![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Kinetics |
Study of reaction rate |
|
|
|
Reaction rate |
Speed of a chemical reaction. (Kinetics) |
|
|
|
What two things occur during a chemical reaction? These two things happen at the same rate. |
Products appear; products disappear |
|
|
|
What theee factors affect reaction rate? |
1. Reactant concentration 2. Temperature 3. Nature of a reactants |
|
|
|
What is reactant concentration |
Used to control reaction rate |
|
|
|
What needs to happen with molecules during a reaction? |
The molecules need to collide. |
|
|
|
What generally happens to the reaction rate when the temperature raises every 10 C°? |
The reaction rate doubles for every 10 C° increase |
|
|
|
Concentrations depend on this for solute-to-solution ratios. |
Molarity |
|
|
|
M= |
M= moles of solute/liters of solution |
Used for kinetics |
|
|
Rate |
How much a quantity changes in a given period of time |
|
|
|
How can time be represented? |
M/hr M/min M/sec |
|
|
|
What symbol is this: Δ |
Delta |
|
|
|
Rate = |
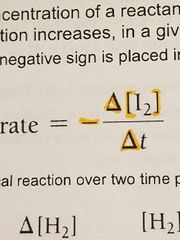
|
|
|
|
What does [ ] represent in a rate equation? |
Concentration |
|
|
|
Concentration |
Equals M (molarity) |
|
|
|
What equation is used for a rate of chemical reaction over two time periods? |
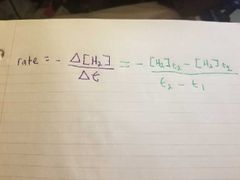
|
|
|
|
In a rate equation, the rate must be... |
Positive. This is why there is a negative sign on the right side of the equation. This will make the rate positive. |
|
|
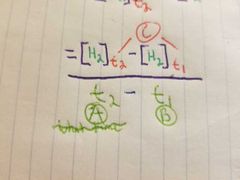
What is the breakdown of the two time period rate equation? |
A) the time that we stopped timing B) the time we starter timing C) time |
|
|
|
What are the two "rate equations"? |
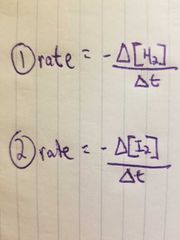
|
|
|
|
In a rate equation... A) & B) |
A. If coefficients are present: Rate= rate of reaction B. If coefficients are NOT present: Rate= rate of change |
|
|
|
What is the symbol for rate of reaction? |
Δ[ ] / coefficient Δt |
|
|
|
What is the rate for change? |
Δ [ ]/ Δ t |
|
|
|
aA + bB 》 cC dD What does the lower case represent? |
Coefficient |
|
|
|
Review this formula |
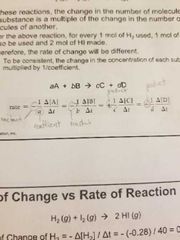
|
|
|
|
The rest of this equation is? Rate of reaction = And give its relation equation. |
Rate of reaction = 1/coefficient × (rate of change) Or Rate of reaction (coefficient) = rate of change |
|
|
|
Define Rate law |
Equation that relates the initial reactant concentration to the initial rate of the reaction. |
This rate law MUST be determined experimentally |
|
|
What is the rate law? |
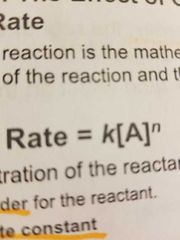
|
|
|

What do the n and k represent? |
n= order for the reactant k= rate constant |
|
|
|
For reaction "aA + bB > products", the rate law will appear as |

|
|
|

What do m and n represent in this equation? |
They are called the orders for each reactant |
|
|
|
What are the exponents on each reactant in a rate law? |
Orders |
|
|
|
Can exponents be negative or fractions in a rate law? |
Yes |
|
|
|
What order is: Rate = k[A]^n |
Zero order |
|
|
|
The rate of the reaction does not change. What order is this? |
Zero order |
|
|
|
Exponent (order) of 0 receives what value? |
Zero order receives order of 1. This means the value does not change. |
|
|
|
Zero order rate constant k units: |
M/s = m x s^-1 |
|

