![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Radioactivity |
The emission of high-energy particles that can: penetrate living tissues and kill cells by damaging DNA |
Kill cells damage _____ and penetrate living ______. |
|
|
When is Radiation the most dangerous? |
When exposure is uncontrolled and when it (radiation) covers most or all of the body |
|
|
|
Matter |
Anything that occupies space and has mass |
Space and ______ |
|
|
Matter is in three physical spaces: |
1) solid 2) liquid 3) gas (vapor) |
Slg |
|
|
What three spaces does water occupy? |
1) ice 2) water 3) vapor |
Iwv |
|
|
How many natural occurring elements are there? |
92 elements like Carbon, Oxygen, Gold, Hydrogen (are common) |
|
|
|
Mass |
Measure of amount of material in an object |
|
|
|
Element |
Substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions |
|
|

Memorize where the atomic # is and what it represents |
Atomic # = # of protons Atomic mass = mass of average atom of that element |
|
|
|
Of the naturally occurring elements _______ are essential to people... |
25 |
|
|
|
Four of these elements make up about 96% of the weight of our body...what are they? |
1) oxygen (O) 2) carbon (C) 3) hydrogen (H) 4) nitrogen (N) |
|
|
|
Besides O, C, H, and N, what other elements are we made of? |
Calcium (Ca), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), Sulfur (S), Sodium (Na), Chlorine (Cl), Magnesium (Mg) |
|
|
|
Trace elements |
-required in only small amounts -essential for life |
|
|
|
When elements combine |
Compound so substances that contain two or more elements in a fixed ratio |
Common compound examples: NaCl (table salt and chlorine), & H2O = water |
|
|
Atom |
Smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element |
|
|
|
What is the structure of an atom? |

|
Acronym: pen |
|
|
Nucleus |
The atom's central core |
|
|
|
Atom's mass # |
Sum of the protons and neutrons in its nucleus |
|
|
|
Isotopes |
Manipulate and are the alternate mass forms of an element, they also have the same # protons and electrons but DIFFER in neutrons |
|
|
|
How do I add for the mass #? |
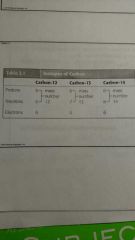
|
|
|
|
Radioactive isotope |
An isotope which the nucleus decays spontaneously |
|
|
|
Chemical bonds |
Reactions in which atoms remain close together, held by attractions |
|
|
|
Ions |
Atoms or molecules that are electrically charged as a result of gaining or losing electrons |
|
|
|
Ionic bonds |
Are formed between oppositely charged ions |
|
|
|
Ionic compounds |
Compounds like table salt that are held together by ionic bonds |
|
|
|
Ionic bonds ....need |
To ionize to come together |
|
|
|
Covalent bond |
Forms when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons |
|
|
|
Covalent bonds ____________ |
-are the strongest of the various bonds -hold atoms together in a molecule |
|
|
|
Sharing one pair = |
Single covalent bond |
|
|
|
Why is water special? |

1) it's sharing, but it's uneven sharing aka a polar molecule 2) because it is electro negative and has a special type of attraction |
|
|
|
An uneven distribution of charge... |
Polar molecule |
|

