![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Common Experiments Involving Gases
|
solid potassium chlorate decomposes to solid potassium chloride and oxygen gas with heat and Manganese IV Oxide as catalyst;
Ammonium ions react with hydroxide ions to ammonia gas and water; solid calcium carbonate reacts with aq hydrochloric acid to form carbon dioxide gas, water, and aq calcium chloride; aq hydrochloric acid reacts with solid zinc to form aq zinc chloride and hydrogen gas |
|
|
When does the pressure of a gas equal to the atmospheric pressure? (Pgas = Patm)
|
When the water level in the bottle is equal to the water level in the trough
|
|
|
At what conditions does ideal gas law not work very well?
|
Gases under high pressures or at very low temperatures HPLT!
|
|
|
What happens as a real gas is cooled or compressed?
|
The distance between particles decreases dramatically, and these real volumes can no long be ignored as with ideal gases, they can
|
|
|
What equation is used wtih real gases?
|
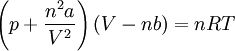
The van der Waals equation
|
|
|
What are the five postulates of kinetic molecular theory?
|
-Gases consist of molecules or atoms in CONTINUOUS RANDOM motion
-Collisions between these molecules and/or atoms in a gas are elastic -The volume occupied by the atoms and/or molecules is negligibly small -The attractive or repulsive forces between the atoms are negligible -The average kinetic energy of a molecule or atom in a gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature of the gas |
|
|
What is Boyle's Law?
|
Shows the inverse relationship between Pressure and Volume at a constant temperature (pressure increases, volume
will decrease, vice versa) P1V1=P2V2 |
|
|
What is Charles' Law?
|
At a constant pressure, volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature (temperature decreases, volume will decrease)
note: when you heat up a balloon the gas will expand v1/t1 = v2/t2 |
|
|
What is Gay Lussac's Law?
|
At a constant volume, pressure of a gas will be directly proportional to its temperature
(temperature increases means that particles move faster and strike the container walls more frequently thus causing the increase in pressure as well) |
|
|
What is STP and how does it affect gases?
|
STP is standard temperature and pressure (1.00 atm and 273 K) The volume of a gas at these conditions will always occupy 22.4 L
|
|
|
What is pressure and its relationship to volume and temperature?
|
Definition: Force exerted per unit area.
Chem-wise: pressure is the force that is generated by the collisions of striking of the gas particles with its container walls. Increasing volume will provide more room for the particles to strike the container walls and therefore less collisions means less pressure and vice versa. Increasing temperature would increase the speed of the particles. By doing so, the collisions would be more frequent and with more force and thus resulting in a higher pressure. |
|
|
How do you find partial pressures?
|
Pressures of individual gases from a mixture of gases can be found by multiplying the total pressure by the mole fraction of the individual gas.
|
|
|
What is Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures?
|
When two gases are mixed together, the gas particles tend to act independently of each other. When added up the total pressure is equal to the sum of the pressures of all the components in the mixture.
|
|
|
What is the ideal gas law?
|
PV=nRT
p=pressure in atm v=volume n=moles of gas R=universal constant T=temperature in K |
|
|
What is Graham's Law of Effusion
|
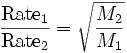
When the rates at which two gases will effuse through a hole in a container are compared, they are found to be inversely related to the square roots of the masses of the gas particles. The greater the pressure, the more likely that it will effuse due to
more collisions |

