![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the major events of week three of embryonic development?
|
3 layer embryo established
Primitive streak formed Signalling centers established: node, notocord, anterior visceral endoderm L-R asymmetry established Neural induction |
|
|
What two structures does the inner cell mass turn into?
|
Hypoblast
Epiblast |
|
|
What does the epiblast give rise to?
|
Embryo
|
|
|
What does the hypoblast give rise to?
|
Extraembryonic structures: lining of the yolk sac, embryonic blood
|
|
|
When does the second lineage decision occur?
|
Right before implantation
During the second week |
|
|
What are the three germ layers?
|
Ectoderm
Mesoderm Endoderm |
|
|
What tissues does the ectoderm give rise to?
|
Skin
Nervous tissue Amnion |
|
|
What tissues does the mesoderm give rise to?
|
Muscle
Blood Connective tissue |
|
|
What tissues does the endoderm give rise to?
|
Epithelial lining
Gut Lung GU tract Inner linings of everything except for the blood vessels |
|
|
What is the signalling center that patterns the mesoderm?
|
Primitive node
|
|
|
What is the axis for mesoderm development during development?
|
Cranial - caudal
|
|
|
What does the axial mesoderm form? Where does it migrate?
|
Notochord
Pre-chordal plate Along the midline |
|
|
What does the paraxial mesoderm form? Where does it migrate?
|
Somites
Cartilage Skeletal muscle Dermis Just caudal to node, migrates slightly laterally |
|
|
What does the lateral plate mesoderm form? Where does it migrate?
|
Circulatory system
Bones (sternum, etc.) Deep connective tissue Laterally |
|
|
What does the extraembryonic mesoderm form? Where does it migrate?
|
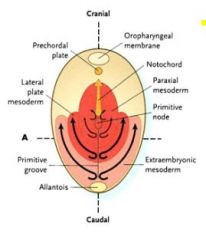
Extraembryonic membranes, blood vessels
Laterally |
|
|
What is the function of the primitive node during gastrulation?
|
Positioning of the primitive streak
Patterns the mesoderm Induces neural differentiation |
|
|
What is the function of the notochord during gastrulation?:
|
Patterns the surrounding tissue: ectoderm (overlying) and endoderm (under)
|
|
|
What is the function of the anterior visceral endoderm during gastrulation?
|
Positions primitive streak in the posterior, pattern overlying mesoderm
Pattern head formation |
|
|
What mechanical event is responsible for the L-R patterning of the embryo?
|
Beating of cilia the leftward direction
|
|
|
What genes are responsible for the turning on of the left-side genes during development
|
Sonic hedgehog
FGF-8 |
|
|
What are the "left-sided" genes of gastrulation?
|
Nodal
Pitx2 |
|
|
What is one consequence of defective cilia action in gastrulation?
|
Organ asymmetry
|
|
|
What type of drugs could cause an asymmetry in an embryo?
|
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors:
Serotonin increases the expression of Shh. If it can't be broken down, you'll get it all over the place, leading to asymmetries |
|
|
What are three potential causes of asymmetry in an embryo?
|
Genetic efects within cilia
Mechanical defects within cilia MAO inhibitors |
|
|
What is Kartagener syndrome?
|
A defect in cilia
|
|
|
What is the function of BMP-4 in gastrulation?
|
Preventing the ectoderm from becoming the brain
|
|
|
What signalling center induces neural formation? How?
|
Primitive node
Secreting a BMP-4 antagonist |
|
|
What is the "default" tissue of ectoderm?
|
Neural tissue
|
|
|
What is the protein that is responsible for preventing the ectoderm from developing into nervous tissue?
|
BMP-4
|
|
|
What signalling center is responsible for the development of the head?
|
AVE
Anterior visceral endoderm |
|
|
What is a consequence of not having an AVE?
|
No head!
|
|
|
What is one example of an AVE defect seen in humans?
|
Holoprosencephaly
The brain doesn't cleave at the midline. -No corpus callosum -Eyes are close together (sometimes 1 eye) -One upper incisor |
|
|
What are the symptoms of caudal agenesis?
|
VATeR:
Vertebral defects Anal atresia Tracheo-esophageal fistula Renal defects |
|
|
What is a result of an overactive primitive node in a baby?
|
Sacrococcageal teratoma
All 3 germ layers |
|
|
What are the three fetal membranes? From where do they arise?
|
Chorion: trophoblast
Amnion: epiblast Yolk sac: primitive endoderm |
|
|
Where does hematopoesis first occur in an embryo?
|
Yolk sac
|
|
|
How is the amniotic fluid taken up by the fetus?
|
Swallowing
|
|
|
What are two pathologies related to amniotic fluid equilibrium? What is a consequence of one of them?
|
Polyhydramnois: swallowing, gut defect; too much fluid
Oligohydramnios: too little fluid. Clipping off of limb buds |
|
|
What fetal defects are associated with oligohydramnois?
|
Amputation of limbs due to ensnaring of limb buds by the amniotic sac
|
|
|
What is a complication of twinning, possibly?
|
Twins share a placenta --> conjoined
One can live, the other dies. |

