![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
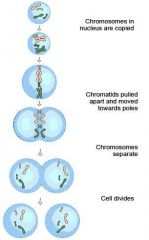
Mitosis |
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle process by which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. Includes Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase. |
|

Interphase |
G1 phase is the first of four phases of the cell cycle where the cell grows in size and synthesizes mRNA and proteins in preparation for subsequent steps leading to mitosis. G1 phase ends when the cell passes the G1 checkpoint and moves into the S phase. S phase is when the DNA is replicated before the G2 phase, where the cell makes it's final preparation for cell division. First it must pass the G2 checkpoint to ensure all DNA is favorable. |
|
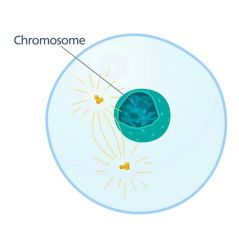
Prophase |
Prophase -the first stage of mitosis, during which the chromosomes condense and become visible, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and the spindle apparatus forms at opposite poles of the cell |
|
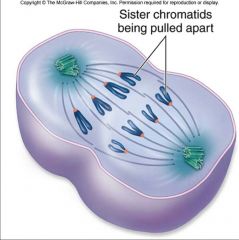
Anaphase |
During anaphase, the two sister chromatids of each chromosome are pulled apart by the spindle and dragged by their centromere toward opposite poles of the cell. The movement results from a shortening of the spindle microtubules. |
|
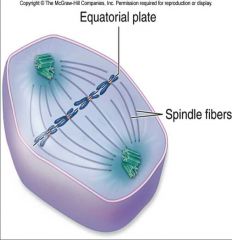
Metaphase |
Metaphase — the second stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle — the chromosomes, pulled by the spindle fibers, line up along the middle of the cell, halfway between the centrosomes in the middle of the dividing cell. |
|

Telophase |
Telophase - the final stage of Mitosis or Meiosis, the nuclear membranes re-form around each set of chromatids, the nucleoli also reappear, creating sister cells. Spindle fibres degenerate.The chromosomes also unwind back into the expanded chromatin that is present during interphase. |
|
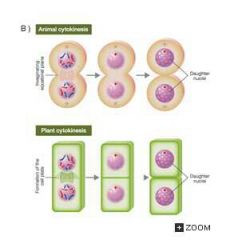
Cytokinesis |
Cytokinesis is the physical process of cell division, which divides the cytoplasm of a parental cell into two daughter cells. |
|
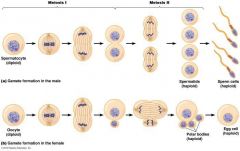
Meiosis |
Meiosis begins with a parent cell that is diploid, meaning it has two copies of each chromosome. The parent cell undergoes one round of DNA replication followed by two separate cycles of nuclear division. The process results in four daughter cells that are haploid, which means they contain half the number of chromosomes of the diploid parent cell. |
|
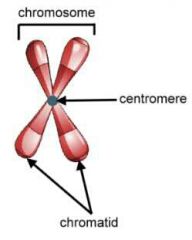
|
A chromosome is a strand of DNA that is encoded with genes. In most cells, humans have 22 pairs of these chromosomes plus the two sex chromosomes (XX in females and XY in males) for a total of 46. |
|
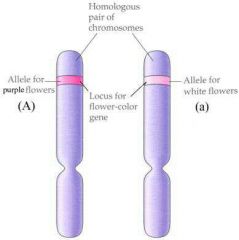
|
Heterozygous |

