![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
285 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Packages can be defined by what three things? |
the product category, the substrate, or the end-user |
|
|
Consumer packaging is targeted directly at the ________ _______, and usually covers all products that are considered“_____ ______” |
householdconsumer, fast moving |
|
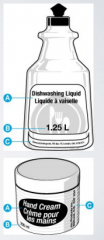
What is "A" on this image? |
The common or generic name of the product |
|
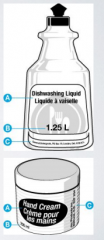
What is "B" on this image? |
A declaration of net quantity, generally in numericalcount or metric units of measurement (althoughsupplementary non-metric measurements may also beused) |
|
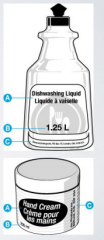
What is "C" on this image? |
The identity and address of the person by or for whomthe product was manufactured, sold, or imported (i.e.,the dealer identification). |
|
|
How will the "Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act; makingOntario Accessible by 2025" apply to packaging? |
Making packaging accessible through the use of braille and printed electronics. Also includes the talking package |
|
|
What are three traits of the primary package? |
1. Holds the product directly 2. Usually smallest unit of packaging 3. Goes home with the consumer |
|
|
What does secondary packaging do? |
Holds groups of primary packages together |
|
|
In what situation would some people call the secondary package a primary package? |
When you are buying a case that goes home, like a case of Coke. |
|
|
What is tertiary packaging? |
Bulk handling and warehouse storage |
|
|
What are the 6 functions of a package? |
1. Contain 2. Protect 3. Preserve 4. Provide convenience 5. Give information 6. Sell the product |
|
|
What are 4 points about the CONTAIN function of a package? |
1. Keep the product together 2. Can hold other packages together (secondary + tertiary) 3. We want to prevent leaks/spills 4. Lab testing is used to ensure thepackage contains 5. Specialized cameras manage riskareas during production |
|
|
In a carton, what causes the containment failure of "glue seams split" |
Wrong adhesives for board and conditons of use; por control of adhesive application conditions |
|
|
In a carton, what causes the containment failure of "tuck-in flaps work loose, tear"
|
Wrong board weight for the weight of the product; por cutting and creasing of the carton |
|
|
In bottles/caps, what causes the containment failure of "leakage at neck, misalignent of cap"
|
Dimensional inaccuracies in bottle and/or cap finish; wrong cap application force; wrong wadding material |
|
|
In bottles/caps, what causes the containment failure of "leakage at mould part line and/or injection point (plastic)"
|
Poor control of moulding conditions |
|
|
In sachets, what causes the containment failure of "leakage in seal areas"
|
Wrong sealing layer; poor control of sealing conditions; product in seal area |
|
|
In sachets, what causes the containment failure of "leakage in body of sachet"
|
Puncture by product or by external means |
|
|
In tubes, what causes the containment failure of "leakage at neck, misalignment of cap"
|
Dimensional inaccuracies in tube and/or cap finish; wrong cap application force; wrong dimension of orifice |
|
|
In tubes, what causes the containment failure of "leakage at base of tube"
|
Wrong sealing layer; poor control of sealing conditions; product in seal area |
|
|
What are three points about the PROTECT function of a package |
1. Product must besafe inside thepackage 2. Any time theproduct is handledthe package shouldprotect it 3. Fragile productshave moredemands |
|
|
What are 7 possible types of damages that can happen to a package or the product inside the package? |
1. Shock 2. Vibration 3. Static compression 4. Dynamic compression 5. Puncture 6. Environment (RH, temp, light,organisms) 7. Tampering |
|
|
What are the causes of shock damage? |
Falls from conveyors, pallets, vehicles, possibly due to poor stacking; shunts due to irregular movement along conveyors; drops due to manual handling; impacts in transit due to driving over poor road surfaces |
|
|
What are the effects of shock damage? |
Breakage; deformation |
|
|
What are the causes of vibration damage? |
Vibration occurs naturally in all types of transport. In road transport the effects are enhanced over the rear axle of the vehicle, and by any imbalance in the load. Irregular road surfaces also increase vibration |
|
|
What are the effects of vibration damage? |
Breakage; scuffng; product separation and/or settlement; loosening of screw caps; garments falling from hangers |
|
|
What are the causes of static compressiondamage?
|
Stacking in storage, made worse by damp conditions
|
|
|
What are the effects of static compression damage?
|
Breakage; crushing; load collapse |
|
|
What are the causes of dynamic compression damage?
|
Clamp truck pressure; severe vibration during transport |
|
|
What are the effects of dynamic compression damage?
|
Breakage, crushing, stack resonance |
|
|
What are the causes of puncture damage? |
Poor quality pallets, bad handling practices |
|
|
What are the effects of puncture damage?
|
Breakage; product spoilage; load collapse |
|
|
What are the causes of Environment damage (In terms of both Changes to Relative Humidity and Temperature)?
|
:oads left outside; goods stored in damp warehouses, or where climatic conditions are not controlled; goods shipped via and to different climate |
|
|
What are the effects of Environment damage (In terms of Changes to Relative Humidity )?
|
Product spoilage, e.g. corrosion; packaging failure, e.g. damp corrugated board case |
|
|
What are the effects of Environment damage (In terms of Changes in Temperature )?
|
Product spoilage; drying out of paper/board materials; |
|
|
What are the causes of Environment damage (In terms of exposure to Insects, rodents, birds, dust, dirt)?
|
Goods stored in warehouses not cleaned or treated for pest control, or where doors/windows are left open or badly ftting |
|
|
What are the effects of Environment damage (In terms of exposure to Insects, rodents, birds, dust, dirt)?
|
Product spoilage due to poor hygiene; contamination of product and pack |
|
|
What are the causes of Pilferage and tampering damage?
|
Goods exposed to uncontrolled personnel access; display on shelf |
|
|
What are the effects of Pilferage and tampering damage?
|
Loss of products; damaged packs and products; contamination; counterfeit products |
|
|
What 3 questions must we ask to decide what willprotect the product? |
1. What is the product? 2. What is the environment? 3. What are the properties(including cost) of availableprotective packagingmaterials? |
|
|
What are three points about the PRESERVE function of a package? |
1. Mostly applies to food/bev/pharma/cosmetics 2. You want to prevent/reduce changes due tobiological and chemical hazards that lead tospoilage 3. Always looking to extend shelf life |
|
|
What are teo types of spoliage? |
1. Biotic 2. Abiotic |
|
|
What causes biotic spoilage? |
microorganisms |
|
|
What causes abiotic spoilage? |
external factors such as oxygen,moisture, light, temperature, loss/gain of volatiles |
|
|
What do we monitor to avoid spoilage? |
water, light, temperature, oxygen, humidity,acidity |
|
|
REMINDER FOR ME: |
MAKE Q CARDS ON TABLE 3.7 FROM LECTURE 1 |
|
|
What are some convenience features on a package that benefits consumers? |
Special opening, perfs,reseals, lids, portiondispensing features, ring pullson cans, boil in a bag, bake inthe box, etc. |
|
|
What are some convenience features on a package that benefit Fillers/distributors/retailers?
|
Specialized structures, codingsystems for tracking, displaysystems |
|
|
Packaging is the main wayproducts are ______
|
Identified |
|
|
Packaging is a last chance at _______ |
Advertising |
|
|
Packaging is an opportunity for linkingmultiple ____ and ____ methods |
Media, Printing |
|
|
On a package there are ______ regulations toprovide certaininformation |
legal |
|
|
What are 8 examples of some of the information that go on a package? |
1. ingredients, 2. sell by dates, 3. price, 4. specialoffers, 5. manufacturersaddress, 6. contactinformation, 7. product title, 8. barcode |
|
|
The material on which we print is referred to as a _______ |
Substrate |
|
|
materials used in packaging that we do not directlyprint on we can call simply ________. |
materials |
|
|
What is one of the oldest forms of packaging? |
glass |
|
|
What are 3 common colours that glass comes in? |
-clear (flint) -green -amber |
|
|
What are the 6 steps in the general glass making workflow? |
Ingredients are: -mixed -melted -formed -annealed -coated -inspected |
|
|
What is cullet? |
recycled glass
|
|
|
What are 4 ingredients included in glass? |
-Silica sand -soda ash -lime stone - cullet |
|
|
At what temperature are the ingredients to the glass melted? |
over 1000 deg. celsius
|
|
|
What is Gob? |
the amount of glass needed to make a bottle |
|
|
What are the 5 advantages of glass as a packaging choice? |
-Inert (does not interact with or taint what it contains) -Great for long term storage -Good vertical strength for stacking -Can be hot-filled -Highly recyclable |
|
|
An advantage of glass is that it is inert. What segments of the market for which this advantage is especially important? |
Food and Pharmaceuticals |
|
|
What are the 5 disadvantages of glass as a packaging choice? |
-Heavy -Dangerous when broken -High energy costs for manufacturing -Cleaning glass is not so “green” -Expensive equipment |
|
|
What is another word for a blank mold for a glass package? |
parison
|
|
|
When forming glass you first make a parison or blank mold to be formed further by either: 1. _______ 2. ______ 3. _______ |
1. Blow-and-blow (BB) 2. Press-and-blow (PB) 3. Narrow neck press-and-blow (NNPB) |
|
|
What 2 things happen in the annealing stage f the glass making process? |
-Glass leaves the former at about 450 dec. celsius -The annealing lehr cools it slowly so it doesn’tcrack |
|
|
Glass is prone to surface_____ from friction |
scratches |
|
|
What is done to glass to prevent surface scratches from friction? |
Friction coating |
|
|
In terms of friction coating, glass can be both ____ and____ coated but the key isto reduce possible damageand therefore breakage |
hot, cold |
|
|
Glass breakage is a ____ risk, therefore all glass must be______ |
safety, inspected |
|
|
Mechanical systems use _____, ______ and ______ to ensure the glass containersare not damaged |
sensors, light, pressure |
|
|
Who is often credited withpushing canning innovation? |
Napoleon |
|
|
Who responded to Napolean's pressure and actually started canning as a package choice? |
Nicolas Appert |
|
|
There are _______ of cans in ourpackaging stream today |
billions |
|
|
Moving from ____ to seamless_______ was a big advancement(1960’s for beer) |
tin, aluminum |
|
|
The aluminum beer bottle wasintroduced in ______! |
2000 |
|
|
Metal is ___ - ___% of the cost in canmaking |
60 - 70
|
|
|
__ piece cans are faster than ___ piece cans,but limited in size |
2, 3 |
|
|
Cans are made of either ____ or ______. |
aluminum, steel |
|
|
What is often done to cans to prevent corrosion? |
coating |
|
|
Can coating can be sprayed or appliedthrough a set of ______ |
rollers |
|
|
What happens if you don’t coat the can correctly? |
the tin can leak into the food making people sick
|
|
|
What is a shallow draw 2-piece can and what is an example of one? |
-Depth no greater than diameter -Ex. pet food |
|
|
What is a Draw and redraw 2-piece can and what is an example of one?
|
-Depth greater than diameter -Ex. Soup |
|
|
What is a Drawn and iron 2-piece can and what is an example of one? |
-Walls thinner than bottom -Similar to DWD but coating happenslater -Can be printed in line (drinks) or havea label applied after (food) -Ex. Soda |
|
|
What is an Impact extrusion 2-piece can. |
-Used for aerosol cans and metal tubes -Starts with a slug not a blank |
|
|
What is it called when metal cans are cooked during the process of making the can? |
retort |
|
|
Beading cans can increase strength especially during _______ |
retort |
|
|
What type of metal in a can is not usually used for retort because it is not strong enough? |
aluminum |
|
|
What are 3 types of can closures? |
-plain (need a can opener) -ringpull -stay-on-tab |
|
|
Where the closires are applied on a can, what type of seal do we need? |
hermetic seal |
|
|
Using heat to sterilize a can is called _____ |
retort |
|
|
During retort, how hot are the materials pressure cooked, and for how long? |
113 - 132 deg. celsius 5min to 1hr+ |
|
|
What are 7 advantages of canning as a packaging choice? |
-Low cost -Thermally stable -Easy to process on high-speed lines -Readily recyclable -Good moisture and light barriers -Excellent for long term storage -Strong (think about transportation,warehousing and storage) |
|
|
What are 2 defects that can happen in all can bodies? |
-low tin coating weight -badly formed flanges |
|
|
What are 5 defects that can happen in the coated surfaces of cans? |
-pinholes -poor adhesion -undercutting -underfilm staining -cracks in coating after necking in drink cans and after curling can ends |
|
|
What are 2 defects that can happen in three-piece can bodies? |
-poor weld strength -badly formed/incomplete weld |
|
|
What is a defect that can happen in three-piece can bodies two-piece draw and wall ironed can bodies? |
pinholes in body or flange area |
|
|
What is a defect that can happen in can ends (plain)? |
lining compound incorrect weight and bad placement |
|
|
What are 3 defects that can happen in can ends (easy-open)? |
-broken/leaking rivets -residual score out ofspecification -pop and pull loads out of specification |
|
|
What are 4 things that paperboard is also known as? |
-cartonboard -cardboard -boxboard -board |
|
|
Paperboard has a grammage of ____ gsm orover |
250
|
|
|
Paperboard is not only for boxes, it is also for, ____, ______, ____, etc |
Tubes, Liquid cartons (milk), Trays |
|
|
Flaps on a paperboard package impact ____ layout and how much paper we use |
nesting |
|
|
Paperboard packages often use _____ product supports |
interior |
|
|
What are 4 types of paperboard? |
-Solid bleached board (SBB) -Solid unbleached board (SUB) -Folding boxboard (FBB) -White lined chipboard (WLC) |
|
|
What are 2 characteristics of Solid bleached board (SBB)? |
-paperboard made from virgin bleachedchemical pulp -Also called SBS or solid bleached sulphate |
|
|
What are 3 characteristics of Solid unbleached board (SUB)? |
- paperboard made mainly fromunbleached virgin chemical pulp -Also called SUS or solid unbleached sulphate -A layer of bleached fibre is sometimes added to the top to providegreater whiteness |
|
|
What is Folding boxboard (FBB)? |
made from a layer orlayers of mainly virgin mechanical pulp sandwichedbetween layers of virgin chemical pulp. |
|
|
What is White lined chipboard (WLC)? |
made frommulti-layers of recycled fibres. |
|
|
The filling line in paperboard is important. What are 2 types of filling lines? |
-Side fill -vertical fill |
|
|
What are 2 types of lining for paperboard that are not ideal for recycling? |
-aluminum film -polymer film |
|
|
What type of packaging is often used in shipping? |
Corrugated |
|
|
There are ____ around thetypes of boxes that can goon truck and on rail |
rules |
|
|
Corrugated boxes can be ___ for appearance. |
lined |
|
|
Corrugate is a paper-based substrate made from what 3 things? |
-Liner -Fluting material -Adhesive |
|
|
What type of substrate that makes egg cartons that is also considered corrugate? |
moulded pulp |
|
|
What are 4 types of corrugate? |
-kraft -mottled -bleached -coated |
|
|
what are 4 types of carton walls in corrugate? |
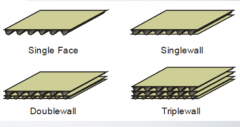
|
|
|
In corrugated packages, the larger the flute, the greater the ____-___ _______ |
edge-on stiffness
|
|
|
In corrugated packages, the finer the flute, the better the _______
|
printing |
|
|
What type of flute is rarely used for general shipping containers but has the highest top tobottom strength? |
A-Flute |
|
|
What flute has some application for triple-wall boards? |
A-Flute |
|
|
What type of flute is used where box compression strength is important |
C-flute |
|
|
What type of flute has a compression strength that is about 10% less than C-flute |
B-flute |
|
|
T or F, B-flute prints better than C-flute |
True |
|
|
What is finished corrugated board described by? |
component grammar (themass in grams per square metre) |
|
|
If you see "From out to in - 170/127C/170" to describe corrugate, what does that mean? |
-Outside liner = 170 g -Medium = 127 g formed to a C-fute -Inside liner = 170 g |
|
|
In corrugate, the length of a case is always the ____ of theflap opening dimensions. |
greater |
|
|
What is the depth of a corrugated box? |
the inside dimension between thetop and bottom inner flaps |
|
|
On a corrugated box, the order in which dimensions are reported ____ where the opening will be |
records
|
|
|
What are 3 styles of corrugated boxes? |
-Regular slotted containers (RSCs) -Die-cut containers -Multi-component designs |
|
|
What style of corrugated box has varying flap styles for added strength? |
Regular slotted containers (RSCs)
|
|
|
What style of corrugated box can be used to make ‘box and lid’?
|
Regular slotted containers (RSCs) |
|
|
What are 3 ways of getting print onto a corrugated box? |
-Post print -Pre print -Litho label or lamination |
|
|
Most types of plastics are ____ _____ derivatives |
crude oil
|
|
|
T or F, Plastics are not lightweight |
F |
|
|
What are 2 ways in which plastic packages are formed? |
-Extruded -thermoformed |
|
|
T or F, plastics are very versatile…there is aplastic for pretty much everyapplication |
True |
|
|
What are 6 types of plastics? |
-Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) -Polystyrene (PS) -Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) -Bio-based polymers -Polyethylenes (PE) -Polypropylene (PP) |
|
|
What are 2 characteristics of Polyethylenes (PE)? |
-Low density and linear low density isfilm primarily used for shrink wrapping -High density, more opaque/rigid/strongthan LD, used for household chemicalbottles |
|
|
What are 2 characteristics of Polypropylene (PP)? |
-Can be used to hot fill -Used as a film in snacks, cookies, cakesand right for thermoformed containersfor things like yogurt (called thin wallpackaging) |
|
|
What are 2 characteristics of Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)? |
-Today more popular in construction than inpackaging -Concerns about manufacturing and migrationof chemicals into food |
|
|
What is a characteristic of Polystyrene (PS)?
|
High Impact (HI) used in fruit and veggie trays— the poor barrier properties help fruit“breathe” |
|
|
What are 3 characteristics of Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)?
|
-for Water bottles, jars -Good oxygen barrier -Moving into cosmetics and even beer |
|
|
What are Bio-based polymers? |
Made from biomass likesugar cane wich is arenewable resource |
|
|
Mixing materials and substrates means difficulty _______ |
recycling |
|
|
What are 5 things that the brand owner is responsible for? |
1. Identify the need for a product 2. Identify the market sector 3. Determine the price 4. Determine the distribution strategy 5. Determine the brand values, product, packattributes |
|
|
What are 6 brand packaging needs? |
1. Coherence 2. Uniqueness 3. Relevance 4. Distinctiveness 5. Market Appeal 6. Protectable |
|
|
What are the 4 P's of the marketing mix? |
-PRODUCT -PRICE -PROMOTION -PLACE |
|
|
What are 5 areas of research for product market research? |
-Product Viability -Consumer Needs -Market Segmentation -Consumer Research -Demographics |
|
|
What is Psychographics? |
"What is the motivationbehind a consumer’spurchasing decision?" |
|
|
What 3 questions should a consumer panel answer? |
-Does the product standout? -Is the product easilyidentified? -Does it present theexpected intention? |
|
|
What is a test market? |
When you launch the product only at a specific retailer or region. |
|
|
What are 7 possible cross functional groups that can be involved in the design brief? |
-Plant manager -Plant manager -Printer/Prepress -Finance -Legal -Product Development -Supply Chain |
|
|
What are 4 market considerations in market research? |
-Product Positioning -Brand Values -The Market -Target audience |
|
|
What are 3 technical considerations in technical research? |
-Containment,Protection,Preservation,Compatibility -Production,Distribution, POS -Environment |
|
|
What are 5 sources of inspiration when generating design concepts? |
-Working in teams -Bringing in samples -Simulating an environment -A day in the life of -Brainstorming |
|
|
What are 2 ways of working when generating design concepts? |
-Sketching -3D mockups |
|
|
What des structural design concern? |
shape andmaterials |
|
|
What should structural design address? |
all basicrequirements of the packageat minimum |
|
|
What should structural design accommodate? |
all requiredinformation (attractively) |
|
|
Conceptual graphic design often runs parallelwith ______ ________ (but sometimes after) |
structural design
|
|
|
what are 7 considerations when doing he graphic design? |
-Substrate -# of ink stations -Photography vs illustration - Branding (logos, colours, typography) -Romance copy -Required copy -Panels |
|
|
What are 7 considerations of the principle display panel? |
-Communicates the marketing/brandstrategy and message -Presents information in a hierarchy -Suggests the function, usage, andpurpose -Differentiates the product -Represents itself appropriately andcompetitively -Reflects the value perception -Performs durably |
|
|
Once concepts are finalized, a ______ isprepared and presented to the client (marketer)by the creative agency |
proposal |
|
|
It's is more likely that prepress and printing are done by ____ ______. |
separate companies
|
|
|
What are 3 new stakeholders? |
-Structural designer -Diemaker -Consumer product company (CPC) or brand owner |
|
|
What kind of software do you need to manage all thepieces and the stakeholders |
Project management software |
|
|
What kind of software is Esko? |
CAD (Computer Aided Design) |
|
|
What kind of software is capesystems.com |
Palletization software |
|
|
What does palletization software do? |
Maximize the palette and prevent damages |
|
|
For what kind of order is palletization software especially important? |
small/partial orders |
|
|
What does a pallette refer to? |
How the boxes are stacked |
|
|
you can only make about __% of the Pantone library withCMYK alone |
30 |
|
|
What are 4 reasons to use spot colours? |
-To protect brand identity -To print using a colourCMYK cannot make (likeneon pink or silver) -To save money on a 2colour job -To use the extended gamutmethod |
|
|
By adding orange and green(sometimes violet) you cancover ___-___% of the Pantonelibrary —this is called______ printing |
- 50-90 -hexachrome |
|
|
Hexachrome is difficult to move through_____ and hard tocontrol on _____ |
prepress, press |
|
|
What are 2 ways to achieve metal(shine) finishes withoutusing ink? |
-Foil stamping -Substrate selection |
|
|
____/____ is used for creating packagingstructure and layouts for cutting tables |
CAD/CAM |
|
|
What is reprographics? |
Going from graphic designto the selected printingprocess |
|
|
What does dot control mean? |
you control thetonal value increase (TVI) of an inkon press |
|
|
What will happen to text that prints positive in flexo? |
will tendto fatten |
|
|
What will happen to text that is reversed out in flexo? |
will tend to fill in, lose fine lines and serifs,and become plugged |
|
|
Reverse text is sometimes called what? |
negative |
|
|
Type should not be made out of morethan __ inks |
2 |
|
|
The terms blend, vignette, gradation, fade-away,fountain, and graduated tint are used ________ |
interchangeably
|
|
|
The main problem of using vignettes is______ |
banding |
|
|
Blends are very difficult to ____ |
trap |
|
|
Blends containing spot colours are more ______ |
complex |
|
|
What is GSI? |
US organization manages barcode standards in North America |
|
|
What does UPC stand for? |
Universal Product Codes |
|
|
Who provides the appropriate UPC (Universal Product Codes)to products |
GSI |
|
|
What does GTIN stand for? |
Global Trade Item Number |
|
|
What kind of barcode has 12 digits? |
GTIN |
|
|
Can you test a barcode with WebCenter? |
Yes |
|
|
What are 5 considerations of barcodes? |
-Direction of web printed substrates -Substrate choice -Location -Colour contrast -Quiet zones |
|
|
Each ______ ______ has it’s own RIP processand plate type |
printing process
|
|
|
What is digital proofing? |
using inkjet or electrophotography |
|
|
What is wet proofing? |
using a sample run with actual inks andsubstrates |
|
|
What are Concept/collaborative proofs? ( 2 points) |
-Used during initial design stages -Not colour profiled |
|
|
What are Colour target proofs? (3 points) |
-Ideal colour proof -Some colours cannot be produced when printing -Helps manage expectations |
|
|
What are Comprehensive proof/mock-ups? (2 points) |
-Constructed into the final product -Not typically colour accurate (but can be) |
|
|
What are Profiled contract proofs? (4 hours) |
-Colour accurate proofs -Simulate TVI and contrast -Set the expectation for what the print willlook like off the press -Challenging in packaging because of thehigh spot colour usage |
|
|
What are Soft proofs? |
-On screen concept proof - Can be viewed both flat and as a 3Dmock-up -There are even iPhone apps to previewpackages! |
|
|
Historically, _______ could not match thequality of offset printing. This is changing rapidly. |
flexography
|
|
|
Where are test elements typically placed on a package? |
under flaps, in a glue zone or on the waste matrix |
|
|
Some packaging requires the test elements to remain _____ on the finished package. |
Visible |
|
|
When we design packages we need to leave the glue tabs free of___ so it doesn’t interfere with the adhesive |
ink |
|
|
Sometimes you need to keep an area on the pack ___ for futureprinting (like best before dates) |
clear |
|
|
How does and image go to screenprinting? |
light sensitive emulsionprinted by inkjet is cured. Image areais unexposed and emulsion washedaway so ink can squeeze through |
|
|
How does an image go to gravure? |
direct laser engraving of acopper surface (chrome plated).Image area is engraved out to holdink |
|
|
How does an image go from computer to relief plate? |
a photopolymer plate with amask. Image area is ablated and thencured with UV, heat, or other wash outprocedure. |
|
|
How does an image go fro computer to offset litho? |
a metal plate with anemulsion is exposed (with light or heat)to harden the image area. The nonimage area is then processed away |
|
|
A good ink is what 4 things? |
-controllable -dries (or sets) at thespeed of printing -conveys information -can be used with manysubstrates |
|
|
What are conventional inks? |
-use organic solvents likealcohol -dry when solventevaporates |
|
|
What are UV inks? |
-dry using UV light (noVOCs) |
|
|
What is an in-line press? (4 points) |
-Each ink has it’s own station with an impression -The more colors you have the longer the line of units -Can often do perfecting (printing on two sides) -Can do a web or sheet |
|
|
What are Central Impression (CI)Presses? (4 points) |
-A single cylinder is usedfor impression -Take up less space -Hold tighter register -Cannot perfect |
|
|
What are stack presses? (3 points) |
-Printing units are separatebut stacked instead ofbeing in line -Less space -Can do perfecting |
|
|
What are 2 different formats of screenprinting? |
Flat bed or rotary |
|
|
Screenprinting has slower drying ____ andrelatively ____ process overall |
-inks -slow |
|
|
Screenprinting has relatively __ quality for detail |
low |
|
|
Screenprinting has a ____ ink film thickness which is great for special effects. |
thick |
|
|
What kind of inks does letterpress use? |
very thick paste inks |
|
|
What is dry offset letterpress? |
image is a assembled on ablanket and transferred |
|
|
What is dry offset letterpress used for? |
cans or tubs(cylindrical shapes) |
|
|
Gravure is an _____ process which means image areas are ______. |
Inaglio, recessed |
|
|
Is the gravure image carrier expensive or inexpensive? |
Expensive |
|
|
Gravure is used for ___ runs |
long |
|
|
Gravure uses uses a metal _____ whichis _____ for image transfer |
cylinder, etched |
|
|
What process is used a lot to print wallpapers? |
gravure |
|
|
Gravure is _____ ______ even in long-runsituations |
high quality |
|
|
Sceenprinting can print on almost _____ substrate. |
any |
|
|
T or F, gracure can print on many substrates |
True |
|
|
In gravure, higher ink film thicknessmeans it is good forspecialty _____ but bad for_____. |
inks, drying |
|
|
What kind of printing is similar to gravure? |
Tampo (pad) printing? |
|
|
How is a plate made for tampo (pad) printing? |
plate is etched out ofnylon, steel orphotopolymer |
|
|
How does the image transfer work in tampo (pad) printing? |
pad is inked and then pad transfers the image |
|
|
What kind of printing method is flexo? |
relief |
|
|
In flexo, what is used to transfer ink onto the plate? |
Anilox Roller |
|
|
Flexo is a competitive process for ______, ______, and ________ |
labels, flexibles, and cartons |
|
|
In flexo, the image carrier can be a _____ or a ____. |
Sheet, sleeve |
|
|
What kind of process is lithography? |
planographic |
|
|
Is lithography high quality? |
Yes |
|
|
In lithography there are ___ pigment inks which are great for_____ ______ |
high, vibrant colour |
|
|
In lithography, there is ____ ink film thickness which is not great for______ ______. |
low, specialty inks |
|
|
In lithography, the image area is separated byaffiliation of water and oil which is also known as _____/________ |
oleophilic/hydrophobic |
|
|
What is non-impact printing? |
No plate so the images canchange on the fly |
|
|
What is Electrophotographic printing? (2 points) |
-uses toner and electricalcharges to make imagearea -heat fuses the toner tothe substrate |
|
|
What are 2 different types of inkjet processes? |
-Continuous -Drop on demand (DOD) |
|
|
What is continuous inkjet? |
constant stream of inkand electrical staticcharge |
|
|
What is Drop on demand (DOD) inkjet? |
ink is “shot” from a nozzleto create image areas |
|
|
Digital labels are a growingmarket in digital with _____%projected growth by 2020globally (from $10.5 to 19.8billion) |
16.2 |
|
|
What are common lead times for label production? |
2-3 weeks |
|
|
What are common lead times for Folding cartons production? |
6 weeks (can pay for 4 weeks) |
|
|
What are common lead times for films production? |
6-8 weeks |
|
|
What are common lead times for Shippers production? |
4 weeks
|
|
|
What are 8 printing defects? |
-Colour variation -Hickies/splashing -Misregistration -Scumming -Bleeding and feathering -Screen clash -Dot gain/TVI -Ghosting, repeating |
|
|
What does varnishing/lacquering protect the print against |
rub off, abrasion, light, etc. |
|
|
What are two ways in which foil blocking/stamping can be applied? |
flat or rotary |
|
|
What is hot foil? |
heat is used to bind thetransfer material to the substrate |
|
|
What is cold foil? |
can be cured with UV,faster and cheaper but lowerquality |
|
|
What is embossing usually used with? |
foil blocking |
|
|
What is heat transfer and ceramic/glass decal usually used for? |
T-shirts and mugs |
|
|
The transfer inheat transfer and ceramic/glass decal has to be printed. Today, how is it typically printed? |
digitally |
|
|
What is metallising? |
Application of a thin film ofaluminum |
|
|
What kind of printing is metallising used in? |
holographic printing |
|
|
What kind of packaging is metallising often used on? |
cartons |
|
|
Printing is a ______ step in the packagingprocess |
middle |
|
|
Printers may be asked to set uppackages in a particular way for the nextmanufacturing ___ |
step |
|
|
Tracking inventory of packaging isvery important for ____ as materials(substrates and adhesives) breakdown over time |
QC |
|
|
We know that quality control issues in packaging can havedangerous implications for ______ |
brands |
|
|
What is manual sampling? |
You take a few products for testing in aproduction run |
|
|
What is manual sampling also called? |
batch sampling |
|
|
With inspection, ____ ___-_____ systems are more automated |
Visual in-line |
|
|
T or F, some tests you need to do to a package are regulated? |
True |
|
|
What are 3 types of visual in-line testing systems? |
-Photo electric sensors (simple contrastscanners) -Laser sensors and scanning sensors -Machine vision systems |
|
|
What kind of visual in-line testing system can be used to scan QR codes? |
Laser sensors and scanning sensors |
|
|
What kind of visual in-line testing system can be used to scan monitor placement? |
Laser sensors and scanning sensors |
|
|
What kind of visual in-line testing system uses Strobe or freeze frame to take a stillimage?
|
Machine vision systems |
|
|
________ _______ is whatallows a company to recall asmall section of damagedproduct instead of ALLproduct |
Batch traceability |
|
|
What can an RFID tag be used for. |
track full shipments |

