![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the second most common cause of cancer death in the US? |
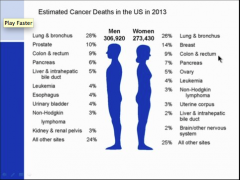
Colon |
|
|
Is cancer of the SI common? What percent of americans will develop CRC? What percent will die? All are what type? |

|
|
|
Describe the hyper plastic polyp? What is it due to?
What are hamartomas? What are they a feature of?
What are juvenile polyps? |

|
|
|
What configuration is this? what is the poly type? In what portion of the crypts does this occur?
Is a serrated adenoma limited to upper third? |
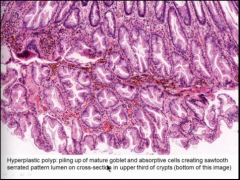
Only see it on upper third (lower part of the screen)
NO! |
|
|
What is the most common type of colon polyp? Does it have malignant potential? Does hyper plastic polyp have maligns potential? Are inflammatory polyps malignant? Do they have increased risk of cancer? |

|
|
|
Why is CRC more common in developed countries? Think diet. What factors may be protective?
Is CRC decreasing or increasing? |

|
|
|
What are the risk factors of CRC? What can decrease your risk (drugs, supplements, replacements, foods)? |

|
|
|
What is the biggest risk factor for CRC? What diseases? Others? |
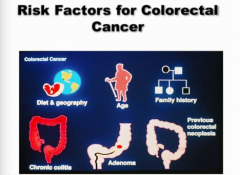
Age |
|
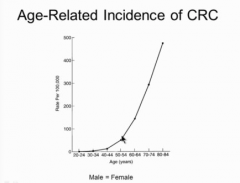
More than 50 is biggest risk factor for CRC |

|
|
|
What is the genetic progression of CRC? How long does it take? |
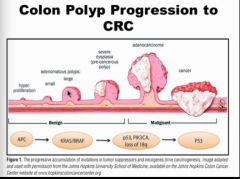
10 years |
|

|

|
|
|
What do you do with colonoscopy when you see a polyp? |

|
|

|

|
|
|
What is probability of colon cancer related to in terms of properties of the polyp? |
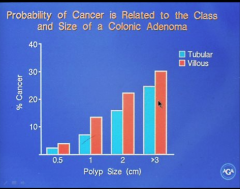
Larger polyp and villous more likely to become malignant? |
|
|
Does family history play a role? What carries the greatest risk? |

|
|
|
What are some signs and symptoms of colon cancer?
Which side for obstructions? |
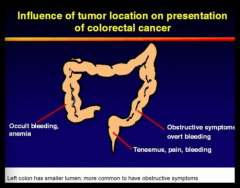
Tenesmus = incomplete evacuation |
|

|
Right colon = anemia Left colon = overt bleeding |
|
|
How do you diagnose CRC? What will it show? |

APPLE CORE LESION IN DESCENDING COLON |
|

|
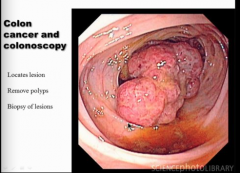
Probably present with iron deficiency |
|
|
How do you treat if polyp is stalked and cancer localized to head? How do you look for metastatic disease? What is the mainstay of treatment? |

|
|
|
Does colon cancer prognosis worsen as extent of invasion increase? |
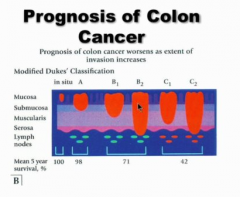
Deeper into wall = worse prognosis |
|

Don't memorize |

|
|
|
When is chemotherapy recommended in CRC? |
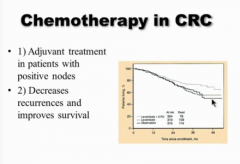
Usually see metastatic disease several years later (local recurrences not common) |
|
|
What are tumor suppressor genes?
Can abnormalities be inherited? |

|
|
|
What are oncogenes?
What is activation usually from? Are they inherited? |

Not inherited usually. |
|

|

|
|
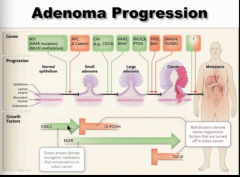
Draw this out. Green arrow = oncogene Red = tumor suppressor |

|
|
|
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
Dominant or recessive? When do polyps start? Do all develop CRC?
What other symptoms? |

|
|
|
What do patients with FAP inherit? Where is this condition present? When does polyp growth begin (2-hit)? |

|
|
|
What type of mutation is HNPCC? What percent of CRC in US? Where are lesions located? What other cancer associations? |

Colonoscopy may not be effective screen |
|
|
How do you diagnose HNPCC? Don't memorize. |

|
|
|
Are most CRCs hereditary or sporadic? Which are the least common? |

|
|
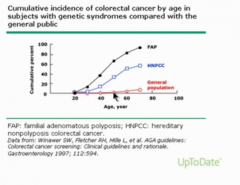
Should you start screening earlier for mutated people? |
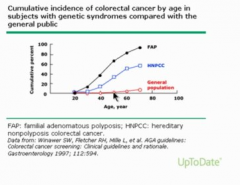
Yep! |
|

|

|
|
|
When do you start and stop CRC screening?
What are some high risk? |
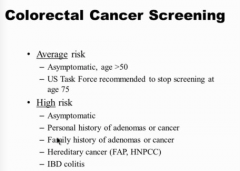
Must do colonoscopy only for high risk |
|
|
Is fecal occult blood used anymore? What is the principle? |

|
|
|
What is the stool test used more commonly now? What does it only respond to? What about UGI bleed? How many stool samples? |

More expensive and mores specific, but not 100% because not all polyps bleed.
Positive test => colonoscopy |
|

|

|
|
|
When do you begin screening? What is the used every 5 years, every 10 years? |

|
|
|
What is a helical CT alternative to screening? |
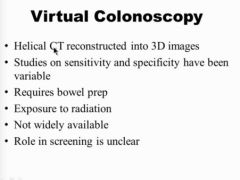
INSURANCE DOES NOT COVER! Positive test requires colonoscopy |
|

|
Not enough GIs to screen. Patients do not like the prep. Risk of bleeding and perforation. |
|
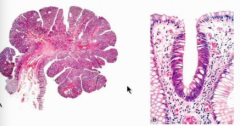
What type of tubular adenoma (shape)?
What configuration are the cells crowded into? |
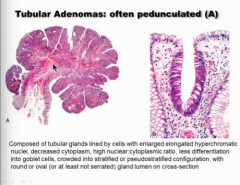
Enlarged, elongated, hyperchromatic nuclei
Normal on right side of right image, abnormal of left side of right image (bigger nuclei, elongated, crowded, pseudo stratified, NOT AS MANY goblet cells). |
|
|
What is the second most common type of adenoma? What does the epithelium between resemble? |
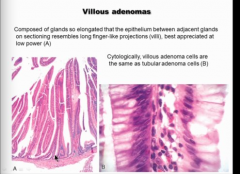
Finger-like projections.
Different architecture are low low ever, but villous is the same as tubular at high power. |
|
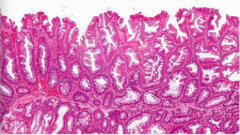
What type of adenoma? Location? Which part of colon (right or left)? |
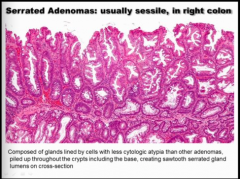
SSAs = right colon! Left side usually just hyperplastic polyp.
Piling up in cells goes ALL the way to the BOTTOM OF THE CRYPTS! |
|
|
Draw out the APC/WNT pathway. Up to 80% of what type of colon cancer use tho pathway? Is this early or late? What mutation is in 50% of colon cancers (later)? What mutation in 80% of colon cancers (later)?
What are some other names for this pathway?
What drug will not work is KRAS present? |

Cituximab? |
|
|
Draw out the MIS pathway? What are the gene defects? What percent of sporadic colon cancer? What type of precursor lesion usually?
What type of CRC? Location? What mutation is common? What two mutations are often lacking? |

BRAF targeted therapy = vemurafenib |
|
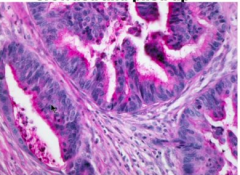
Is this colon cancer invading? |
Yep Muscular wall being invaded. |
|
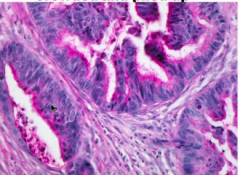
Describe cell nuclei, cytoplasm. |

|
|

|

|
|

|
True = age more than 50 True = any test is better than nothing True = will have next colonoscopy in 5 years |
|

|
False = symptoms, need colonoscopy True True
|

