![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Phase |
Homogeneous part of the system in contact with other parts of the system but separate from them by a well defined boundary |
|
|
Intermolecular forces |
Attractive forces between molecules |
|
|
Intramolecular forces |
Attractive forces that hold atoms together in a molecule |
|
|
Which is weaker? Intermolecular forces or intramolecular forces? |
Intermolecular forces |
|
|
Dipole-dipole forces |
Attractive forces between polar molecules |
|
|
Ion-Dipole Forces |
Attractive forces between ion and polar molecules |
|
|
Dispersion (London) forces |
Temporary dipoles induced in atoms or molecules |
|
|
Polarizability |
Ease with which the electrons distribution in the atom or molecule can be distorted |
|
|
Polarizability increases with... |
Greater number of electrons or more diffuse of electron cloud |
|
|
Dispersion force usually increases with... |
Molar Mass |
|
|
Hydrogen Bond |
Special dipole-dipole interaction between the hydrogen atom in a polar N-H, O-H, or F-H bond and an electronegative O,N, or F atom |
|
|
What makes hydrogen bond different? |
-decreasing molar mass -decreasing boiling point |
|
|
Surface tension |
Amount of energy required to stretch or increase the surface of a liquid by one unit area |
|
|
Cohesion |
Intermolecular attraction between like molecules |
|
|
Adhesion |
Attraction between unlike molecules |
|
|
Viscosity |
Measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It is a result of strong intermolecular forces |
|
|
Crystalline solid |
Possesses rigid and long range order. When they are solid, atoms, molecules, or ions occupy specific (predictable) positions |
|
|
Amorphous Solid |
Does not possess a well defined arrangement and long range molecular order |
|
|
Unit cell |
Basic repeating structural unit of a crystalline solid |
|
|
Equallibrium vapor pressure |
Vapor pressure measured when a dynamic equallibrium exists between condensation and evaporation |
|
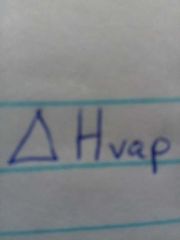
Molar heat of vaporization |
Energy required to vaporize 1 mole of a liquid at it's boiling point |
|
|
Boiling point |
The temperature when equallibrium vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the external pressure |
|
|
Normal boiling point |
The temperature when a liquid boils when the external pressure is 1 atm |
|
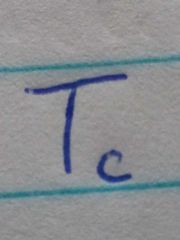
Critical temperature |
The temperature above which the gas cannot be made to liquify no matter how much pressure applied |
|
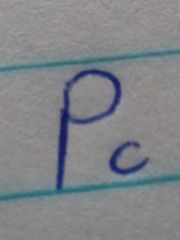
Critical pressure |
The minimum pressure that must be applied that bring the liquidation at the critical temperature |
|
|
Melting point of a solid and freezing point of a liquid |
Temperature at which the solid and liquid coexist in equallibrium |
|
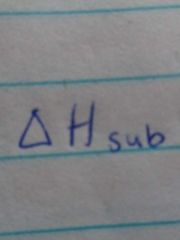
Molar heat of sublimation |
Energy required to sublime 1 mole of a solid |
|
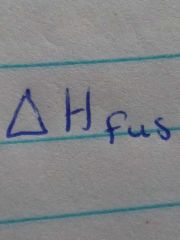
Molar heat of fusion |
Energy required to melt 1 mole of a solid substance at it's freezing point |
|
|
Phase diagram |
Summarizes the conditions at which a substance exists as a solid, liquid, or gas |

