![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Embryonic Disk
|
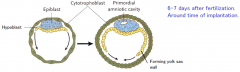
Made up of the ICM, which separate into the epiblast, (epi = above), and the hypoblast, (hypo = below).\
High columnar in appearance Cells from the epiblast form all parts of the embryo itself. |
|
|
Epiblast
|
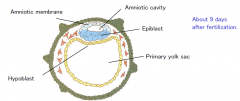
Separates into two layers to form the amniotic cavity.
Only the epiblast cells in contact with the hypoblast will form the embryo. Amniotic fluid will protect the embryo. |
|
|
Primitive Streak
|
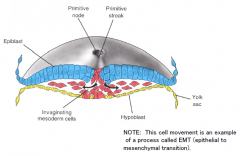
The point where epiblast cells have migrated towards the midline and then ingressed.
|
|
|
First cells to ingress from the primitive streak
|
Insert into and displace the hypoderm
Form the embryonic Endoderm |
|
|
Second set of cells to ingress through the primitive streak
|
Insert between the hypo/endoderm and the epiderm layer to form the Mesoderm.
|
|
|
The Notochord
|
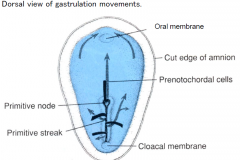
Formed by cells immediately migrating from the primitive node.
A transient embryonic structure that acts as a temporary spine for the embryo. A center for signaling (by growth factors) to adjacent tissues. Later integrated into spinal cord as the nucleus pulpus of the intervertebral disk |
|
|
Ectoderm
|
Outer layer of skin (epidermis) and neural tissues.
|
|
|
Mesoderm
|
Skeletal and smooth muscle,
heart and blood vessels, blood, bones, dermis of skin. Supporting tissue between skin and gut tube. |
|
|
Endoderm
|
Visceral organs, including gut tube, bladder, liver
pancreas and lungs. |
|
|
Summary of ICM development
|
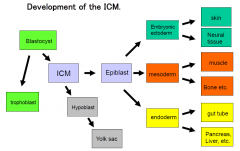
|
|
|
Totipotent cells
|
Can theoretically develop into any cell or tissue.
iPS = Induced Pluripotent stem cells hESC = Human embryonic stem cells |

