![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gest - Theory |
The whole is worth more than the sum of its parts |
|
|
Gest - Strengths |
- Explains fictions and illusions well - Explains ambiguous figures well |
|
|
Gest - Weaknesses |
- Can't explain any other distortion than the Muller-Lyer illusion - Uses different explanations at different times, can sometimes explain something and sometimes can't |
|
|
Distortions (ML illusion) |
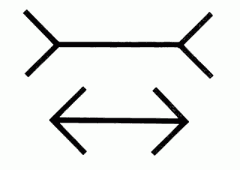
- Top line looks shorter than the bottom line because of the arrows direction - We 'add' them to the line perceiving the 'whole' snap to be larger/smaller - Muller-Lyer Illusion |
|
|
Fictions |
- We make an 'incomplete' figure whole using closure - We complete the edges to make a regular/familiar shape - Necker Cube |
|
|
Ambiguous figures |

- When we see a shape with 2 possible interpretations, due to the different colours, only one can be seen - Rubin Vase Illusion |
|
|
Greg - Theory |
When we judge an object to be far, we scale it up, distant objects make smaller images on the retina |
|
|
Greg - Strengths |
- Explains distortions well - Explains many illusions when angled lines are used as depth cues |
|
|
Greg - Weaknesses |
- Can't explain Muller-Lyer Illusion with circles instead of arrows/fins |
|
|
Greg - Ponzo Illusion |

- Top line looks bigger than the bottom line, because, if the tracks are used as depth cues to linear perspective, the top line would be further away, so its scaled up so it seems bigger |
|
|
Greg - Hering Illusion |

Radiating lines look like a linear perspective cue, so the people at the back appear larger |
|
|
Greg - Muller-Lyer Illusion |
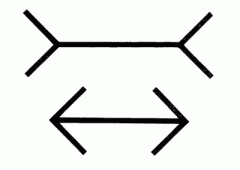
- Top line looks shorter than the bottom line because of the arrows direction - We 'add' them to the line perceiving the 'whole' snap to be larger/smaller - Muller-Lyer Illusion |
|
|
Distortions |
Where our perception is deceived by some aspect of the stimulus, this can affect the shape or size of an object |
|
|
Schema |
- Framework of knowledge about something that has resulted from personal experiences |
|
|
Palmer (1975) |
Aim - Find out if context would affect perception Ad - Timed - Told what to do - Unfair test results excluded DisAd - Some may've tried harder - Fewer results (results excluded) |
|
|
Serial Reproduction |
Task where a piece of information is passed in a chain or‘series’ from one participant to the next (differences are measured) |
|
|
Repeated Reproduction |
Task where the participants are given a story/picture toremember. They recall it several times after delays (differences are measured) |

