![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What takes place in the mitochondria?
|
Most of the reactions for respiration.
|
|
|
What can pass through a semi-permeable cell membrane during osmosis?
|
Oxygen, Glucose, Amino Acids and Water
|
|
|
What can't pass through a semi-permeable cell membrane during osmosis?
|
Starch and Protein.
|
|
|
What is made in the ribosomes?
|
Proteins.
|
|
|
What is the order of cell organisation?
|
Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ Systems.
|
|
|
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
|
Carbon Dioxide + Water ---(Sunlight)---> Glucose + Oxygen
CO2 + H2O ---> C6 H12 O6 + O2 |
|
|
How many cells make up yeast?
|
1 - Yeast is a single celled organism.
|
|
|
What is in a yeast cell?
|
Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Mitochondria.
|
|
|
What is unique about bacterial cells?
|
There is no nucleus and they have no mitochondria but can still respire aerobically.
|
|
|
What are enzymes?
|
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions.
|
|
|
What denatures an enzyme?
|
If the temperature is too hot or too cold.
|
|
|
What is respiration?
|
A series of chemical reactions that release energy by breaking down large food molecules.
It happens in every living cell. |
|
|
What are the two types of respiration?
|
Aerobic and Anaerobic
|
|
|
Which type of respiration releases more energy?
|
Aerobic as it releases more energy per glucose molecule.
|
|
|
What is the equation for aerobic respiration?
|
Glucose + Oxygen ---> Carbon Dioxide + Water (+ Energy Released)
C6 H12 O6 + 6O2 ---> 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ Energy Released) |
|
|
What is the equation for anaerobic respiration?
|
Animals and Plants
Glucose ---> Lactic Acid (+ Energy Released) Plants and Microorganisms Glucose ---> Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide (+ Energy Released) |
|
|
What are the three main ways plants use glucose?
|
Respiration, Makes Chemicals For Growth and Is Stored As Starch.
|
|
|
What are the three factors that effect the rate of photosynthesis?
|
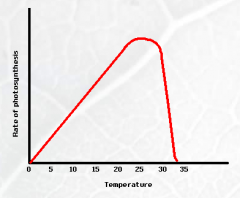
Light, Carbon Dioxide and Temperature.
|
|
|
What is DNA?
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid.
A DNA molecule has two strands coiled together in the form of a double helix. |
|
|
What are DNAs four different bases?
|
Adenine ---- Thymine
Guanine ---- Cytosine. |
|
|
What are the pairs of the bases that make up DNA?
|
A-T
C-G |
|
|
What is a gene?
|
A section of DNA that contains instructions for one particular protein.
|
|
|
How do cells make proteins?
|
They join amino acids together in a particular order.
|
|
|
How many sets of bases in the DNA codes for one amino acid?
|
Three bases (called a triplet).
|
|
|
What is Messenger RNA?
|
A molecule that copies one strand of the DNA and uses base paring to ensure an exact match.
|
|
|
How does the DNA reach the ribosomes?
|
The messenger RNA molecule moves the single strand of DNA out of the nucleus to the ribosomes as the original DNA would be too big to leave the nucleus.
|
|
|
After the messenger RNA reaches the ribosomes what is the ribosomes job?
|
Its job is to stick amino acids together in a chain to make proteins.
|
|
|
What happens during the first stage of Mitosis?
|
The cell physically grows so that when the cell duplicates the DNA has enough space to be contained.
|
|
|
What happens during the second stage of Mitosis?
|
Once the cell has two copies of its DNA the cell goes through division where the cell forms x-shaped chromosomes with each arm being a duplicate of the other.
|
|
|
What happens during the second stage of Mitosis?
Pt. 2 (After the X-shaped chromosomes are made.) |
The chromosomes line up in the centre of the cells and cell fibres pull them apart, the two arms of each chromosome go to opposite ends of the cell, membranes form around each of the sets of the chromosomes to become the nucleus and then the cytoplasm divides into two separate but genetically identical cells.
|
|
|
What are sperm cells and egg cells called and what do they combine into?
|
They are both gametes and combine to make a zygote.
|
|
|
Why do gametes only contain half the chromosomes?
|
Gametes contain half the chromosomes so that it can have half of the chromosomes from each parent.
|
|
|
Gametes are produced by Meiosis. What is Meiosis?
|
Meiosis is a form of cell division which causes the cells to have half the amount of the normal number of chromosomes (this only happens during the reproductive cycle).
|
|
|
During meiosis what happens before the first division?
|
It duplicates its DNA into X-shaped chromosomes.
(There are two sets of DNA (1 from the father and 1 from the mother)). |
|
|
What happens during the first division during meiosis?
|
They line up in the centre of the cell and are then pulled apart so each new cell only has one copy of each chromosome, both some of the fathers and some of the mothers chromosomes go into each cell.
|
|
|
What happens during the second division during meiosis?
|
The chromosomes of the singular DNA line up and the arms of the X-shaped chromosomes are split apart and you end with four gametes with only a single set of chromosomes in it.
|
|
|
What happens after two gametes join together at fertilisation?
|
The zygote grows repeatedly dividing though mitosis.
|
|
|
What are embryonic stem cells?
|
A zygote that has divided through mitosis to provide undifferentiated cells so they can produce any type of specialised cell.
|
|
|
How is cloning used to make stem cells?
|
The genetic material is removed from an egg and a nucleus from an adult body cell is inserted into the newly emptied egg cell than (under the right conditions) the inactive genes are reactivated to form an embryo from which embryonic stem cells can be extracted.
|
|
|
What is a meristem?
|
A meristem is a tissue which contains the only cells that are mitotically active (can be divided by mitosis) and are located in areas where the plant is growing (such as the roots and shoots).
|
|
|
What does a meristem allow?
|
It allows unspecialised cells to be divided limitlessly for as long as the plant lives.
|
|
|
How does cloning a plant work?
|
Plants can be cloned by taking cuttings from the original plant and putting in soil as the plant will have meristem tissues in it meaning it would have unlimited stem cells to create a new plant.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of rooting powder?
|
As cuttings of plants don't always grow adding rooting powder releases auxins (plant hormones) which produces roots rapidly which means that plants can be cloned very quickly.
|
|
|
What is phototropism?
|
When a plant grows towards or away from light.
|
|
|
What is positive phototropism?
|
When the leaves and stems of a plant grow towards the light as it is needed of photosynthesis.
|
|
|
What is negative phototropism?
|
When the roots of the plant grow away from the sunlight to absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
|
|
|
What are auxins?
|
Chemicals that speed up the growth near the roots, tips, and shoots of a plant. Auxins in the tips diffuse backwards to stimulate cell elongation, If auxins are removed the plant may stop growing. Auxins in the tips concentrate themselves in the shaded area of the tip to speed up the elongation of the plant towards the sunlight.
|
|
|
What is the nervous system made up of?
|
The Central Nervous System (CNS), Sensory Neurons, Motor Neurons, Effectors and Receptors
|
|
|
What makes up the Central Nervous System?
|
The brain and the spinal cord.
|
|
|
What are sensory neurons?
|
The neurons that carry impulses from the receptors to the CNS.
|
|
|
What are motor neurons?
|
The neurons that carry impulses from the CNS to effectors.
|
|
|
What are effectors?
|
They make up muscles and glands which respond to nervous impulses and bring about a change.
|
|
|
What are receptors?
|
Cells that detect stimuli such as sound, taste and light.
|
|
|
What is the CNS?
|
The CNS is a processing centre - it receives information from the receptors and then coordinates a response.
|
|
|
What is the order from a stimulus to a response?
|
Stimulus ---> Receptor ---> Sensory Neurone ---> CNS ---> Motor Neurone ---> Effector ---> Response.
|
|
|
How is information transmitted around the body?
|
Information is transmitted around the body as electrical impulses through the axon of a neurone.
|
|
|
What are axons?
|
Axons are the cytoplasm of a cell which has been stretched out into a long fibre which is surrounded by a cell membrane.
|
|
|
Why do some neurons have fatty sheaths?
|
The fatty sheathes act as an electrical insulator shielding the neurone from neighbouring cells and speeding up the electrical impulse.
|
|
|
What is the gap between two neurones called?
|
A synapse.
|
|
|
How are electrical impulses transmitted between neurones through synapses?
|
When an electrical impulse reaches the end of the neurone it triggers the release of transmitter chemicals into the synapse, these chemicals diffuse across the synapse and binds the receptor molecules to the membrane of the next neurone. However only specific chemicals can bind the receptor molecules on the neurone and when the chemicals bind to the right receptors the create a new electrical impulse in the next neurone.
|
|
|
What does ecstasy do to the synapses?
|
It blocks the sites of the brain where the chemical serotonin levels are removed which means that the concentration of serotonin increases.
|
|
|
What is serotonin?
|
Serotonin is a chemical made in the body that is thought to affect things like pain, aggression, appetite and a persons mood. (More serotonin, happier mood.)
|
|
|
What are reflexes?
|
Reflexes are involuntary responses which are rapid, automatic responses to certain stimuli.
|
|
|
What is the route of a reflex?
|
The Reflex Arc which goes through the CNS to the sensory and motor neurones. (This is involuntary and rapid.)
|
|
|
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration in yeast?
|
Glucose ---> Ethanol + CO2
|
|
|
What is active transport?
|
The overall movement of chemicals across a cell membrane from low concentration to a higher concentration using energy from respiration.
|
|
|
How can reflex responses be modified?
|
They can be modified and learned by introducing a secondary stimulus. (A good example of this is Pavlov's dogs.)
|

