINS |

|
|
|
|
FOOD WEBS |
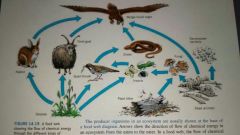
|
|

